Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Using AngularJS to Build Dynamic Web Pages with Amazon Athena Data
Use the CData Connect Server to create Amazon Athena OData feeds and build single-page applications with live Amazon Athena data.
AngularJS (Angular) is a structural framework for dynamic web apps and can be paired with CData Connect Server to build single-page applications (SPAs) with access to live data from Amazon Athena. The CData Connect Server creates a virtual database for Amazon Athena and can be used to generate an OData API (natively consumable from Angular) for Amazon Athena. This article will walk through setting up CData Connect Server and creating a simple SPA that has live access to Amazon Athena data. The SPA will dynamically build and populate an HTML table.
About Amazon Athena Data Integration
CData provides the easiest way to access and integrate live data from Amazon Athena. Customers use CData connectivity to:
- Authenticate securely using a variety of methods, including IAM credentials, access keys, and Instance Profiles, catering to diverse security needs and simplifying the authentication process.
- Streamline their setup and quickly resolve issue with detailed error messaging.
- Enhance performance and minimize strain on client resources with server-side query execution.
Users frequently integrate Athena with analytics tools like Tableau, Power BI, and Excel for in-depth analytics from their preferred tools.
To learn more about unique Amazon Athena use cases with CData, check out our blog post: https://www.cdata.com/blog/amazon-athena-use-cases.
Getting Started
Connect to Amazon Athena from AngularJS
To work with live Amazon Athena data in our Angular app, we need to connect to Amazon Athena from Connect Server, provide user access to the new virtual database, and create OData endpoints for the Amazon Athena data.
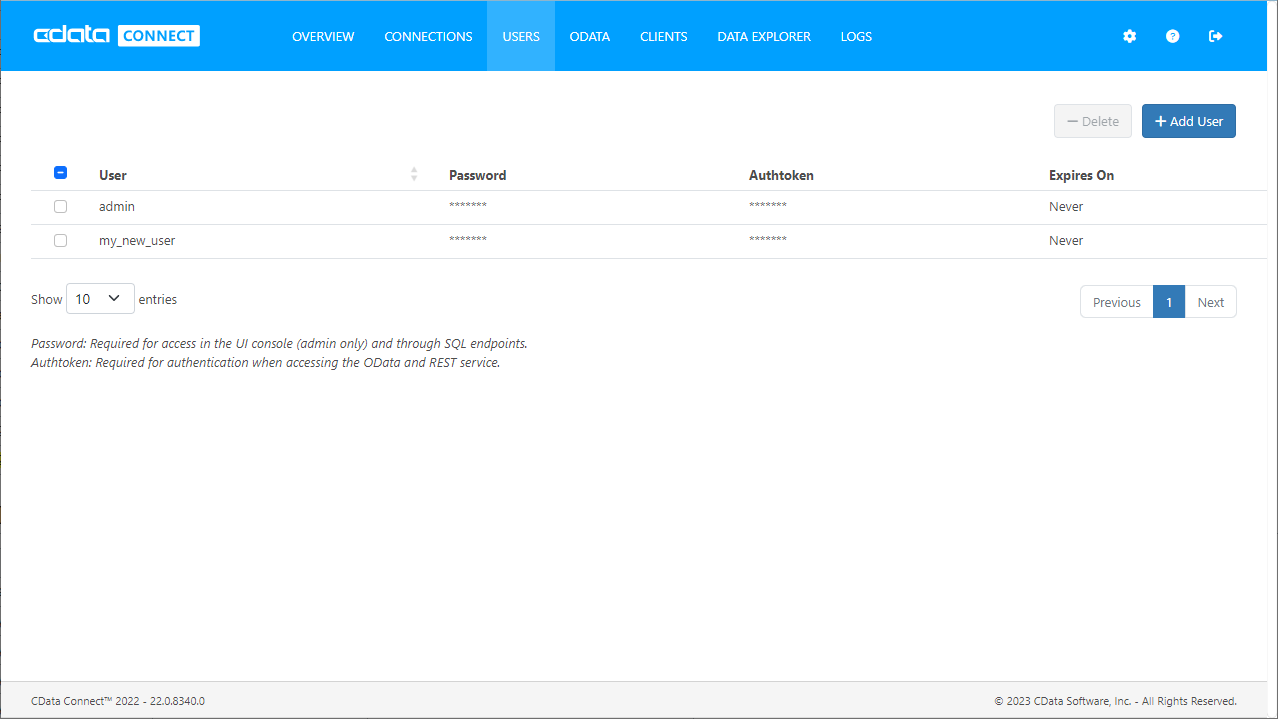
Add a Connect Server User
Create a User to connect to Amazon Athena from Angular through Connect Server.
