Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Access Live Microsoft Dataverse Data in AWS Lambda
Connect to live Microsoft Dataverse data in AWS Lambda using the CData JDBC Driver.
AWS Lambda is a compute service that lets you build applications that respond quickly to new information and events. AWS Lambda functions can work with live Microsoft Dataverse data when paired with the CData JDBC Driver for Microsoft Dataverse. This article describes how to connect to and query Microsoft Dataverse data from an AWS Lambda function built in Eclipse.
At the time this article was written (June 2022), Eclipse version 2019-12 and Java 8 were the highest versions supported by the AWS Toolkit for Eclipse.
With built-in optimized data processing, the CData JDBC Driver offers unmatched performance for interacting with live Microsoft Dataverse data. When you issue complex SQL queries to Microsoft Dataverse, the driver pushes supported SQL operations, like filters and aggregations, directly to Microsoft Dataverse and utilizes the embedded SQL engine to process unsupported operations client-side (often SQL functions and JOIN operations). In addition, its built-in dynamic metadata querying allows you to work with and analyze Microsoft Dataverse data using native data types.
About Microsoft Dataverse Data Integration
CData provides the easiest way to access and integrate live data from Microsoft Dataverse (formerly the Common Data Service). Customers use CData connectivity to:
- Access both Dataverse Entities and Dataverse system tables to work with exactly the data they need.
- Authenticate securely with Microsoft Dataverse in a variety of ways, including Azure Active Directory, Azure Managed Service Identity credentials, and Azure Service Principal using either a client secret or a certificate.
- Use SQL stored procedures to manage Microsoft Dataverse entities - listing, creating, and removing associations between entities.
CData customers use our Dataverse connectivity solutions for a variety of reasons, whether they're looking to replicate their data into a data warehouse (alongside other data sources)or analyze live Dataverse data from their preferred data tools inside the Microsoft ecosystem (Power BI, Excel, etc.) or with external tools (Tableau, Looker, etc.).
Getting Started
Gather Connection Properties and Build a Connection String
You can connect without setting any connection properties for your user credentials. Below are the minimum connection properties required to connect.
- InitiateOAuth: Set this to GETANDREFRESH. You can use InitiateOAuth to avoid repeating the OAuth exchange and manually setting the OAuthAccessToken.
- OrganizationUrl: Set this to the organization URL you are connecting to, such as https://myorganization.crm.dynamics.com.
- Tenant (optional): Set this if you wish to authenticate to a different tenant than your default. This is required to work with an organization not on your default Tenant.
When you connect the Common Data Service OAuth endpoint opens in your default browser. Log in and grant permissions. The OAuth process completes automatically.
NOTE: To use the JDBC driver in an AWS Lambda function, you will need a license (full or trial) and a Runtime Key (RTK). For more information on obtaining this license (or a trial), contact our sales team.
Built-in Connection String Designer
For assistance constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the Microsoft Dataverse JDBC Driver. Double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.cds.jar
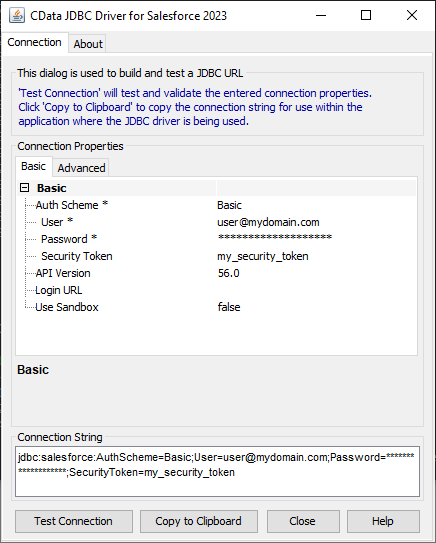
Fill in the connection properties (including the RTK) and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
Create an AWS Lambda Function
- Download the CData JDBC Driver for Microsoft Dataverse installer, unzip the package, and run the JAR file to install the driver.
