Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Access Live Salesforce Pardot Data in AWS Lambda (with IntelliJ IDEA)
Connect to live Salesforce Pardot data in AWS Lambda using IntelliJ IDEA and the CData JDBC Driver to build the function.
AWS Lambda is a compute service that lets you build applications that respond quickly to new information and events. AWS Lambda functions can work with live Salesforce Pardot data when paired with the CData JDBC Driver for Salesforce Pardot. This article describes how to connect to and query Salesforce Pardot data from an AWS Lambda function built with Maven in IntelliJ.
With built-in optimized data processing, the CData JDBC Driver offers unmatched performance for interacting with live Salesforce Pardot data. When you issue complex SQL queries to Salesforce Pardot, the driver pushes supported SQL operations, like filters and aggregations, directly to Salesforce Pardot and utilizes the embedded SQL engine to process unsupported operations client-side (often SQL functions and JOIN operations). In addition, its built-in dynamic metadata querying allows you to work with and analyze Salesforce Pardot data using native data types.
Gather Connection Properties and Build a Connection String
Download the CData JDBC Driver for Salesforce Pardot installer, unzip the package, and run the JAR file to install the driver. Then gather the required connection properties.
Salesforce Pardot supports connecting through API Version, Username, Password and User Key.
- ApiVersion: The Salesforce Pardot API version which the provided account can access. Defaults to 4.
- User: The Username of the Salesforce Pardot account.
- Password: The Password of the Salesforce Pardot account.
- UserKey: The unique User Key for the Salesforce Pardot account. This key does not expire.
- IsDemoAccount (optional): Set to TRUE to connect to a demo account.
Accessing the Pardot User Key
The User Key of the current account may be accessed by going to Settings -> My Profile, under the API User Key row.
NOTE: To use the JDBC driver in an AWS Lambda function, you will need a license (full or trial) and a Runtime Key (RTK). For more information on obtaining this license (or a trial), contact our sales team.
Built-in Connection String Designer
For assistance constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the Salesforce Pardot JDBC Driver. Double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.salesforcepardot.jar
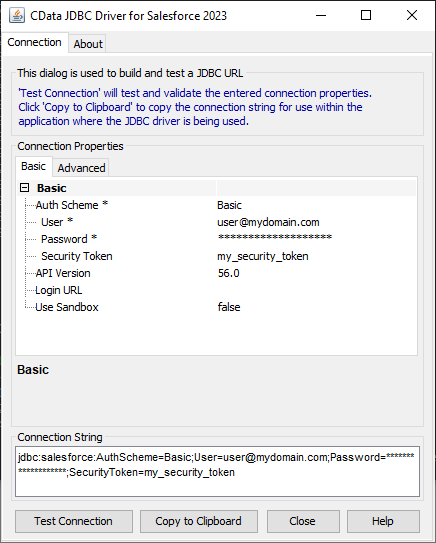
Fill in the connection properties (including the RTK) and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
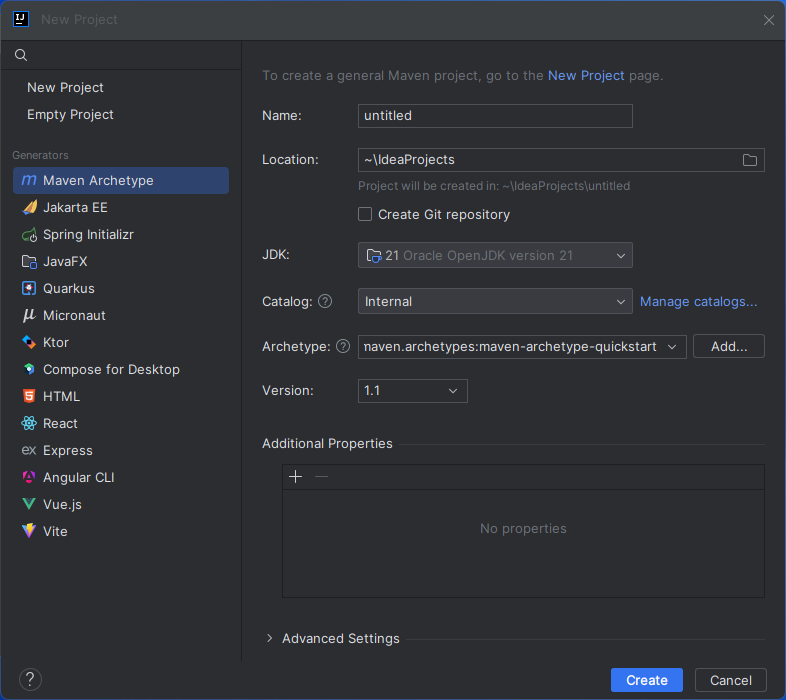
Create a Project in IntelliJ
- In IntelliJ IDEA, click New Project.
