Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Analyze Live SingleStore Data in SAS Viya
Use CData Connect Cloud to connect to SingleStore data from SAS Viya and deploy self-service analytics using live SingleStore data.
SAS Viya is an analytics platform that enhances data management, machine learning, and analytics, fostering efficient decision-making and insights. When paired with CData Connect Cloud, you get instant, cloud-to-cloud access to SingleStore data for building predictive models, crafting stunning insights to make data-driven decisions, and more. This article shows how to connect to Connect Cloud from the SAS Viya cloud platform and integrate live SingleStore data into your self-service AI and analytics deployments.
CData Connect Cloud provides a pure SQL, cloud-to-cloud interface for SingleStore, allowing you to easily integrate with live SingleStore data in SAS Viya — without replicating the data. CData Connect Cloud looks exactly like a SQL Server database to SAS Viya and uses optimized data processing out of the box to push all supported SQL operations (filters, JOINs, etc.) directly to SingleStore, leveraging server-side processing to return SingleStore data quickly.
Configure SingleStore Connectivity for SAS Viya
Connectivity to SingleStore from SAS Viya is made possible through CData Connect Cloud. To work with SingleStore data from SAS Viya, we start by creating and configuring a SingleStore connection.
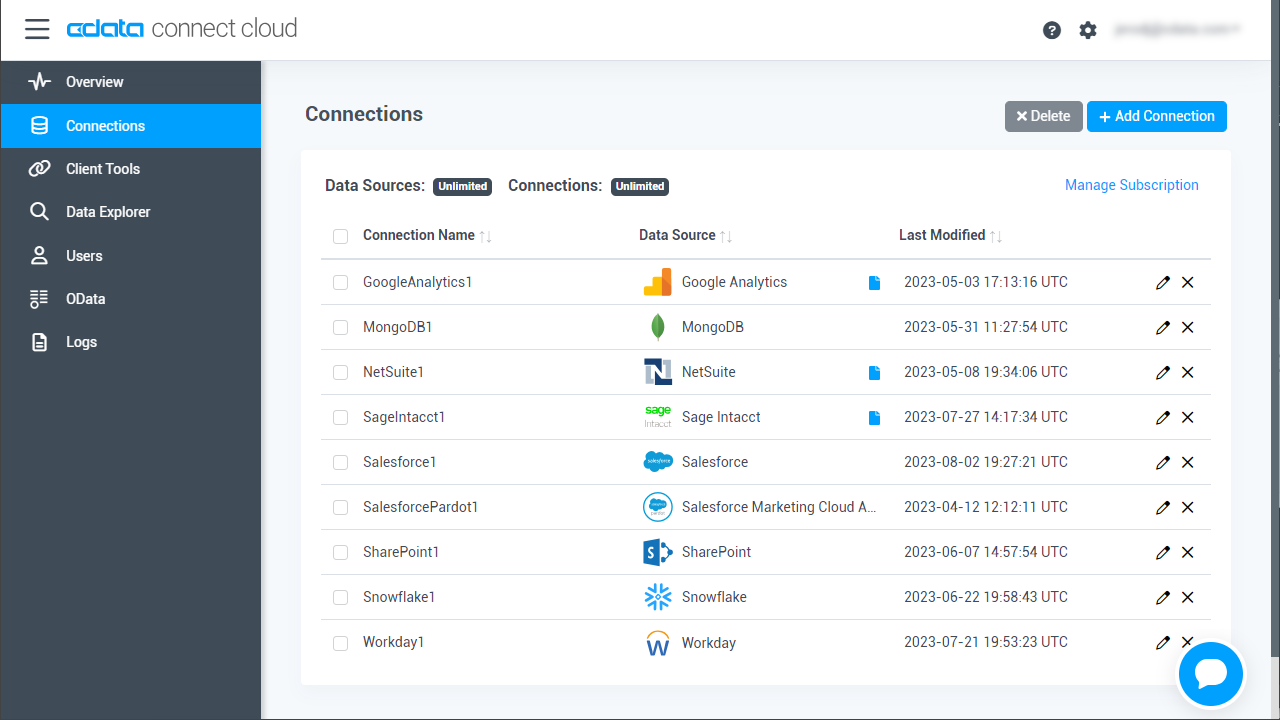
- Log into Connect Cloud, click Connections and click Add Connection.
