Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Access JSON Services from MySQL in HeidiSQL
Use CData ODBC Driver and SQL Gateway to connect and query live JSON services from HeidiSQL.
HeidiSQL is an open-source database administration tool that natively supports MariaDB, MySQL, SQL Server, and PostgreSQL. When paired with the CData ODBC Driver for JSON and SQL Gateway, HediSQL's reach extends to include access to live JSON services. This article demonstrates how to connect to on-premise JSON and query JSON services in HeidiSQL.
Connect to JSON Services
If you have not already done so, provide values for the required connection properties in the data source name (DSN). You can use the built-in Microsoft ODBC Data Source Administrator to configure the DSN. This is also the last step of the driver installation. See the "Getting Started" chapter in the help documentation for a guide to using the Microsoft ODBC Data Source Administrator to create and configure a DSN.
See the Getting Started chapter in the data provider documentation to authenticate to your data source: The data provider models JSON APIs as bidirectional database tables and JSON files as read-only views (local files, files stored on popular cloud services, and FTP servers). The major authentication schemes are supported, including HTTP Basic, Digest, NTLM, OAuth, and FTP. See the Getting Started chapter in the data provider documentation for authentication guides.
After setting the URI and providing any authentication values, set DataModel to more closely match the data representation to the structure of your data.
The DataModel property is the controlling property over how your data is represented into tables and toggles the following basic configurations.
- Document (default): Model a top-level, document view of your JSON data. The data provider returns nested elements as aggregates of data.
- FlattenedDocuments: Implicitly join nested documents and their parents into a single table.
- Relational: Return individual, related tables from hierarchical data. The tables contain a primary key and a foreign key that links to the parent document.
See the Modeling JSON Data chapter for more information on configuring the relational representation. You will also find the sample data used in the following examples. The data includes entries for people, the cars they own, and various maintenance services performed on those cars.
When you configure the DSN, you may also want to set the Max Rows connection property. This will limit the number of rows returned, which is especially helpful for improving performance when designing reports and visualizations.
Configure the SQL Gateway
See the SQL Gateway Overview to set up connectivity to JSON services as a virtual MySQL database. You will configure a MySQL remoting service that listens for MySQL requests from clients. The service can be configured in the SQL Gateway UI.
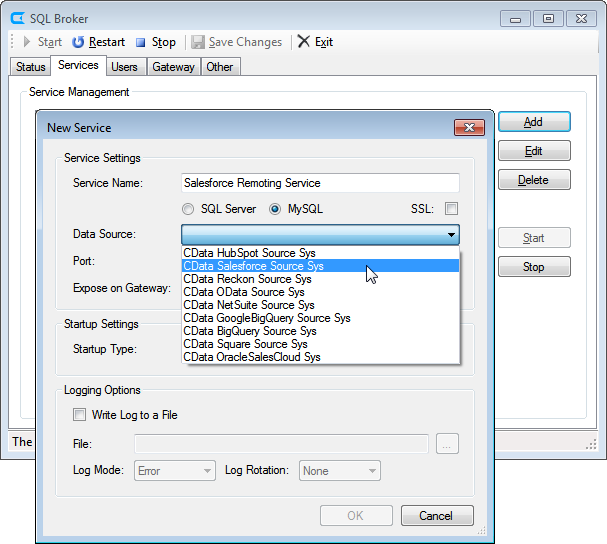
To connect to the SQL Gateway from HeidiSQL, you will need to run the SQL Gateway on a web-facing machine. After configuring the SQL Gateway, make note of the following information:
- The IP address or domain name of the machine hosting the SQL Gateway
- The data source name (likely CData JSON Sys) of the MySQL service
- The port number of the MySQL service
- The credentials of a SQL Gateway user with access to the service
Configure Remote Access
If your ODBC Driver and the remoting service are installed on-premise (and not accessible from HeidiSQL), you can use the reverse SSH tunneling feature to enable remote access. For detailed instructions, read our Knowledge Base article: SQL Gateway SSH Tunneling Capabilities.
Connect to JSON in HeidiSQL
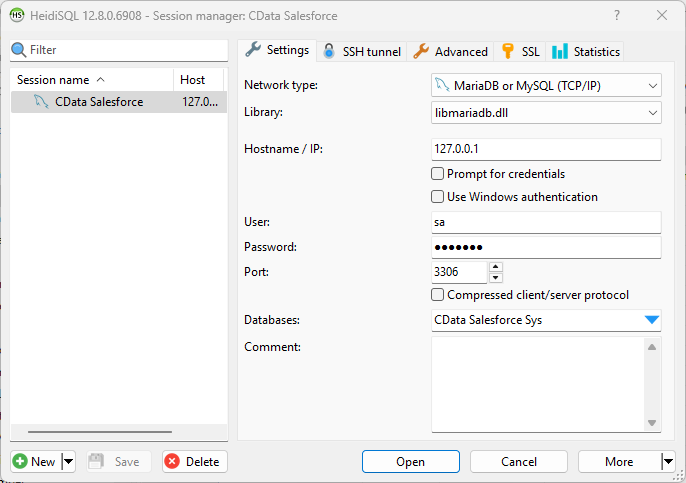
Once you have a MySQL Service configured for the CData ODBC Driver for JSON, you are ready to connect to the data in HeidiSQL. Start by creating a new connection Session in HeidiSQL, then choose the MySQL library type.
Configure the data set using the values for the MySQL service for JSON you configured in SQL Gateway (be sure to use the DSN for the database name). Validate your connection and click Open.
Query JSON from HeidiSQL
- In the database listing on the left, find your connection to JSON configured earlier.
- In the database listing on the left, expand the appropriate connection and to view individual tables or data objects present within JSON.
- Write custom SQL queries targeting these tables, treating the data source like any SQL Server database, or visually explore each tabular data set by selecting the relevant tables
![Querying within HeidiSQL.]()
With the CData ODBC Driver for JSON and SQL Gateway, you are able to easily query data from JSON services in HeidiSQL. If you have any questions, such as needing to access your on-premises data from HeidiSQL, let our Support Team know.