- Select "Maven Archetype" from the Generators
- Name the project and select "maven.archetypes:maven-archetype-quickstart" Archetype.
- Click "Create"
![]()
Install the CData JDBC Driver for Salesforce Pardot JAR File
Use the following Maven command from the project's root folder to install JAR file in the project.
mvn install:install-file -Dfile="PATH/TO/CData JDBC Driver for Salesforce Pardot 20XX/lib/cdata.jdbc.salesforcepardot.jar" -DgroupId="org.cdata.connectors" -DartifactId="cdata-salesforcepardot-connector" -Dversion="23" -Dpackaging=jar
Add Dependencies
Within the Maven project's pom.xml file, add AWS and the CData JDBC Driver for Salesforce Pardot as dependencies (within the <dependencies> element) using the following XML.
- AWS
<dependency> <groupId>com.amazonaws</groupId> <artifactId>aws-lambda-java-core</artifaceId> <version>1.2.2</version> <!--Replace with the actual version--> </dependency> - CData JDBC Driver for Salesforce Pardot
<dependency> <groupId>org.cdata.connectors</groupId> <artifactId>cdata-salesforcepardot-connector</artifaceId> <version>23</version> <!--Replace with the actual version--> </dependency>
Create an AWS Lambda Function
For this sample project, we create two source files: CDataLambda.java and CDataLambdaTest.java.
Lambda Function Definition
- Update CDataLambda to implement the RequestHandler interface from the AWS Lambda SDK. You will need to add the handleRequest method, which performs the following tasks when the Lambda function is triggered:
- Constructs a SQL query using the input.
- Registers the CData JDBC driver for Salesforce Pardot.
- Establishes a connection to Salesforce Pardot using JDBC.
- Executes the SQL query on Salesforce Pardot.
- Prints the results to the console.
- Returns an output message.
- Add the following import statements to the Java class:
import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.ResultSetMetaData; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.sql.Statement; Replace the body of the handleRequest method with the code below. Be sure to fill in the connection string in the DriverManager.getConnection method call.
String query = "SELECT * FROM " + input; try { Class.forName("cdata.jdbc.salesforcepardot.SalesforcePardotDriver"); cdata.jdbc.salesforcepardot.SalesforcePardotDriver driver = new cdata.jdbc.salesforcepardot.SalesforcePardotDriver(); DriverManager.registerDriver(driver); } catch (SQLException ex) { } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } Connection connection = null; try { connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:cdata:salesforcepardot:RTK=52465...;ApiVersion=4;User=YourUsername;Password=YourPassword;UserKey=YourUserKey;"); } catch (SQLException ex) { context.getLogger().log("Error getting connection: " + ex.getMessage()); } catch (Exception ex) { context.getLogger().log("Error: " + ex.getMessage()); } if(connection != null) { context.getLogger().log("Connected Successfully!\n"); } ResultSet resultSet = null; try { //executing query Statement stmt = connection.createStatement(); resultSet = stmt.executeQuery(query); ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData(); int numCols = metaData.getColumnCount(); //printing the results while(resultSet.next()) { for(int i = 1; i <= numCols; i++) { System.out.printf("%-25s", (resultSet.getObject(i) != null) ? resultSet.getObject(i).toString().replaceAll("\n", "") : null ); } System.out.print("\n"); } } catch (SQLException ex) { System.out.println("SQL Exception: " + ex.getMessage()); } catch (Exception ex) { System.out.println("General exception: " + ex.getMessage()); } return "query: " + query + " complete";
Deploy and Run the Lambda Function
Once you build the function in Intellij, you are ready to deploy the entire Maven project as a single JAR file.