![Adding a Connection]()
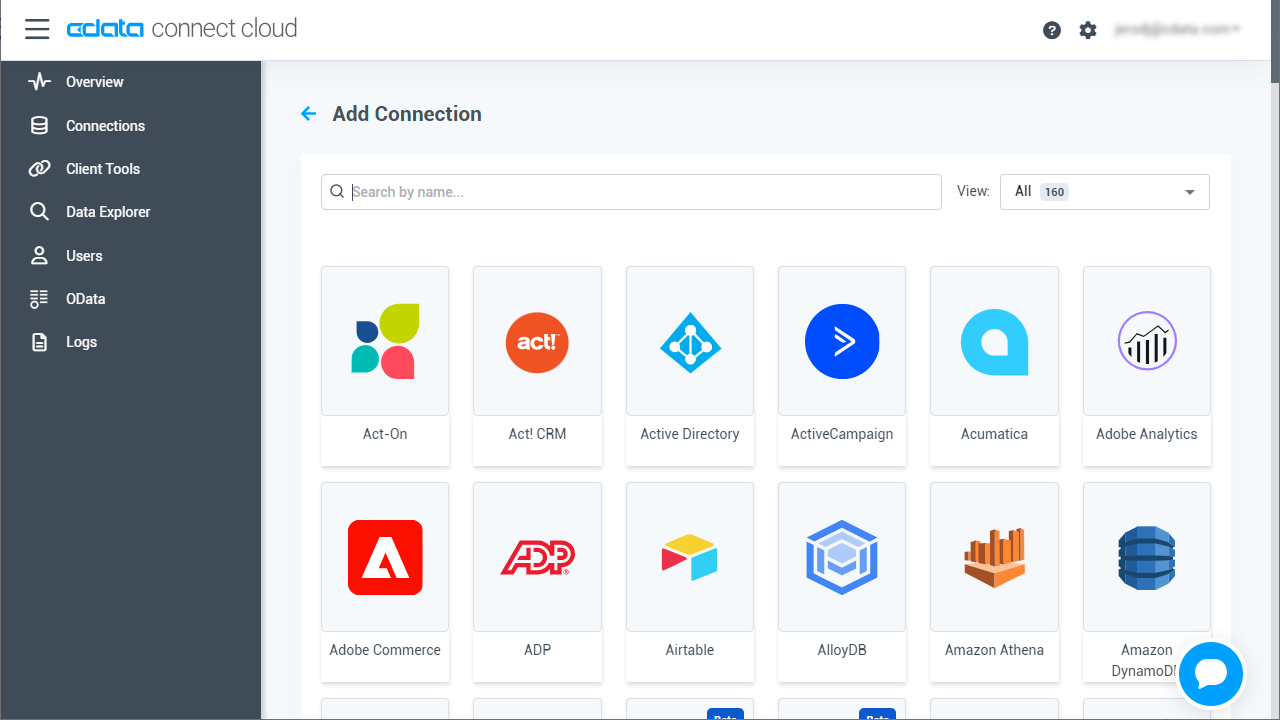
- Select "SingleStore" from the Add Connection panel
![Selecting a data source]()
-
Enter the necessary authentication properties to connect to SingleStore.
The following connection properties are required in order to connect to data.
- Server: The host name or IP of the server hosting the SingleStore database.
- Port: The port of the server hosting the SingleStore database.
- Database (Optional): The default database to connect to when connecting to the SingleStore Server. If this is not set, tables from all databases will be returned.
Connect Using Standard Authentication
To authenticate using standard authentication, set the following:
- User: The user which will be used to authenticate with the SingleStore server.
- Password: The password which will be used to authenticate with the SingleStore server.
Connect Using Integrated Security
As an alternative to providing the standard username and password, you can set IntegratedSecurity to True to authenticate trusted users to the server via Windows Authentication.
Connect Using SSL Authentication
You can leverage SSL authentication to connect to SingleStore data via a secure session. Configure the following connection properties to connect to data:
- SSLClientCert: Set this to the name of the certificate store for the client certificate. Used in the case of 2-way SSL, where truststore and keystore are kept on both the client and server machines.
- SSLClientCertPassword: If a client certificate store is password-protected, set this value to the store's password.
- SSLClientCertSubject: The subject of the TLS/SSL client certificate. Used to locate the certificate in the store.
