Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Author and Share Power BI Reports on Real-Time OData Services
Use the CData ODBC Driver for OData to visualize OData services in Power BI Desktop and then upload to the Power BI service.
With built-in support for ODBC on Microsoft Windows, CData ODBC Drivers provide self-service integration with self-service analytics tools such as Microsoft Power BI. The CData ODBC Driver for OData links your Power BI reports to operational OData services. You can monitor OData services through dashboards and ensure that your analysis reflects OData services in real time by scheduling refreshes or refreshing on demand. This article details how to use the ODBC driver to create real-time visualizations of OData services in Microsoft Power BI Desktop and then upload to Power BI.
The CData ODBC Drivers offer unmatched performance for interacting with live OData services in Power BI due to optimized data processing built into the driver. When you issue complex SQL queries from Power BI to OData, the driver pushes supported SQL operations, like filters and aggregations, directly to OData and utilizes the embedded SQL Engine to process unsupported operations (often SQL functions and JOIN operations) client-side. With built-in dynamic metadata querying, you can visualize and analyze OData services using native Power BI data types.
About OData Data Integration
CData simplifies access and integration of live OData services data. Our customers leverage CData connectivity to:
- Access OData versions 2.0, 3.0, and 4.0, working with legacy services and the latest features and capabilities.
- Leverage advanced query options, including $filter, $select, and $expand, enhancing data retrieval from 3rd party tools.
- Use Server-side execution of aggregation and grouping to minimize data transfer and boost performance.
- Authenticate securely using a variety of schemes, including Azure AD, digest, negotiate, NTLM, OAuth, and more means secure authentication with every connection.
- Use SQL stored procedures to manage OData service entities - listing, creating, and removing associations between entities.
Customers use CData's solutions to regularly integrate their OData services with preferred tools, such as Power BI, MicroStrategy, or Tableau, and to replicate data from OData services to their databases or data warehouses.
Getting Started
Connect to OData as an ODBC Data Source
If you have not already, first specify connection properties in an ODBC DSN (data source name). This is the last step of the driver installation. You can use the Microsoft ODBC Data Source Administrator to create and configure ODBC DSNs.
The User and Password properties, under the Authentication section, must be set to valid OData user credentials. In addition, you will need to specify a URL to a valid OData server organization root or OData services file.
After creating a DSN, follow the steps below to connect to the OData DSN from Power BI Desktop:
- Open Power BI Desktop and click Get Data -> ODBC. To start Power BI Desktop from PowerBI.com, click the download button and then click Power BI Desktop.
- Select the DSN in the menu. If you know the SQL query you want to use to import, expand the Advanced Options node and enter the query in the SQL Statement box.
- Select tables in the Navigator dialog.
![The available tables. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
Click Edit to edit the query. The table you imported is displayed in the Query Editor. In the Query Editor, you can enrich your local copy of OData services with other data sources, pivot OData columns, and more. Power BI detects each column's data type from the OData metadata retrieved by the driver.
Power BI records your modifications to the query in the Applied Steps section, adjusting the underlying data retrieval query that is executed to the remote OData services. When you click Close and Apply, Power BI executes the data retrieval query.
Otherwise, click Load to pull the data into Power BI.