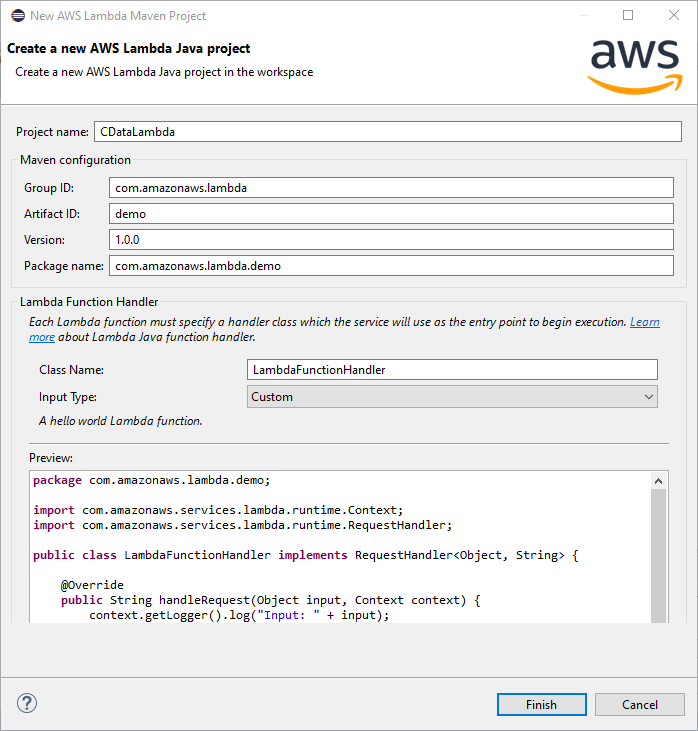
Create a new AWS Lambda Java Project in Eclipse using the AWS Toolkit for Eclipse. You can follow the tutorial from AWS (amazon.com).
For this article, set the Input Type for the project to "Custom" so we can enter a table name as the input.
![Creating a new AWS Lambda Java project]()
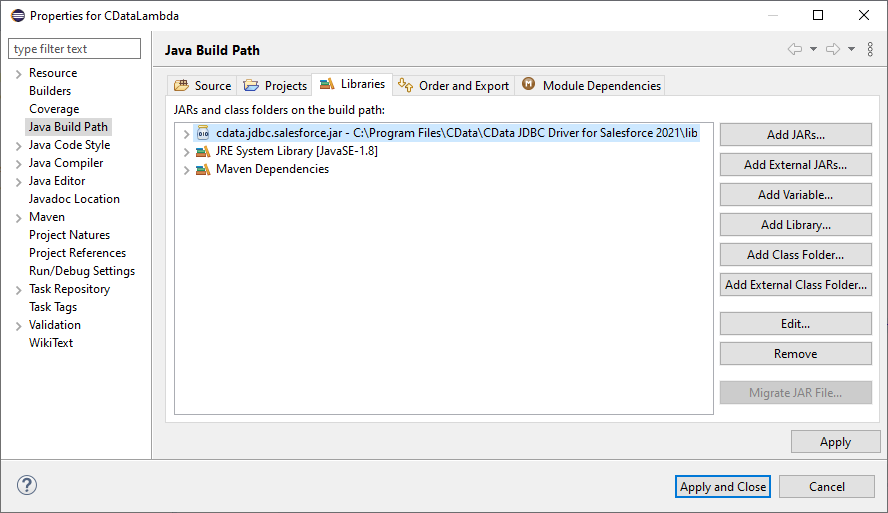
- Add the CData JDBC Driver for Microsoft Dataverse JAR file (cdata.jdbc.cds.jar) to the build path. The file is found in INSTALL_PATH\lib\.
![Adding the JDBC Driver JAR file]()
- Add the following import statements to the Java class:
import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.ResultSetMetaData; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.sql.Statement; Replace the body of the handleRequest method with the code below. Be sure to fill in the connection string in the DriverManager.getConnection method call.
String query = "SELECT * FROM " + input; try { Class.forName("cdata.jdbc.cds.CDSDriver"); } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { context.getLogger().log("Error: class not found"); } Connection connection = null; try { connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:cdata:cds:RTK=52465...;OrganizationUrl=https://myaccount.crm.dynamics.com/InitiateOAuth=GETANDREFRESH"); } catch (SQLException ex) { context.getLogger().log("Error getting connection: " + ex.getMessage()); } catch (Exception ex) { context.getLogger().log("Error: " + ex.getMessage()); } if(connection != null) { context.getLogger().log("Connected Successfully!\n"); } ResultSet resultSet = null; try { //executing query Statement stmt = connection.createStatement(); resultSet = stmt.executeQuery(query); ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData(); int numCols = metaData.getColumnCount(); //printing the results while(resultSet.next()) { for(int i = 1; i <= numCols; i++) { System.out.printf("%-25s", (resultSet.getObject(i) != null) ? resultSet.getObject(i).toString().replaceAll("\n", "") : null ); } System.out.print("\n"); } } catch (SQLException ex) { System.out.println("SQL Exception: " + ex.getMessage()); } catch (Exception ex) { System.out.println("General exception: " + ex.getMessage()); } String output = "query: " + query + " complete"; return output;
Deploy and Run the Lambda Function
Once you build the function in Eclipse, you are ready to upload and run the function. In this article, the output is written to the AWS logs, but you can use this is a template to implement you own custom business logic to work with Microsoft Dataverse data in AWS Lambda functions.