- Click Users -> Add
- Configure a User
![Creating a new user]()
- Click Save Changes and make note of the Authtoken for the new user
![Connect Server users]()
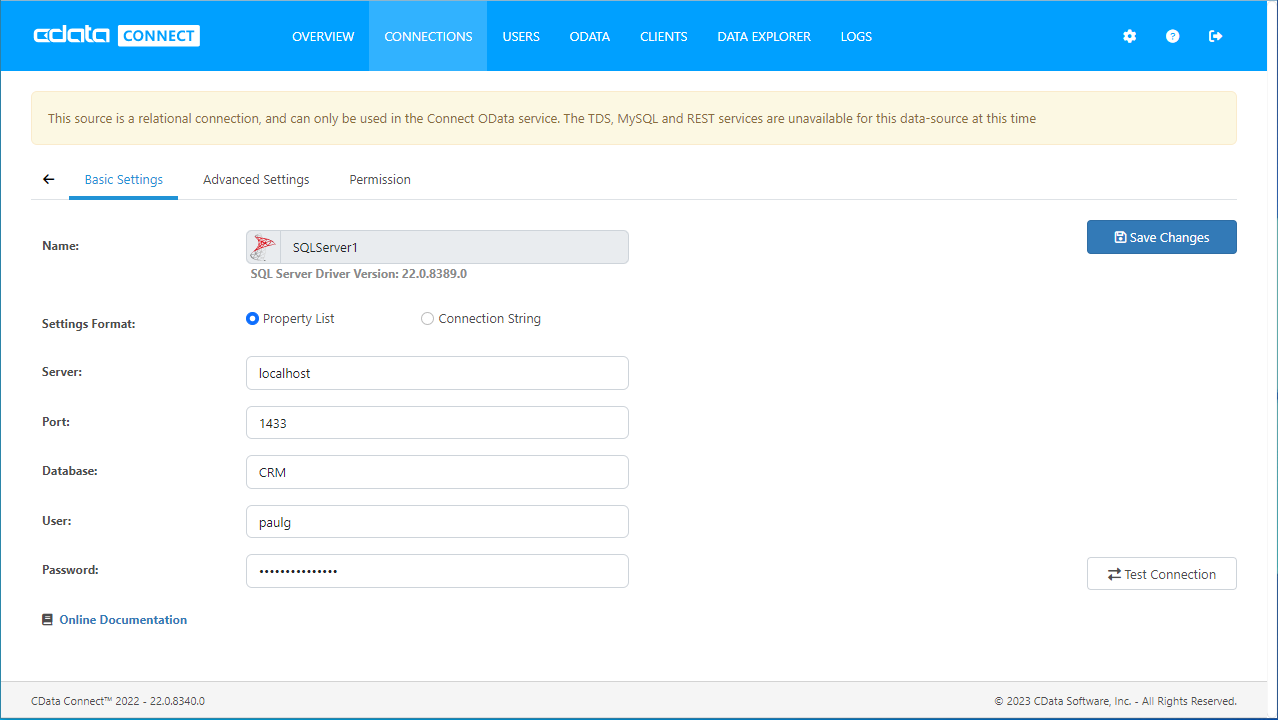
Connect to Amazon Athena from Connect Server
CData Connect Server uses a straightforward, point-and-click interface to connect to data sources and generate APIs.
- Open Connect Server and click Connections
![Adding a connection]()
- Select "Amazon Athena" from Available Data Sources
- Enter the necessary authentication properties to connect to Amazon Athena.
Authenticating to Amazon Athena
To authorize Amazon Athena requests, provide the credentials for an administrator account or for an IAM user with custom permissions: Set AccessKey to the access key Id. Set SecretKey to the secret access key.
Note: Though you can connect as the AWS account administrator, it is recommended to use IAM user credentials to access AWS services.
Obtaining the Access Key
To obtain the credentials for an IAM user, follow the steps below:
- Sign into the IAM console.
- In the navigation pane, select Users.