Create Data Visualizations
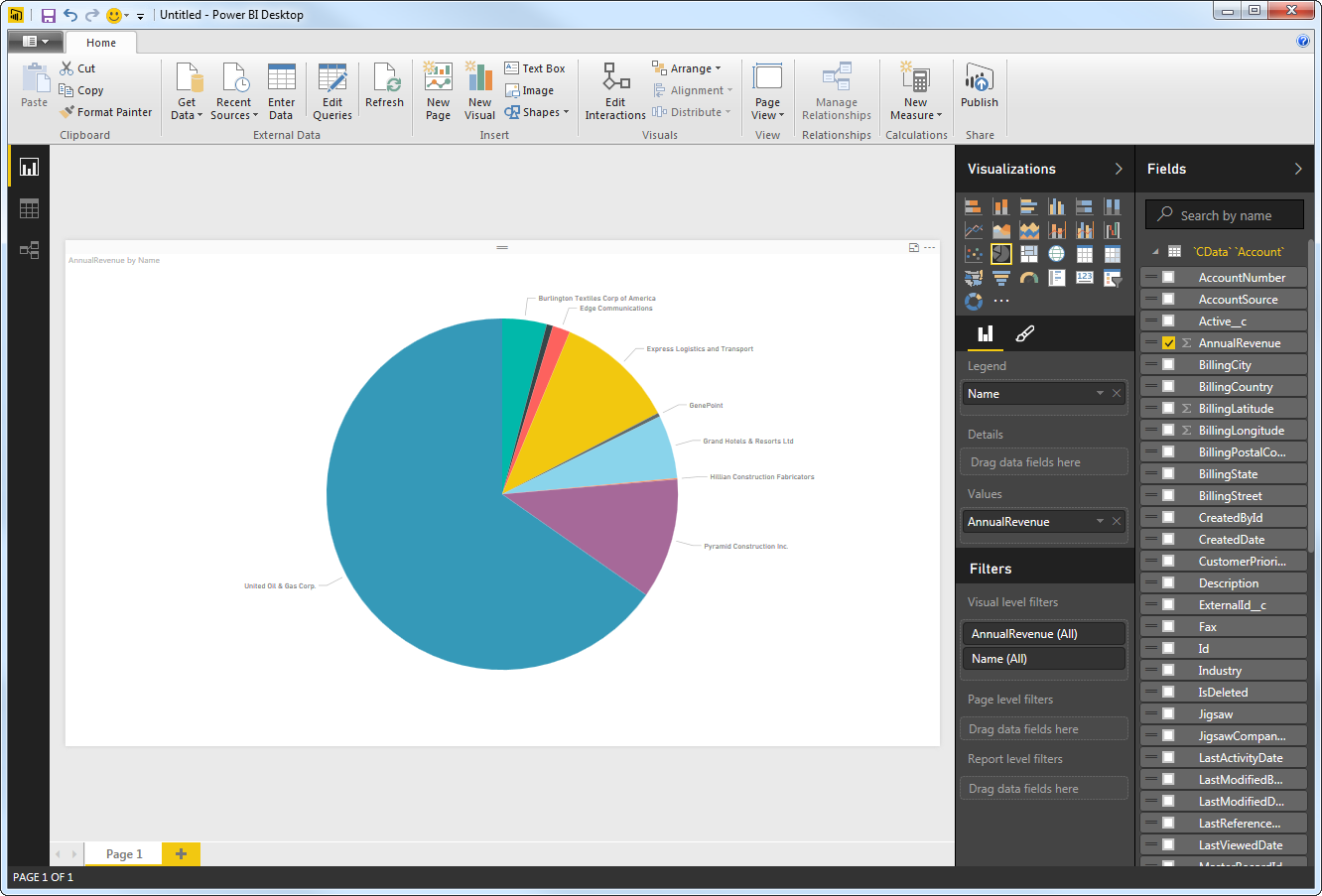
After pulling the data into Power BI, you can create data visualizations in the Report view by dragging fields from the Fields pane onto the canvas. Follow the steps below to create a pie chart:
- Select the pie chart icon in the Visualizations pane.
- Select a dimension in the Fields pane: for example, OrderName.
- Select a measure in the Freight in the Fields pane: for example, Freight.
You can change sort options by clicking the ellipsis (...) button for the chart. Options to select the sort column and change the sort order are displayed.