- SSLClientCertType: The certificate type of the client store.
- SSLServerCert: The certificate to be accepted from the server.
Connect Using SSH Authentication
Using SSH, you can securely login to a remote machine. To access SingleStore data via SSH, configure the following connection properties:
- SSHClientCert: Set this to the name of the certificate store for the client certificate.
- SSHClientCertPassword: If a client certificate store is password-protected, set this value to the store's password.
- SSHClientCertSubject: The subject of the TLS/SSL client certificate. Used to locate the certificate in the store.
- SSHClientCertType: The certificate type of the client store.
- SSHPassword: The password that you use to authenticate with the SSH server.
- SSHPort: The port used for SSH operations.
- SSHServer: The SSH authentication server you are trying to authenticate against.
- SSHServerFingerPrint: The SSH Server fingerprint used for verification of the host you are connecting to.
- SSHUser: Set this to the username that you use to authenticate with the SSH server.
![Configuring a connection (Salesforce is shown)]()
- Click Create & Test
- Navigate to the Permissions tab in the Add SingleStore Connection page and update the User-based permissions.
![Updating permissions]()
Add a Personal Access Token
If you are connecting from a service, application, platform, or framework that does not support OAuth authentication, you can create a Personal Access Token (PAT) to use for authentication. Best practices would dictate that you create a separate PAT for each service, to maintain granularity of access.
- Click on your username at the top right of the Connect Cloud app and click User Profile.
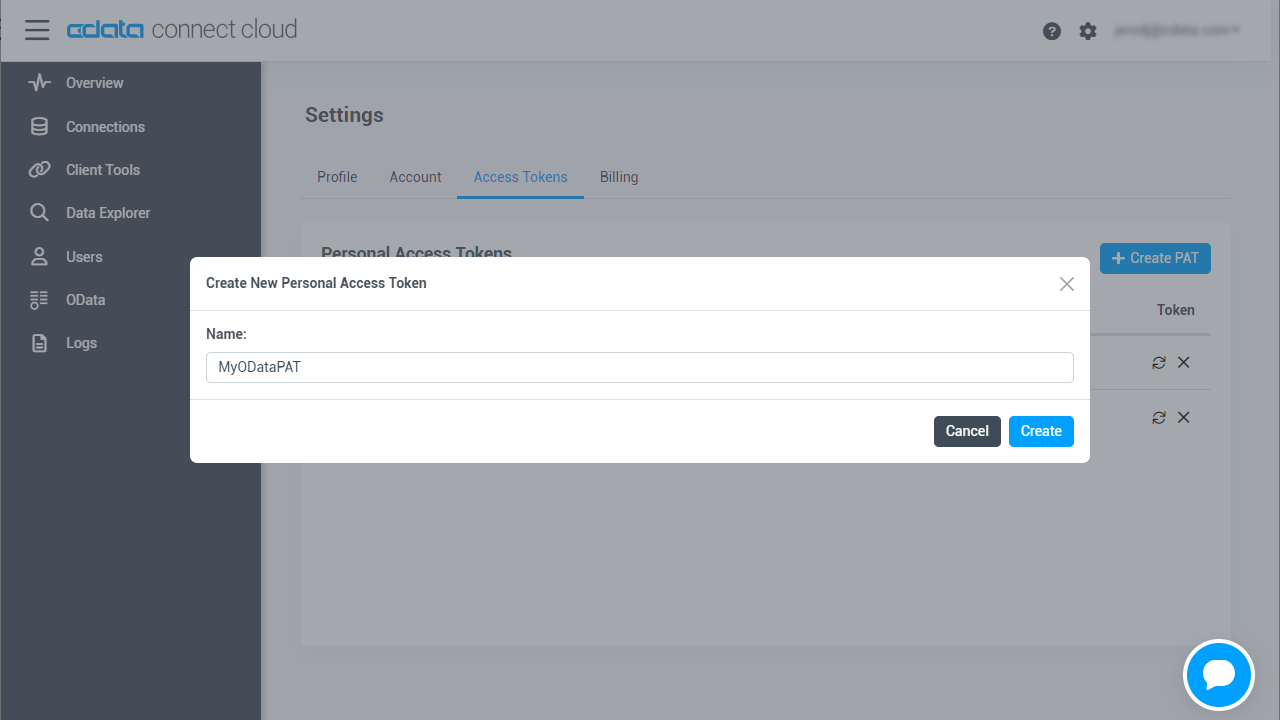
- On the User Profile page, scroll down to the Personal Access Tokens section and click Create PAT.