- To create or manage the access keys for a user, select the user and then select the Security Credentials tab.
To obtain the credentials for your AWS root account, follow the steps below:
- Sign into the AWS Management console with the credentials for your root account.
- Select your account name or number and select My Security Credentials in the menu that is displayed.
- Click Continue to Security Credentials and expand the Access Keys section to manage or create root account access keys.
Authenticating from an EC2 Instance
If you are using the CData Data Provider for Amazon Athena 2018 from an EC2 Instance and have an IAM Role assigned to the instance, you can use the IAM Role to authenticate. To do so, set UseEC2Roles to true and leave AccessKey and SecretKey empty. The CData Data Provider for Amazon Athena 2018 will automatically obtain your IAM Role credentials and authenticate with them.
Authenticating as an AWS Role
In many situations it may be preferable to use an IAM role for authentication instead of the direct security credentials of an AWS root user. An AWS role may be used instead by specifying the RoleARN. This will cause the CData Data Provider for Amazon Athena 2018 to attempt to retrieve credentials for the specified role. If you are connecting to AWS (instead of already being connected such as on an EC2 instance), you must additionally specify the AccessKey and SecretKey of an IAM user to assume the role for. Roles may not be used when specifying the AccessKey and SecretKey of an AWS root user.
Authenticating with MFA
For users and roles that require Multi-factor Authentication, specify the MFASerialNumber and MFAToken connection properties. This will cause the CData Data Provider for Amazon Athena 2018 to submit the MFA credentials in a request to retrieve temporary authentication credentials. Note that the duration of the temporary credentials may be controlled via the TemporaryTokenDuration (default 3600 seconds).
Connecting to Amazon Athena
In addition to the AccessKey and SecretKey properties, specify Database, S3StagingDirectory and Region. Set Region to the region where your Amazon Athena data is hosted. Set S3StagingDirectory to a folder in S3 where you would like to store the results of queries.
If Database is not set in the connection, the data provider connects to the default database set in Amazon Athena.
![Configuring a connection (SQL Server is shown).]()
- Click Save Changes
- Click Privileges -> Add and add the new user (or an existing user) with the appropriate permissions (SELECT is all that is required for Angular).
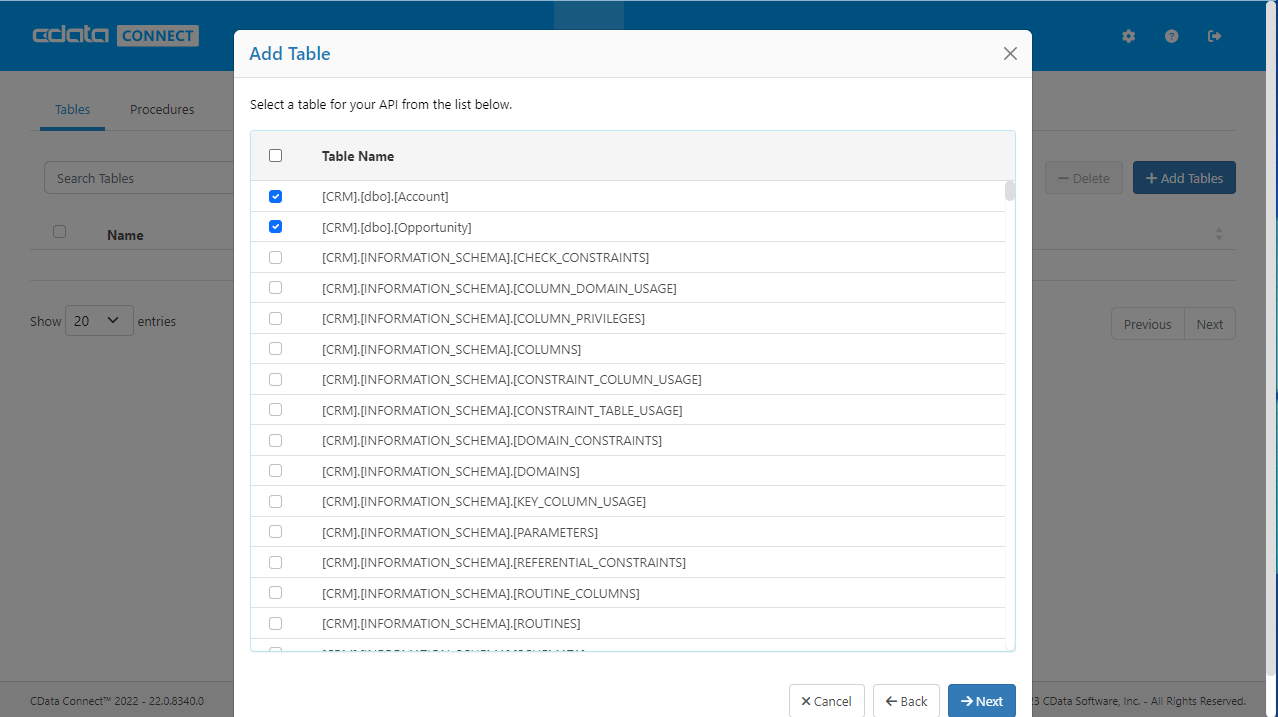
Add Amazon Athena OData Endpoints in Connect Server
After connecting to Amazon Athena, create OData Endpoints for the desired table(s).
