Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Access AlloyDB Data from MySQL in HeidiSQL
Use CData ODBC Driver and SQL Gateway to connect and query live AlloyDB data from HeidiSQL.
HeidiSQL is an open-source database administration tool that natively supports MariaDB, MySQL, SQL Server, and PostgreSQL. When paired with the CData ODBC Driver for AlloyDB and SQL Gateway, HediSQL's reach extends to include access to live AlloyDB data. This article demonstrates how to connect to on-premise AlloyDB and query AlloyDB data in HeidiSQL.
Connect to AlloyDB Data
If you have not already done so, provide values for the required connection properties in the data source name (DSN). You can use the built-in Microsoft ODBC Data Source Administrator to configure the DSN. This is also the last step of the driver installation. See the "Getting Started" chapter in the help documentation for a guide to using the Microsoft ODBC Data Source Administrator to create and configure a DSN.
The following connection properties are usually required in order to connect to AlloyDB.
- Server: The host name or IP of the server hosting the AlloyDB database.
- User: The user which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
- Password: The password which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
You can also optionally set the following:
- Database: The database to connect to when connecting to the AlloyDB Server. If this is not set, the user's default database will be used.
- Port: The port of the server hosting the AlloyDB database. This property is set to 5432 by default.
Authenticating with Standard Authentication
Standard authentication (using the user/password combination supplied earlier) is the default form of authentication.
No further action is required to leverage Standard Authentication to connect.
Authenticating with pg_hba.conf Auth Schemes
There are additional methods of authentication available which must be enabled in the pg_hba.conf file on the AlloyDB server.
Find instructions about authentication setup on the AlloyDB Server here.
Authenticating with MD5 Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to md5.
Authenticating with SASL Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to scram-sha-256.
Authenticating with Kerberos
The authentication with Kerberos is initiated by AlloyDB Server when the ∏ is trying to connect to it. You should set up Kerberos on the AlloyDB Server to activate this authentication method. Once you have Kerberos authentication set up on the AlloyDB Server, see the Kerberos section of the help documentation for details on how to authenticate with Kerberos.
When you configure the DSN, you may also want to set the Max Rows connection property. This will limit the number of rows returned, which is especially helpful for improving performance when designing reports and visualizations.
Configure the SQL Gateway
See the SQL Gateway Overview to set up connectivity to AlloyDB data as a virtual MySQL database. You will configure a MySQL remoting service that listens for MySQL requests from clients. The service can be configured in the SQL Gateway UI.
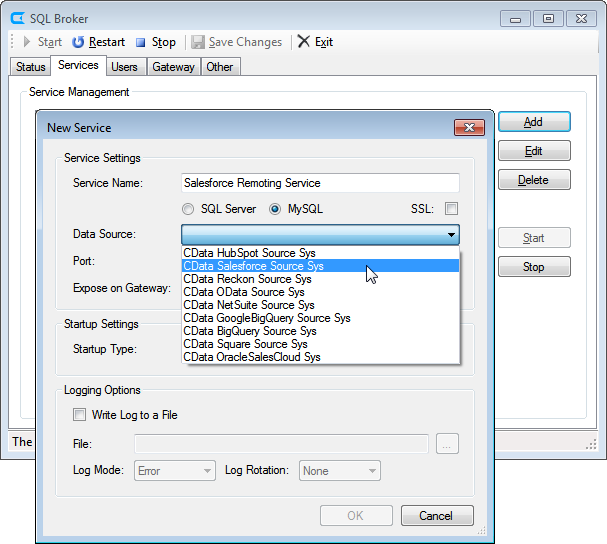
To connect to the SQL Gateway from HeidiSQL, you will need to run the SQL Gateway on a web-facing machine. After configuring the SQL Gateway, make note of the following information:
- The IP address or domain name of the machine hosting the SQL Gateway
- The data source name (likely CData AlloyDB Sys) of the MySQL service
- The port number of the MySQL service
- The credentials of a SQL Gateway user with access to the service
Configure Remote Access
If your ODBC Driver and the remoting service are installed on-premise (and not accessible from HeidiSQL), you can use the reverse SSH tunneling feature to enable remote access. For detailed instructions, read our Knowledge Base article: SQL Gateway SSH Tunneling Capabilities.
Connect to AlloyDB in HeidiSQL
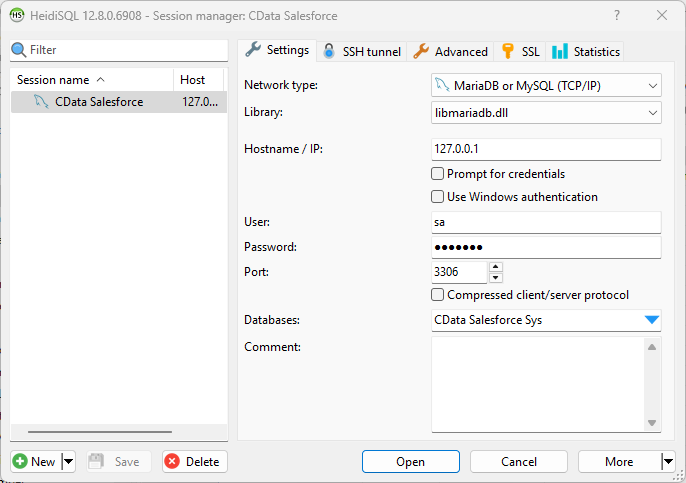
Once you have a MySQL Service configured for the CData ODBC Driver for AlloyDB, you are ready to connect to the data in HeidiSQL. Start by creating a new connection Session in HeidiSQL, then choose the MySQL library type.
Configure the data set using the values for the MySQL service for AlloyDB you configured in SQL Gateway (be sure to use the DSN for the database name). Validate your connection and click Open.
Query AlloyDB from HeidiSQL
- In the database listing on the left, find your connection to AlloyDB configured earlier.
- In the database listing on the left, expand the appropriate connection and to view individual tables or data objects present within AlloyDB.
- Write custom SQL queries targeting these tables, treating the data source like any SQL Server database, or visually explore each tabular data set by selecting the relevant tables
![Querying within HeidiSQL.]()
With the CData ODBC Driver for AlloyDB and SQL Gateway, you are able to easily query data from AlloyDB data in HeidiSQL. If you have any questions, such as needing to access your on-premises data from HeidiSQL, let our Support Team know.






