Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Query NetSuite Data in MySQL Workbench
Create a virtual MySQL database for NetSuite data in CData Connect (or Connect Server) and work with live NetSuite data in MySQL Workbench.
MySQL Workbench allows users to administer MySQL environments and gain better visibility into databases. When paired with CData Connect (on-premise or Connect Server), you get live access to NetSuite data as if it were a MySQL database. This article shows how to create a virtual database for NetSuite in Connect and work with live NetSuite data in MySQL Workbench.
About NetSuite Data Integration
CData provides the easiest way to access and integrate live data from Oracle NetSuite. Customers use CData connectivity to:
- Access all editions of NetSuite, including Standard, CRM, and OneWorld.
- Connect with all versions of the SuiteTalk API (SOAP-based) and SuiteQL, which functions like SQL, enabling easier data querying and manipulation.
- Access predefined and custom reports through support for Saved Searches.
- Securely authenticate with Token-based and OAuth 2.0, ensuring compatibility and security for all use cases.
- Use SQL stored procedures to perform functional actions like uploading or downloading files, attaching or detaching records or relationships, retrieving roles, getting extra table or column info, getting job results, and more.
Customers use CData solutions to access live NetSuite data from their preferred analytics tools, Power BI and Excel. They also use CData's solutions to integrate their NetSuite data into comprehensive databases and data warehouse using CData Sync directly or leveraging CData's compatibility with other applications like Azure Data Factory. CData also helps Oracle NetSuite customers easily write apps that can pull data from and push data to NetSuite, allowing organizations to integrate data from other sources with NetSuite.
For more information about our Oracle NetSuite solutions, read our blog: Drivers in Focus Part 2: Replicating and Consolidating ... NetSuite Accounting Data.
Getting Started
Create a Virtual MySQL Database for NetSuite Data
CData Connect uses a straightforward, point-and-click interface to connect to data sources and generate APIs.
- Login to Connect and click Connections.
![Adding a connection]()
- Select "NetSuite" from Available Data Sources.
-
Enter the necessary authentication properties to connect to NetSuite.
The User and Password properties, under the Authentication section, must be set to valid NetSuite user credentials. In addition, the AccountId must be set to the ID of a company account that can be used by the specified User. The RoleId can be optionally specified to log in the user with limited permissions.
See the "Getting Started" chapter of the help documentation for more information on connecting to NetSuite.
![Configuring a connection (SQL Server is shown).]()
- Click Save Changes
- Click Privileges -> Add and add the new user (or an existing user) with the appropriate permissions.
With the virtual database created, you are ready to connect to NetSuite from MySQL Workbench.
Query NetSuite from MySQL Workbench
The steps below outline connecting to the virtual NetSuite database in Connect from MySQL Workbench and issuing basic queries to work with live NetSuite data.
Connect to NetSuite through Connect
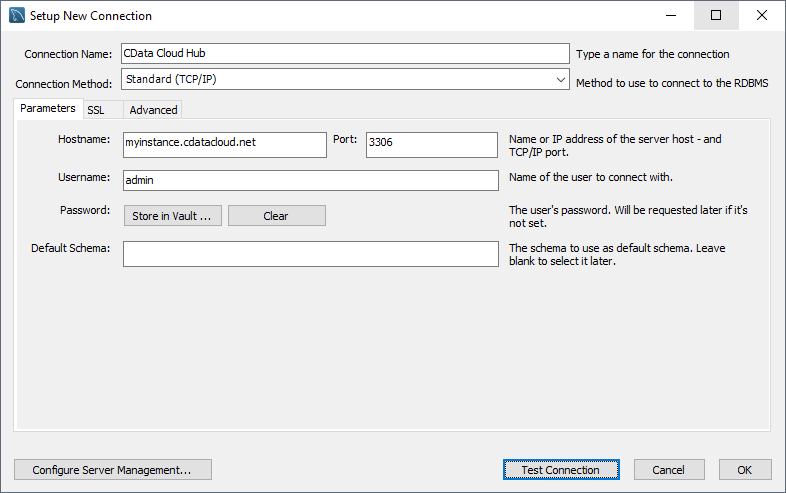
- In MySQL Workbench, click to add a new MySQL connection.
- Name the connection (CData Connect).
- Set the Hostname, Port, and Username parameters to connect to the SQL Gateway.
- Click Store in Vault to set and store the password.
- Click Test Connection to ensure the connection is configured properly and click OK.
Query NetSuite Data
- Open the connection you just created (CData Connect).
- Click File -> New Query Tab.
- Write a SQL query to retrieve NetSuite data, like SELECT * FROM netsuitedb.SalesOrder;
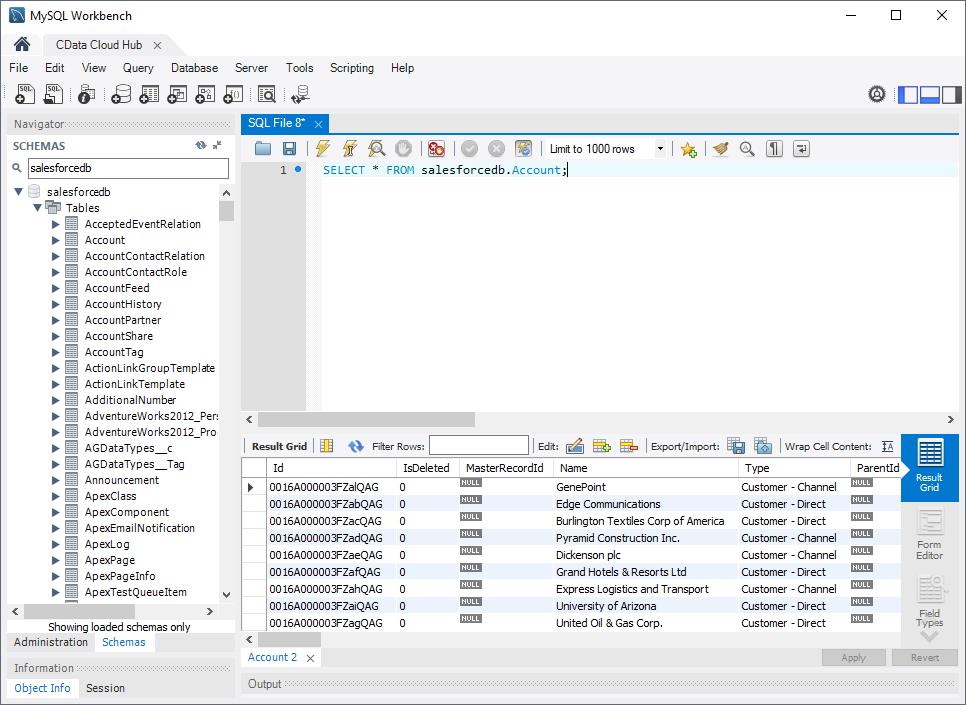
With access to live NetSuite data from MySQL Workbench, you can easily query and update NetSuite, just like you would a MySQL database. Request a demo of the CData Connect and start working with NetSuite just like a MySQL database today.