- Click OData -> Tables -> Add Tables
- Select the Amazon Athena database
- Select the table(s) you wish to work with and click Next
![Selecting a Table (SQL Server is shown)]()
- (Optional) Edit the resource to select specific fields and more
- Save the settings
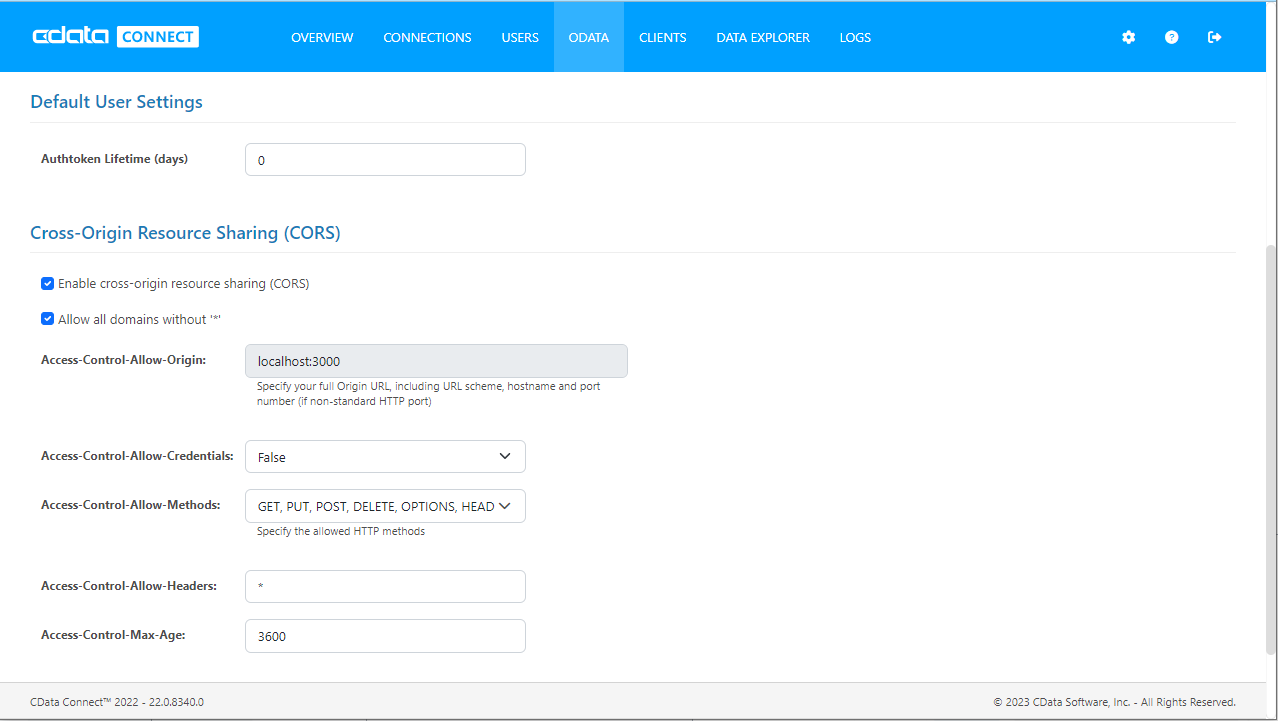
(Optional) Configure Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS)
When accessing and connecting to multiple domains from an application such as Ajax, there is a possibility of violating the limitations of cross-site scripting. In that case, configure the CORS settings in OData -> Settings.