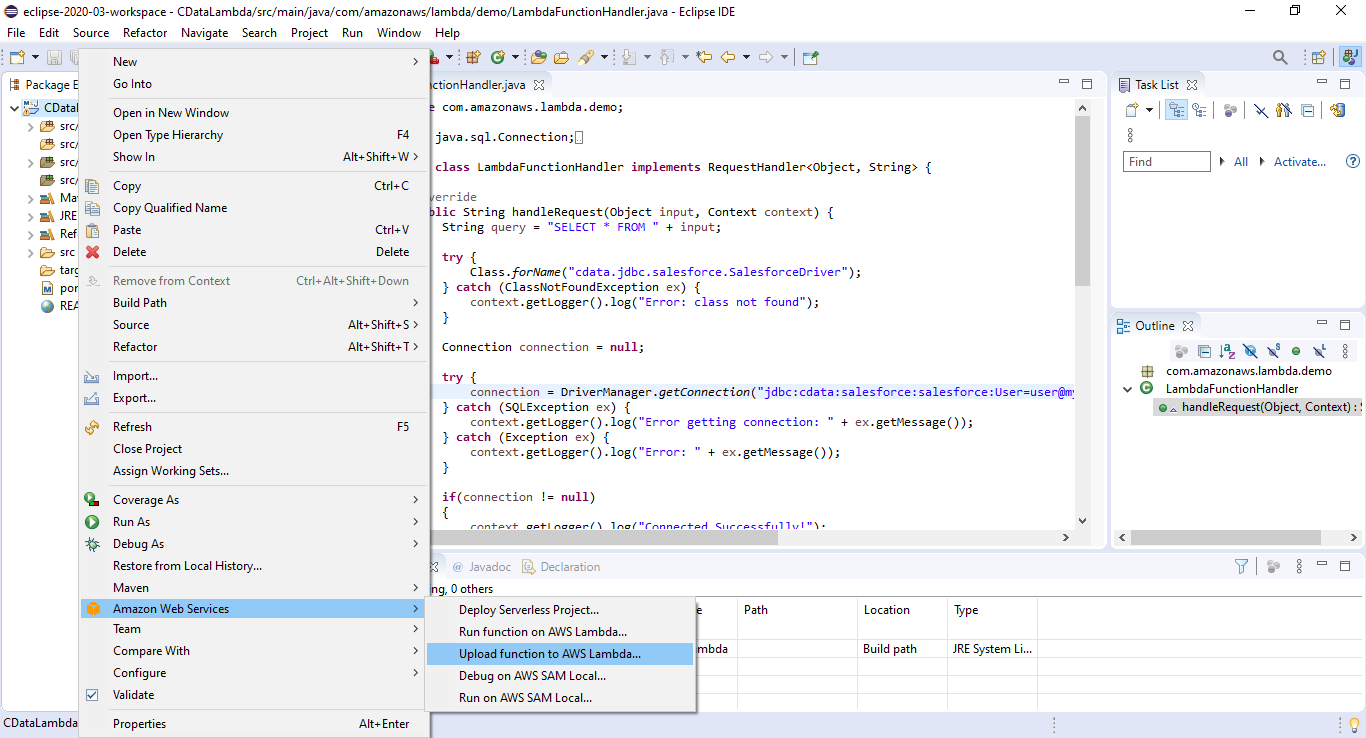
- Right-click the Package and select Amazon Web Services -> Upload function to AWS Lamba.
![Uploading the function to AWS Lambda]()
- Name the function, select an IAM role, and set the timeout value to a high enough value to ensure the function completes (depending on the result size of your query).
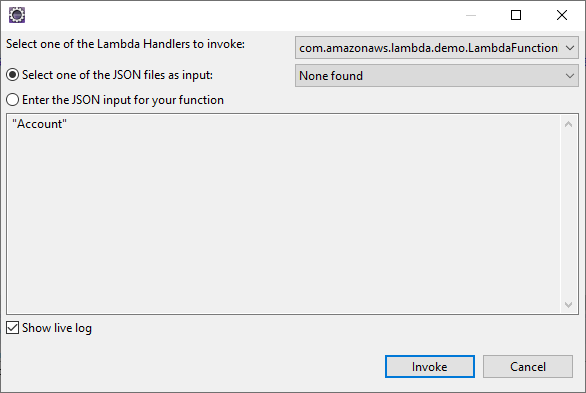
- Right-click the Package and select Amazon Web Services -> Run function on AWS Lambda and set the input to the name of the Microsoft Dataverse object you wish to query (i.e. "Accounts").
