Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →How to Work with HubDB Data in AWS Glue Jobs Using JDBC
Connect to HubDB from AWS Glue jobs using the CData JDBC Driver hosted in Amazon S3.
AWS Glue is an ETL service from Amazon that allows you to easily prepare and load your data for storage and analytics. Using the PySpark module along with AWS Glue, you can create jobs that work with data over JDBC connectivity, loading the data directly into AWS data stores. In this article, we walk through uploading the CData JDBC Driver for HubDB into an Amazon S3 bucket and creating and running an AWS Glue job to extract HubDB data and store it in S3 as a CSV file.
Upload the CData JDBC Driver for HubDB to an Amazon S3 Bucket
In order to work with the CData JDBC Driver for HubDB in AWS Glue, you will need to store it (and any relevant license files) in an Amazon S3 bucket.
- Open the Amazon S3 Console.
- Select an existing bucket (or create a new one).
- Click Upload
- Select the JAR file (cdata.jdbc.hubdb.jar) found in the lib directory in the installation location for the driver.
Configure the Amazon Glue Job
- Navigate to ETL -> Jobs from the AWS Glue Console.
- Click Add Job to create a new Glue job.
- Fill in the Job properties:
- Name: Fill in a name for the job, for example: HubDBGlueJob.
- IAM Role: Select (or create) an IAM role that has the AWSGlueServiceRole and AmazonS3FullAccess permissions policies. The latter policy is necessary to access both the JDBC Driver and the output destination in Amazon S3.
- Type: Select "Spark".
- Glue Version: Select "Spark 2.4, Python 3 (Glue Version 1.0)".
- This job runs: Select "A new script to be authored by you".
Populate the script properties: - Script file name: A name for the script file, for example: GlueHubDBJDBC
- S3 path where the script is stored: Fill in or browse to an S3 bucket.
- Temporary directory: Fill in or browse to an S3 bucket.
- Expand Security configuration, script libraries and job parameters (optional). For Dependent jars path, fill in or browse to the S3 bucket where you uploaded the JAR file. Be sure to include the name of the JAR file itself in the path, i.e.: s3://mybucket/cdata.jdbc.hubdb.jar
- Click Next. Here you will have the option to add connection to other AWS endpoints. So, if your Destination is Redshift, MySQL, etc, you can create and use connections to those data sources.
- Click "Save job and edit script" to create the job.
- In the editor that opens, write a python script for the job. You can use the sample script (see below) as an example.
Sample Glue Script
To connect to HubDB using the CData JDBC driver, you will need to create a JDBC URL, populating the necessary connection properties. Additionally, you will need to set the RTK property in the JDBC URL (unless you are using a Beta driver). You can view the licensing file included in the installation for information on how to set this property.
There are two authentication methods available for connecting to HubDB data source: OAuth Authentication with a public HubSpot application and authentication with a Private application token.
Using a Custom OAuth App
AuthScheme must be set to "OAuth" in all OAuth flows. Be sure to review the Help documentation for the required connection properties for you specific authentication needs (desktop applications, web applications, and headless machines).
Follow the steps below to register an application and obtain the OAuth client credentials:
- Log into your HubSpot app developer account.
- Note that it must be an app developer account. Standard HubSpot accounts cannot create public apps.
- On the developer account home page, click the Apps tab.
- Click Create app.
- On the App info tab, enter and optionally modify values that are displayed to users when they connect. These values include the public application name, application logo, and a description of the application.
- On the Auth tab, supply a callback URL in the "Redirect URLs" box.
- If you're creating a desktop application, set this to a locally accessible URL like http://localhost:33333.
- If you are creating a Web application, set this to a trusted URL where you want users to be redirected to when they authorize your application.
- Click Create App. HubSpot then generates the application, along with its associated credentials.
- On the Auth tab, note the Client ID and Client secret. You will use these later to configure the driver.
Under Scopes, select any scopes you need for your application's intended functionality.
A minimum of the following scopes is required to access tables:
- hubdb
- oauth
- crm.objects.owners.read
- Click Save changes.
- Install the application into a production portal with access to the features that are required by the integration.
- Under "Install URL (OAuth)", click Copy full URL to copy the installation URL for your application.
- Navigate to the copied link in your browser. Select a standard account in which to install the application.