- Enable cross-origin resource sharing (CORS): ON
- Allow all domains without '*': ON
- Access-Control-Allow-Methods: GET, PUT, POST, OPTIONS
- Access-Control-Allow-Headers: Authorization
Save the changes to the settings.
Sample URLs for OData Feeds
Once you have configured a connection to Amazon Athena, created a user, and created OData endpoints in Connect Server, you can access OData feeds for Amazon Athena data. Below, you will see the URLs to access tables and the list of tables. For information on accessing the tables, you can navigate to the API page for Connect Server (click the API link on the top right of Connect Server Web page). For the URLs, you will need the URL of Connect Server, likely in the form: CONNECT_SERVER_URL/. Since we are working with Angular, we will append the @json parameter to the end of URLs that do not return JSON data by default.
| Table | URL | |
|---|---|---|
| Entity (table) List | CONNECT_SERVER_URL/api.rsc/ | |
| Metadata for table Customers | CONNECT_SERVER_URL/api.rsc/Customers/$metadata?@json | |
| Customers | CONNECT_SERVER_URL/api.rsc/AmazonAthena_Customers |
As with standard OData feeds, if you wish to limit the fields returned, you can add a $select parameter to the query, along with other standard OData URL parameters, such as $filter, $orderby, $skip, and $top. See the help documentation for more information on supported OData queries.
Building a Single Page Application
With the setup for Connect Server completed, we are ready to build our SPA. Since this is a simple demonstration, we will include all of our CSS, scripting, and Angular controllers in a single file, deliberately not engaging the functionality provided by AngularJS services, factories, and custom directives.
CSS Definitions & Importing AngularJS Libraries
To start, create some CSS rulesets to modify the table, th, td, and tr elements to format the tables of data. We also need to import the AngularJS libraries for use in our SPA.
<style>
table, th, td {
border: 1px solid grey;
border-collapse: collapse;
padding: 5px;
}
table tr:nth-child(odd) {
background-color: #f1f1f1;
}
table tr:nth-child(even) {
background-color: #ffffff;
}
</style>
<script src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/angularjs/1.7.8/angular.min.js"></script>
Creating & Referencing the Angular App and Controller Objects
Next, add the ng-app and ng-controller directives in the HTML body tag, since the body is the only place we will be using Angular. Then, at the end of the HTML body, we will create the script tag, in which we will create and define the Angular app and controller.
<body ng-app="DataApp" ng-controller="SimpleController">
...
<script>
var app = angular.module('DataApp', []);
app.controller('SimpleController', function($scope, $http) {
//we will add code here
});
</script>
</body>
Defining Our Controller
Our controller for this example will consist of three functions: init to initialize our Angular objects and set up the SPA, getTableColumns to retrieve the columns for a selected table, and getTableData to retrieve data for the selected fields from the selected column. The first action we take when creating the controller is to call the init function. All other functions will be called as needed and it is in these function calls that we make the required HTTP GET calls to Connect Server to retrieve Amazon Athena data.
init();
/*
* Initialize the data object, which will be used with Angular to
* build the different parts of our SPA and to retrieve data from
* Connect Server.
*/
function init() {
$scope.data = {
availableTables: [],
availableColumns: [],
selectedTable: {},
tableData: []
};
/*
* Call to Connect Server to get the list of Tables, select the
* first table by default, and retrieve the available columns.
*
* The call to Connect Server returns standard OData, so the
* data we need is in the value object in the JSON returned.
*/
$http.get("CONNECT_SERVER_URL/api.rsc",{headers: {"x-cdata-authtoken": "MyAuthtoken"}})
.then(function (response) {
$scope.data.availableTables = response.data.value;
$scope.data.selectedTable = $scope.data.availableTables[0];
$scope.getTableColumns();
});
}
/*
* Call to Connect Server to get the list of columns for the
* selected table.
*
* The data returned here is not standard OData, so we drill
* down into the response to extract exactly the data we need
* (an array of column names).
*
* With the column names retrieved, we will transform the array
* of column names into an array of objects with a name and Id
* field, to be used when we build an HTML select.