- Give your PAT a name and click Create.
![Creating a new PAT]()
- The personal access token is only visible at creation, so be sure to copy it and store it securely for future use.
With the connection configured, you are ready to connect to SingleStore data from SAS Viya.
Connecting to CData Connect Cloud from SAS Viya
The following steps detail the process of loading data from SingleStore into SAS Viya using the established connection in CData Connect Cloud.
- Download and install the CData Connect Cloud JDBC driver from the Client Tools section.
![Download and install CData Connect Cloud JDBC driver]()
- Now, log in to SAS Viya and navigate to the Applications Menu at the top-left corner.
- Select Develop Code and Flows from the Analytics Life Cycle topic.
![Select Develop Code and Flows]()
- Navigate to the Explorer tab and click on SAS Server on the left panel.
- Follow the steps to upload the JAR file of the CData Connect JDBC driver:
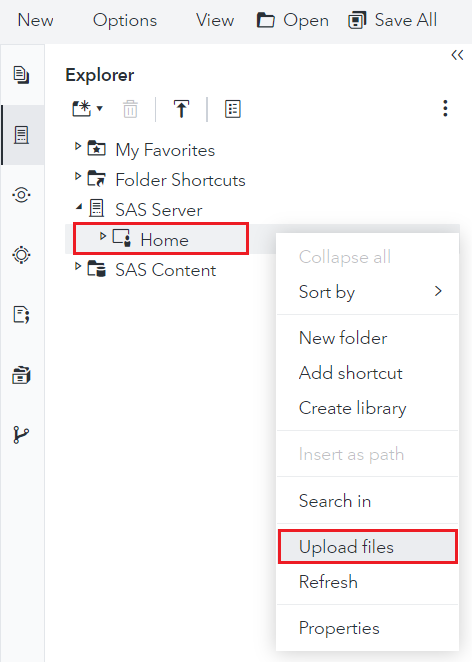
- Right-click on the "Home" directory.
- Click on Upload files.
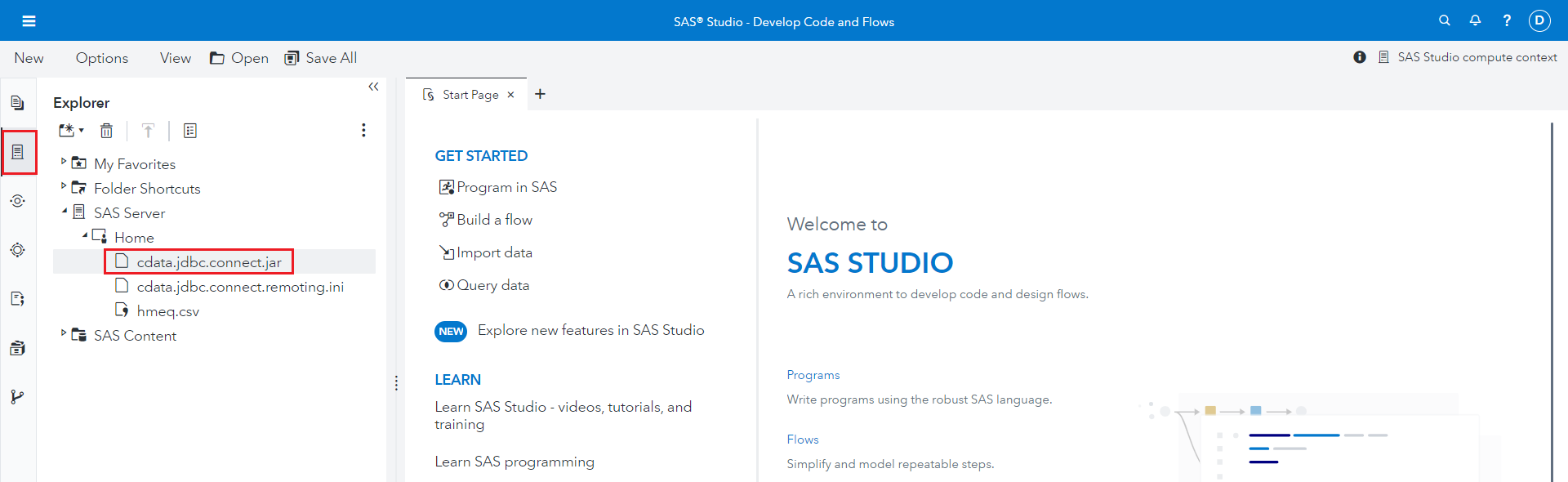
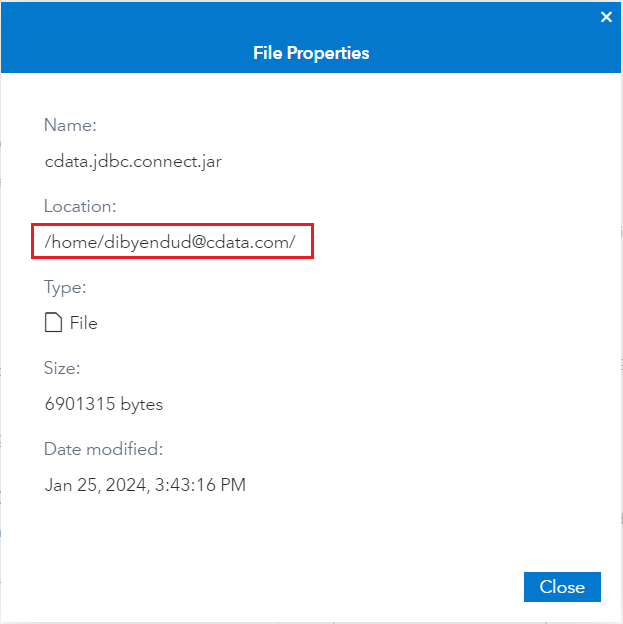
- Place the JAR file in the specified location and note its file path.
![Click on Upload files to upload the JAR file in the Home folder]()
![JAR file uploaded]()
![Save the location of the JAR file from File Properties]()
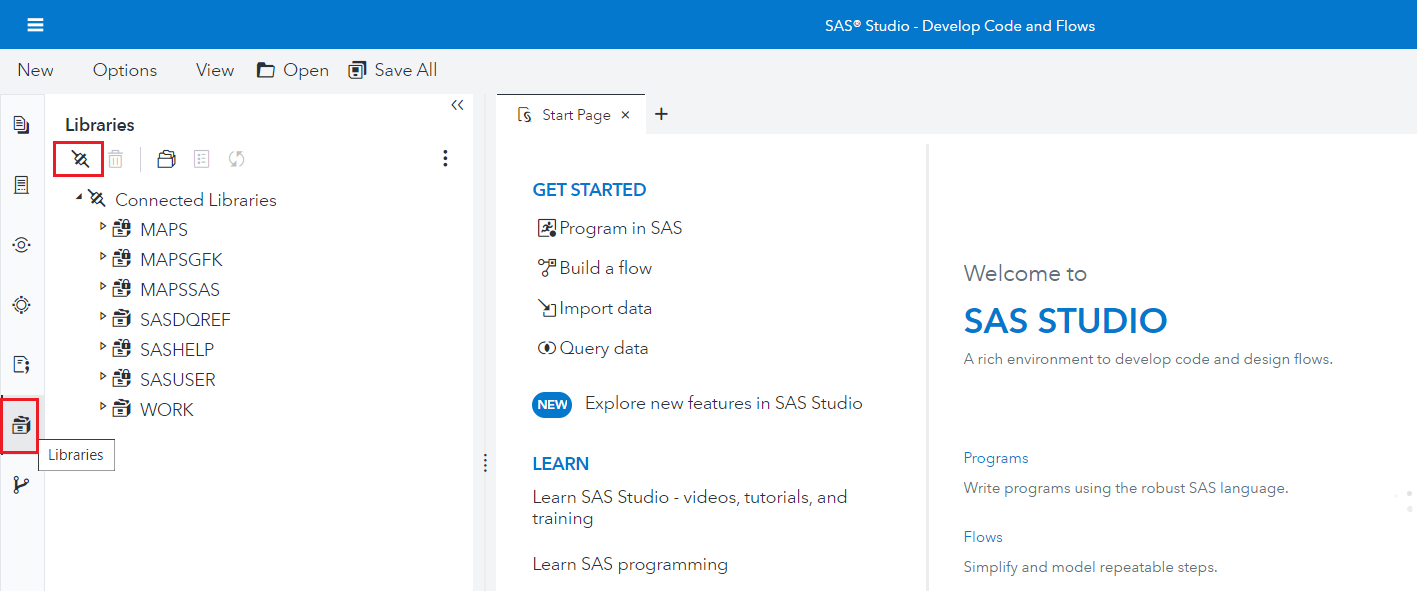
- Once done, navigate to the Libraries tab and click on Create a new library connection (on the top left corner as shown below) for the CData Connect JDBC.