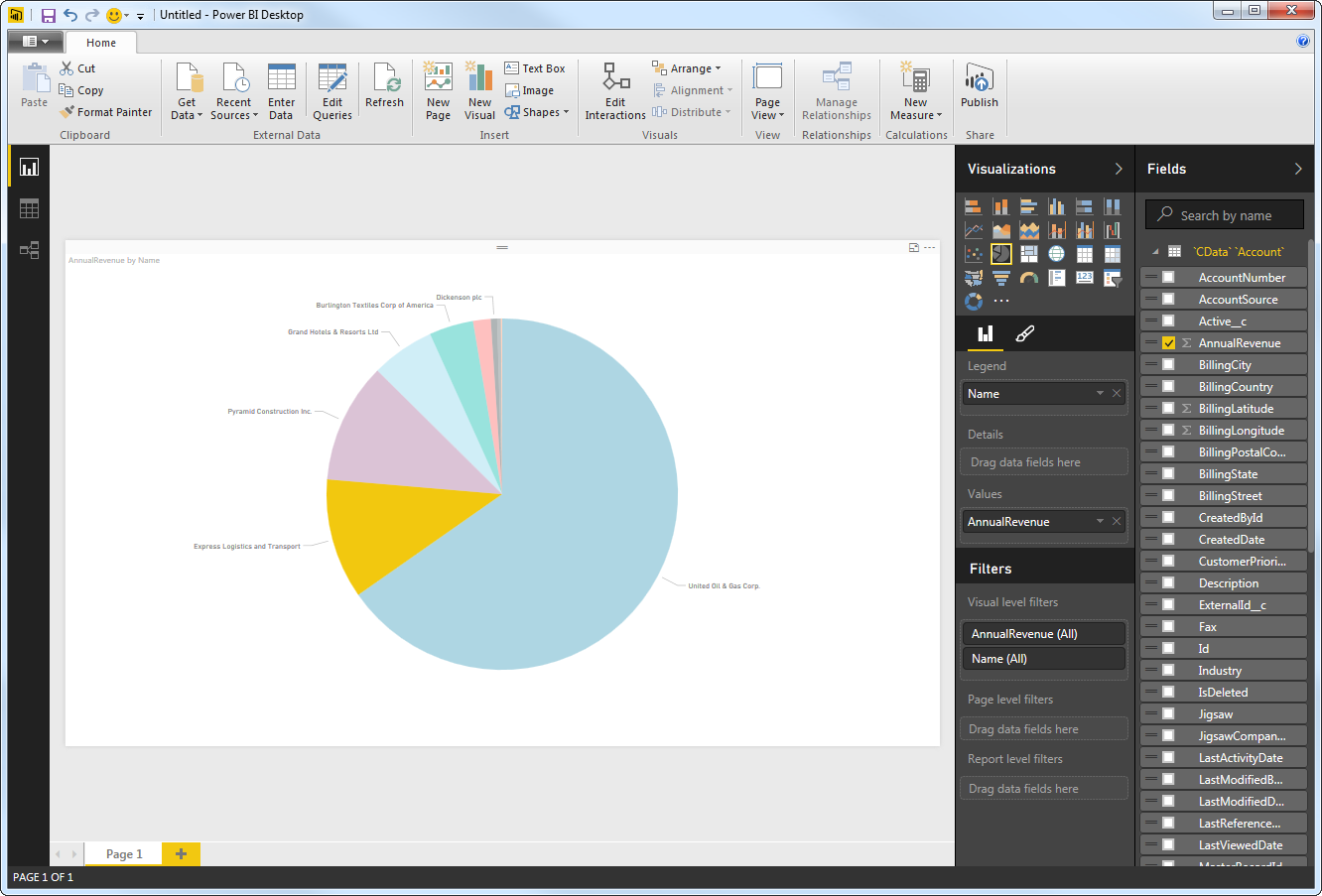
You can use both highlighting and filtering to focus on data. Filtering removes unfocused data from visualizations; highlighting dims unfocused data. You can highlight fields by clicking them:
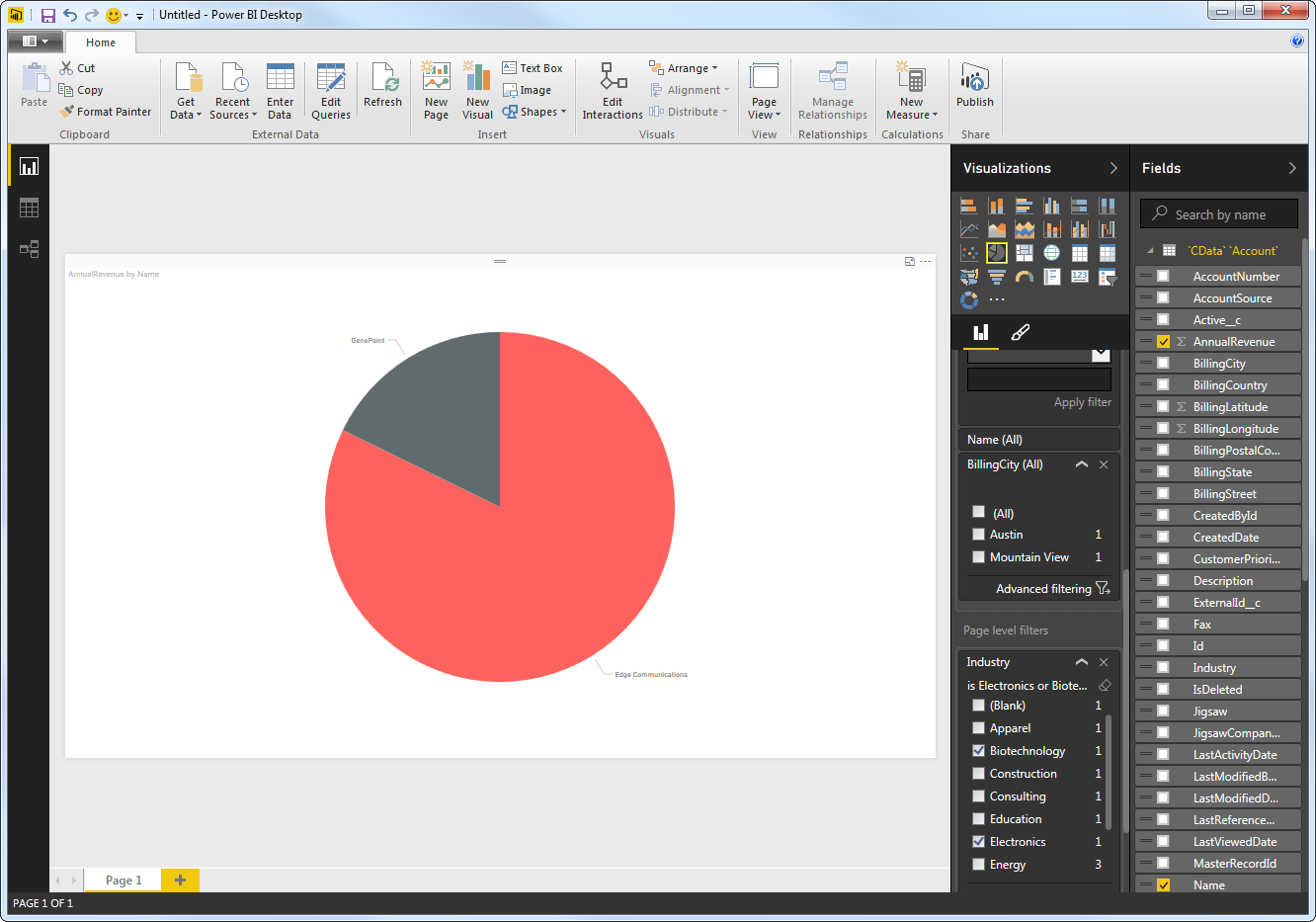
You can apply filters at the page level, at the report level, or to a single visualization by dragging fields onto the Filters pane. To filter on the field's value, select one of the values that are displayed in the Filters pane.
Click Refresh to synchronize your report with any changes to the data.
Upload OData Services Reports to Power BI
You can share reports based on ODBC data sources with other Power BI users in your organization. To upload a dashboard or report, log into PowerBI.com, click Get Data -> Files, and navigate to a Power BI Desktop file or Excel workbook. You can then select the report in the Reports section.
Refresh on Schedule and on Demand
You can use the Power BI Personal Gateway to automatically refresh the dataset associated with your report. You can also refresh the dataset on demand in Power BI. After installing the Personal Gateway, follow the steps below to schedule refreshes for an ODBC DSN:
- Log into Power BI.
- In the Dataset section, right-click the OData Dataset.
- Click Schedule Refresh.
- In the settings for your dataset, expand the Data Source Credentials node and click Edit Credentials in the ODBC section.
- Expand the Schedule Refresh section, select Yes in the Keep Your Data Up to Date menu, and specify the refresh interval.
You can now share real-time OData reports through Power BI.