*/
$scope.getTableColumns = function () {
$scope.data.tableData = [];
$scope.data.selectedColumns = [];
table = $scope.data.selectedTable.url;
if (table != "") {
$http.get("CONNECT_SERVER_URL/api.rsc/" + table + "/$metadata?@json", {headers: {"x-cdata-authtoken": "MyAuthtoken"}})
.then(function (response) {
$scope.data.availableColumns = response.data.items[0]["odata:cname"];
for (i = 0; i < $scope.data.availableColumns.length; i++) {
$scope.data.availableColumns[i] = { id: i, name: $scope.data.availableColumns[i] };
}
});
}
}
/*
* Call to Connect Server to get the requested data. We get the data
* based on the table selected in the associated HTML select.
* Then we create a comma-separated string of the selected columns.
*
* With the table and columns known, we can make the appropriate call
* to Connect Server. Because the driver returns standard OData, the
* table data is found in the value field of the response.
*/
$scope.getTableData = function () {
table = $scope.data.selectedTable.url;
columnsArray = $scope.data.selectedColumns;
columnString = "";
for (i = 0; i < columnsArray.length; i++) {
if (columnString != "") {
columnString += ",";
}
columnString += columnsArray[i].name;
}
if (table != "") {
$http.get("CONNECT_SERVER_URL/api.rsc/" + table + "?$select=" + columnString, {headers: {"x-cdata-authtoken": "MyAuthtoken"}})
.then(function (response) { $scope.data.tableData = response.data.value; });
} else {
$scope.data.tableData = [];
}
}
Building the Webpage
With our Controller defined, we are now ready to build our webpage using Angular. There are four major parts in our simple page: a select box to choose a table, a select (multiple) box to choose columns, a button to retrieve data, and a table to display the data. We will walk through these four parts one at a time, explaining the use of Angular as we go.
Select a Table
In the first select element, we use the ng-options directive to iterate through the available tables (retrieved from the init function mentioned earlier) and populate our select element. With the ng-model directive, we assign the value of the selected option to the data.selectedTable field. If the selected table ever changes, the getTableColumns function is called to repopulate the available columns.
<label>Select a Table</label>
<br />
<select name="tableDropDown" id="tableDropDown"
ng-options="table.name for table in data.availableTables track by table.url"
ng-model="data.selectedTable"
ng-change="getTableColumns()">
</select>
Select Columns
In the second select element, we again use the ng-options directive, but this time to iterate through the available columns (as retrieved by the getTableColumns function). For the sake of usability, the columns are sorted by name before populating the select element. Since this select contains the multiple attribute, you can select more than one column. Each selected column is added to the data.selectedColumns array. You will notice that as you select columns, a table header for each column is created (see the data table section below).
<label>Select Columns</label>
<br />
<select name="columnMultiple" id="columnMultiple"
ng-options="column.name for column in data.availableColumns | orderBy:'name' track by column.id"
ng-model="data.selectedColumns"
multiple>
</select>
Get Table Data
In this button, we simply make a call to the getTableData function whenever the button is clicked. You will notice that we use the ng-disabled directive to disable the button whenever the user has not selected any columns. We also dynamically update the text of the button with the name of the selected table.
<button name="getTableData" id="btnGetTableData"
ng-click="getTableData()"
ng-disabled="data.selectedColumns.length == 0">
Get {{data.selectedTable.name}} Data
</button>
Display the Table Data
This section satisfies the end goal of our SPA, to display the data from the selected table. To do so, we use several ng-repeat directives: one to iterate through the selected columns and create table headers, one to iterate through the rows of data returned, and a last one to iterate through the selected columns and display the corresponding data for a given row of data.
By using Angular, we are able to dynamically determine which columns to display. It is worth noting that only those columns selected *before* the button was clicked will contain data. But it is a simple task to select all of the available columns, click the button to get the table data, and then go back and select/deselect different columns to change the data that is displayed. If you change the selected table, then all of the data will be cleared.