- In IntelliJ, use the mvn install command to build the SNAPSHOT JAR file.
- Create a new function in AWS Lambda (or open an existing one).
- Name the function, select an IAM role, and set the timeout value to a high enough value to ensure the function completes (depending on the result size of your query).
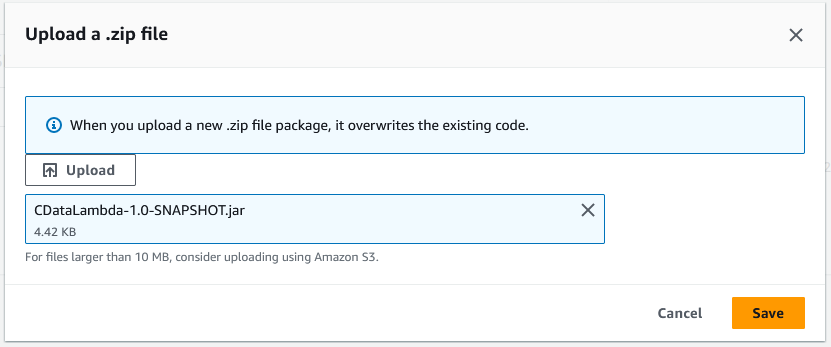
- Click "Upload from" -> ".zip file" and select your SNAPSHOT JAR file.
![Uploading the SNAPSHOT JAR file.]()
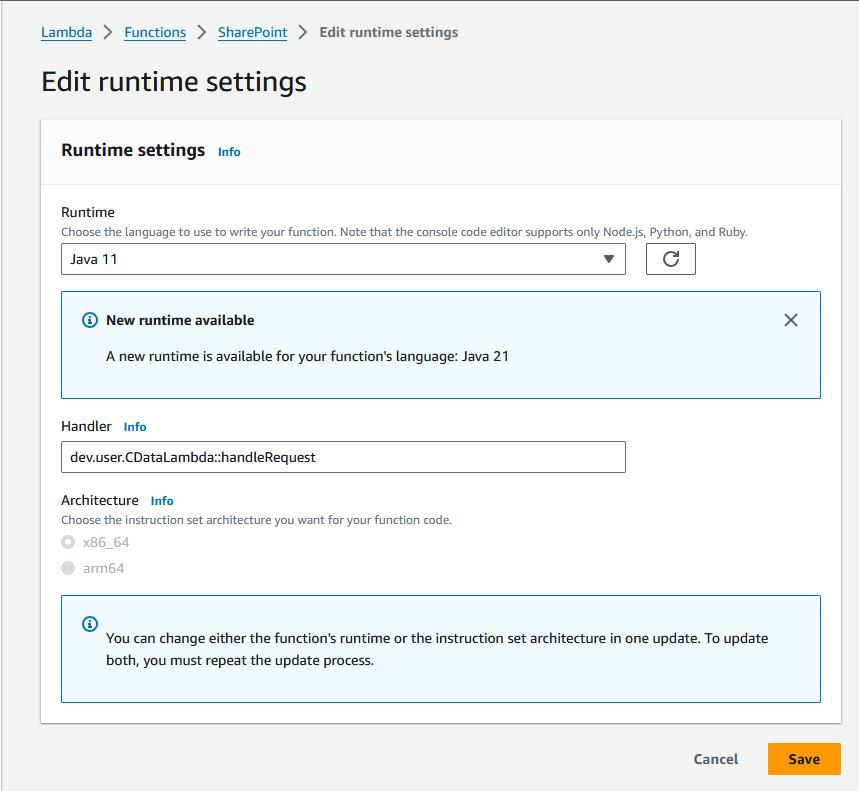
- In the "Runtime settings" section, click "Edit" and set Handler to your "handleRequest" method (e.g. package.class::handleRequest)
![Configuring the runtime handler.]()
- You can now test the function. Set the "Event JSON" field to a table name and click, click "Test"
![Viewing the results.]()
Free Trial & More Information
Download a free, 30-day trial of the CData JDBC Driver for Salesforce Pardot and start working with your live Salesforce Pardot data in AWS Lambda. Reach out to our Support Team if you have any questions.