![Entering the table name as input]()
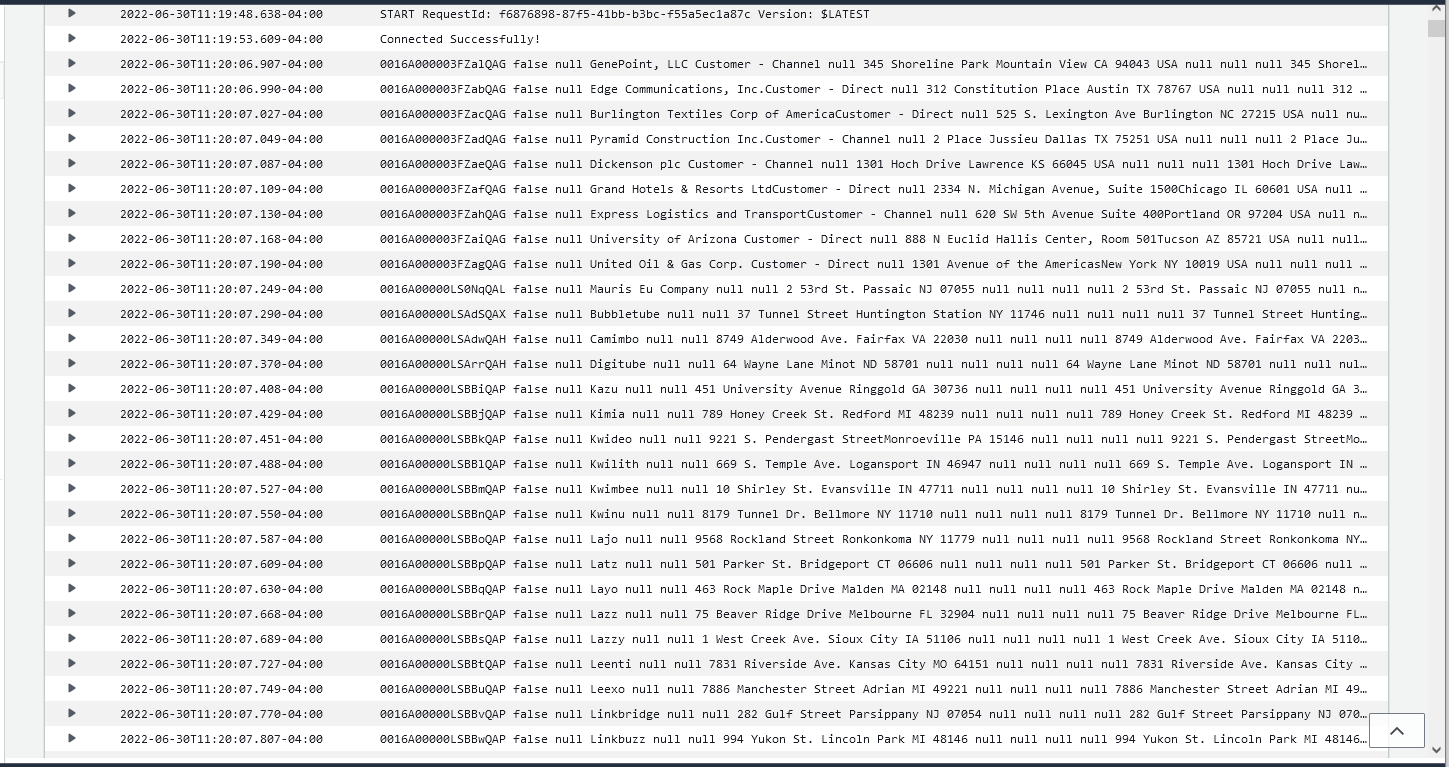
- After the job runs, you can view the output in the CloudWatch logs.
![The data in AWS CloudWatch (Salesforce is shown).]()
Free Trial & More Information
Download a free, 30-day trial of the CData JDBC Driver for Microsoft Dataverse and start working with your live Microsoft Dataverse data in AWS Lambda. Reach out to our Support Team if you have any questions.