<table>
<tr>
<th ng-repeat="column in data.selectedColumns | orderBy:'name'">{{column.name}}</th>
</tr>
<tr ng-repeat="row in data.tableData">
<td ng-repeat="column in data.selectedColumns">{{ row[column.name] }}</td>
</tr>
</table>
Complete App
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<style>
table, th, td {
border: 1px solid grey;
border-collapse: collapse;
padding: 5px;
}
table tr:nth-child(odd) {
background-color: #f1f1f1;
}
table tr:nth-child(even) {
background-color: #ffffff;
}
</style>
<script src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/angularjs/1.7.8/angular.min.js"></script>
<body ng-app="DataApp" ng-controller="SimpleController">
<label>Select a Table</label>
<br>
<select name="tableDropDown" id="tableDropDown"
ng-options="table.name for table in data.availableTables track by table.url"
ng-model="data.selectedTable"
ng-change="getTableColumns()">
</select>
<br>
<br>
<label>Select Columns</label>
<br>
<select name="columnMultiple" id="columnMultiple"
ng-options="column.name for column in data.availableColumns | orderBy:'name' track by column.id"
ng-model="data.selectedColumns"
multiple>
</select>
<br>
<br>
<button name="getTableData" id="btnGetTableData"
ng-click="getTableData()"
ng-disabled="data.selectedColumns.length == 0">
Get {{data.selectedTable.name}} Data
</button>
<br>
<br>
<table>
<tr>
<th ng-repeat="column in data.selectedColumns | orderBy:'name'">{{column.name}}</th>
</tr>
<tr ng-repeat="row in data.tableData">
<td ng-repeat="column in data.selectedColumns">{{ row[column.name] }}</td>
</tr>
</table>
<script>
var app = angular.module('DataApp', []);
app.controller('SimpleController', function($scope, $http) {
init();
/*
* Initialize the data object, which will be used with Angular to
* build the different parts of our SPA and to retrieve data from
* Connect Server.
*/
function init() {
$scope.data = {
availableTables: [],
availableColumns: [],
selectedTable: {},
tableData: []
};
/*
* Call to Connect Server to get the list of tables, select the
* first table by default, and retrieve the available columns.
*
* The call to Connect Server returns standard OData, so the
* data we need is in the value object in the JSON returned.
*/
$http.get("CONNECT_SERVER_URL/api.rsc",{headers: {"x-cdata-authtoken": "MyAuthtoken"}})
.then(function (response) {
$scope.data.availableTables = response.data.value;
$scope.data.selectedTable = $scope.data.availableTables[0];
$scope.getTableColumns();
});
}
/*
* Call to Connect Server to get the list of columns for the
* selected table.
*
* The data returned here is not standard OData, so we drill
* down into the response to extract exactly the data we need
* (an array of column names).
*
* With the column names retrieved, we will transform the array
* of column names into an array of objects with a name and Id
* field, to be used when we build an HTML select.
*/
$scope.getTableColumns = function () {
$scope.data.tableData = [];
$scope.data.selectedColumns = [];
table = $scope.data.selectedTable.url;
if (table != "") {
$http.get("CONNECT_SERVER_URL/api.rsc/" + table + "/$metadata?@json", {headers: {"x-cdata-authtoken": "MyAuthtoken"}})
.then(function (response) {
$scope.data.availableColumns = response.data.items[0]["odata:cname"];
for (i = 0; i < $scope.data.availableColumns.length; i++) {
$scope.data.availableColumns[i] = { id: i, name: $scope.data.availableColumns[i] };
}
});
}
}
/*
* Call to Connect Server to get the requested data. We get the data
* based on the table selected in the associated HTML select.
* Then we create a comma-separated string of the selected columns.
*
* With the table and columns known, we can make the appropriate call
* to Connect Server. Because the driver returns standard OData, the
* table data is found in the value field of the response.
*/
$scope.getTableData = function () {
table = $scope.data.selectedTable.url;
columnsArray = $scope.data.selectedColumns;
columnString = "";
for (i = 0; i < columnsArray.length; i++) {
if (columnString != "") {
columnString += ",";
}
columnString += columnsArray[i].name;
}
if (table != "") {
$http.get("CONNECT_SERVER_URL/api.rsc/" + table + "?$select=" + columnString, {headers: {"x-cdata-authtoken": "MyAuthtoken"}})
.then(function (response) { $scope.data.tableData = response.data.value; });
} else {
$scope.data.tableData = [];
}
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Free Trial & More Information
If you are interested in connecting to your Amazon Athena data (or data from any of our other supported data sources) from web applications built with Angular, sign up for a free trial of the CData Connect Server today! For more information on Connect Server and to see what other data sources we support, refer to our CData Connect page.