![Navigate to the Libraries tab and click on Create a new library connection]()
- Enter the library connection settings:
- Connection name: enter a name for your connection
- Library name (libref): enter a reference for your library
- Library type: choose "SAS/ACCESS to JDBC"
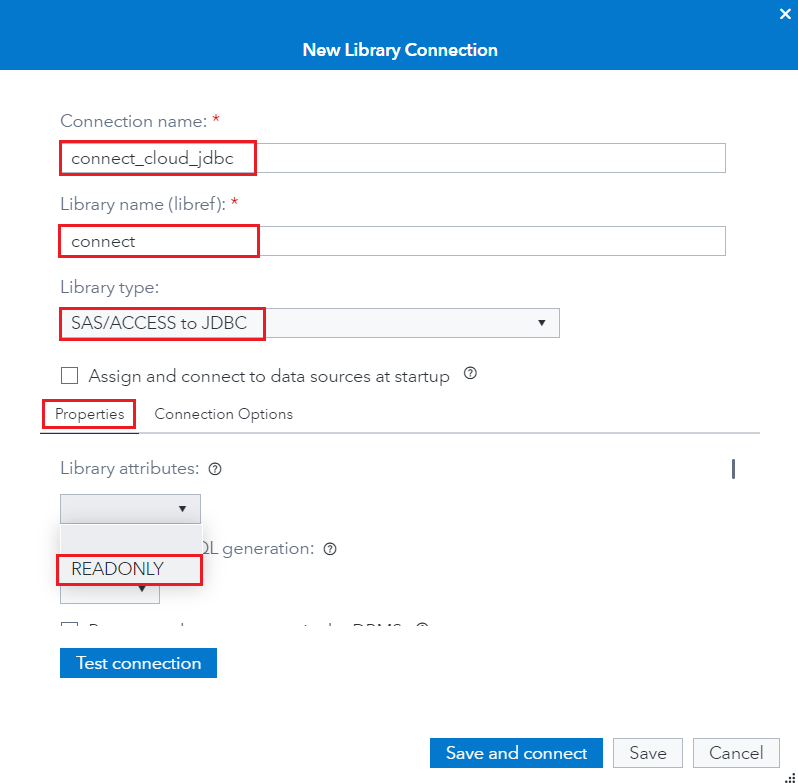
- Click on the Properties tab and set Library attributes to READONLY.
![Click on the Properties tab and set Library attributes to READONLY]()
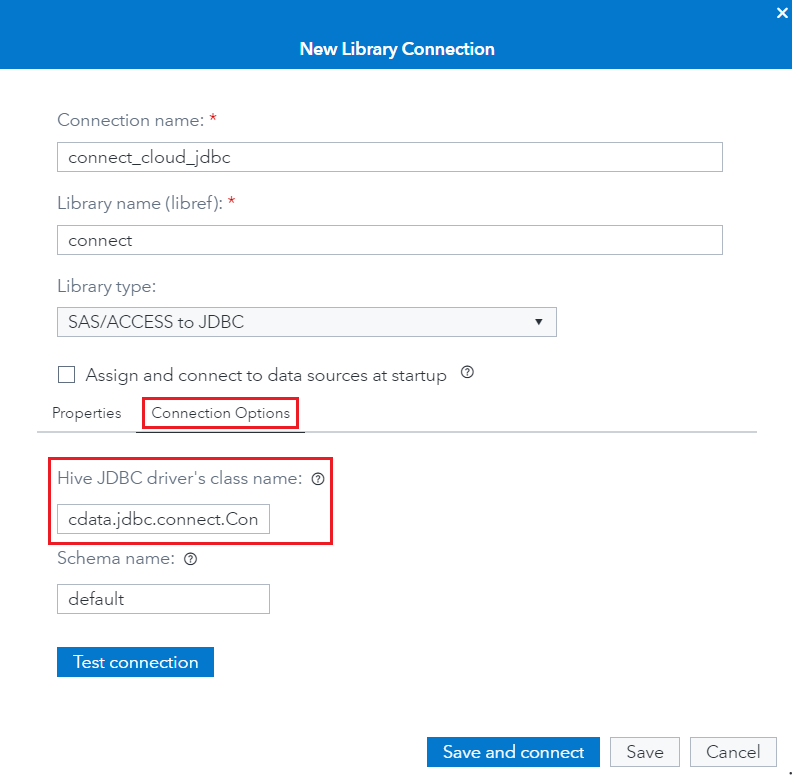
- Click the Connection Options tab and enter the following details:
- Hive JDBC driver's class name: cdata.jdbc.connect.ConnectDriver
- Java CLASSPATH: enter the file path to the JAR driver file (Refer to Step 5)
![Fill Hive JDBC driver's class name]()
![Fill Java CLASSPATH]()
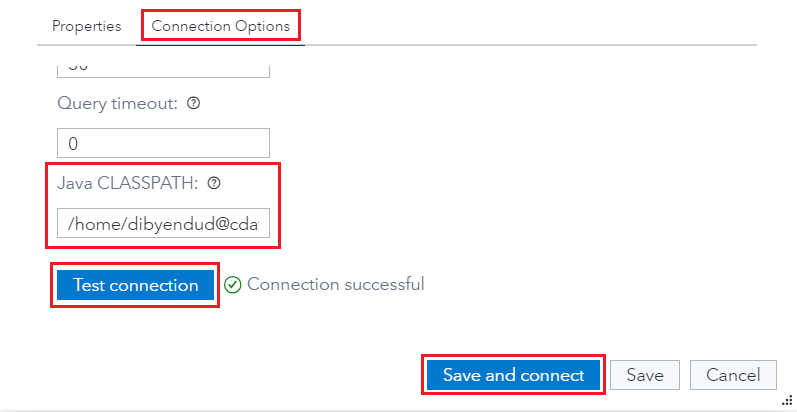
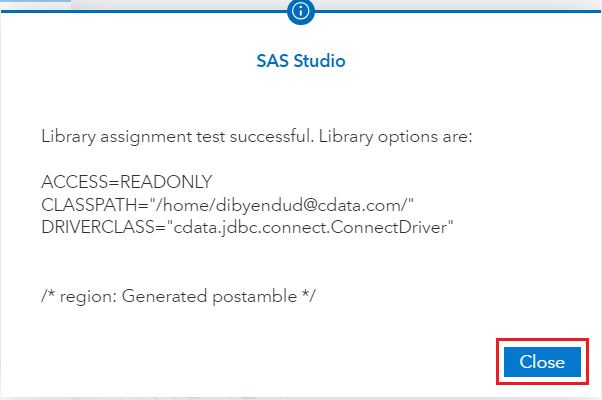
- Click on Test connection. If it succeeds, click on Save and connect.
![Successful test connection]()
- Click on to add a new tab and select SAS program.
![Select SAS program to write SQL Queries]()
- Fill in the code block below with your setup parameters:
- Libref: enter the library reference you defined in Step 9.
- ClassPath: enter the file path to the JAR driver file.
- Username: enter your CData Connect username. This is displayed in the top-right corner of the CData Connect interface. For example, [email protected].
- DefaultCatalog: enter the connection configured in CData Connect Cloud that you want to query.
- Password: enter the PAT you generated in the "Add a Personal Access Token" section.
libname [Libref] JDBC classpath=[ClassPath] class="cdata.jdbc.connect.ConnectDriver" URL="jdbc:Connect:AuthScheme=Basic;User=[Username];DefaultCatalog=[DefaultCatalog];DefaultSchema=dbo;Password=[Password]"; proc sql; SELECT * FROM [Libref].MyTable; quit; - Click on Run. You can see the data load from CData Connect Cloud into SAS Viya.
Live Access to SingleStore Data from Cloud Applications
At this point, you have a direct, cloud-to-cloud connection to SingleStore data from SAS Viya. You can build predictive models, craft insights to make data-driven decisions, and more — all without replicating SingleStore data.
Try Connect Cloud and get real-time data access to 100+ SaaS, Big Data, and NoSQL sources directly from your cloud applications.