- Click Connect app. You can close the resulting tab.
Using a Private App
To connect using a HubSpot private application token, set the AuthScheme property to "PrivateApp."
You can generate a private application token by following the steps below:
- In your HubDB account, click the settings icon (the gear) in the main navigation bar.
- In the left sidebar menu, navigate to Integrations > Private Apps.
- Click Create private app.
- On the Basic Info tab, configure the details of your application (name, logo, and description).
- On the Scopes tab, select Read or Write for each scope you want your private application to be able to access.
- A minimum of hubdb and crm.objects.owners.read is required to access tables.
- After you are done configuring your application, click Create app in the top right.
- Review the info about your application's access token, click Continue creating, and then Show token.
- Click Copy to copy the private application token.
To connect, set PrivateAppToken to the private application token you retrieved.
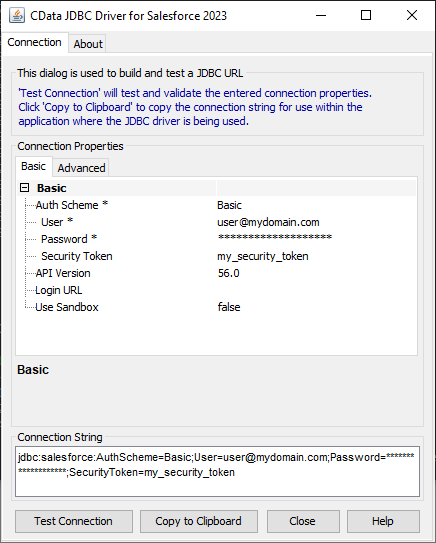
Built-in Connection String Designer
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the HubDB JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the JAR file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.hubdb.jar
Fill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
To host the JDBC driver in Amazon S3, you will need a license (full or trial) and a Runtime Key (RTK). For more information on obtaining this license (or a trial), contact our sales team.
Below is a sample script that uses the CData JDBC driver with the PySpark and AWSGlue modules to extract HubDB data and write it to an S3 bucket in CSV format. Make any necessary changes to the script to suit your needs and save the job.
import sys
from awsglue.transforms import *
from awsglue.utils import getResolvedOptions
from pyspark.context import SparkContext
from awsglue.context import GlueContext
from awsglue.dynamicframe import DynamicFrame
from awsglue.job import Job
args = getResolvedOptions(sys.argv, ['JOB_NAME'])
sparkContext = SparkContext()
glueContext = GlueContext(sparkContext)
sparkSession = glueContext.spark_session
##Use the CData JDBC driver to read HubDB data from the NorthwindProducts table into a DataFrame
##Note the populated JDBC URL and driver class name
source_df = sparkSession.read.format("jdbc").option("url","jdbc:hubdb:RTK=5246...;AuthScheme=OAuth;OAuthClientID=MyOAuthClientID;OAuthClientSecret=MyOAuthClientSecret;CallbackURL=http://localhost:33333;").option("dbtable","NorthwindProducts").option("driver","cdata.jdbc.hubdb.HubDBDriver").load()
glueJob = Job(glueContext)
glueJob.init(args['JOB_NAME'], args)
##Convert DataFrames to AWS Glue's DynamicFrames Object
dynamic_dframe = DynamicFrame.fromDF(source_df, glueContext, "dynamic_df")
##Write the DynamicFrame as a file in CSV format to a folder in an S3 bucket.
##It is possible to write to any Amazon data store (SQL Server, Redshift, etc) by using any previously defined connections.
retDatasink4 = glueContext.write_dynamic_frame.from_options(frame = dynamic_dframe, connection_type = "s3", connection_options = {"path": "s3://mybucket/outfiles"}, format = "csv", transformation_ctx = "datasink4")
glueJob.commit()
Run the Glue Job
With the script written, we are ready to run the Glue job. Click Run Job and wait for the extract/load to complete. You can view the status of the job from the Jobs page in the AWS Glue Console. Once the Job has succeeded, you will have a CSV file in your S3 bucket with data from the HubDB NorthwindProducts table.
Using the CData JDBC Driver for HubDB in AWS Glue, you can easily create ETL jobs for HubDB data, whether writing the data to an S3 bucket or loading it into any other AWS data store.