Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Choosing the Best Method to Connect Salesforce to SQL Server: 5 Options Explained
Discover multiple ways to connect and use Salesforce data from SQL Server, with ideal use cases for developers, SQL Server experts, SSIS users, and business users.
Integrating SQL Server with other systems or applications like Salesforce is essential for modern businesses to leverage their data effectively as it centralizes data management and streamlines operations.
A developer, solution architect, or business user looking to connect their organization's application to SQL Server for improved data analysis or streamlined processes should consider these key questions before selecting a solution:
- Can I build this integration myself?
- Does the application data need to be written to SQL Server?
- Will a linked server be used to virtually access SQL Server?
- Is this part of a broader data analysis platform?
- Will it serve for data integration or business automation?
CData Software's product portfolio addresses all these concerns, offering robust integration solutions to SQL Server that simplify the process.
In this article, we explore five methods provided by CData for connecting to and utilizing Salesforce data from SQL Server, while examining how each method suits specific business use cases.
For data integration and business automation: No-code integration between Salesforce and SQL Server with CData Arc
CData Arc is a server application designed to automate data integration across CData products. It facilitates API integration with SaaS, as well as file and database integration, using no-code and low-code approaches. This product aims to simplify the often-complex process of B2B integration, whether on the cloud or on-premise.
CData Arc comes with CData connectors, enabling seamless use of CData Drivers, which offer the industry's largest number of connection destinations. This allows you to support a wide range of data sources beyond Salesforce, all with a consistent user experience.
All editions of CData Arc feature a robust integration engine and a flexible licensing system tailored to the scale of use. This makes it ideal for first-time users of data integration tools or those seeking a low-code solution that fits their budget. Whether you need integration with SaaS, on-premise systems, or file integration, CData Arc can handle it all.
The integration logic you wish to implement can be configured using the CData Arc flow designer.
Required CData Product: CData Arc
Learn more: CData Arc integrates Shopify data with SQL Server
NOTE: The sample flow above features Shopify, but the same principles apply consistently across all data connectors in CData Arc.
Integrate cloud-based applications with SQL Server: Connect to Salesforce from SQL Server using Connect Cloud
When integrated with CData Connect Cloud, linked servers offer immediate access to cloud-based Salesforce data from your SQL Server database.
CData Connect Cloud provides a native SQL Server interface for Salesforce, enabling you to query Salesforce data without the need for replication to a supported database. With built-in optimized data processing, CData Connect Cloud pushes all supported SQL operations (such as filters, JOINs, etc.) directly to Salesforce, utilizing server-side processing to deliver Salesforce data efficiently and quickly.
Required CData Product: CData Connect Cloud
Learn more: Connect to Salesforce data as a SQL Server Linked Server
If you're good with SQL Server: Access Salesforce data as a linked server with SQL Gateway
SQL Server offers an integration feature called linked servers, which allows you to access other databases directly from SQL Server. By utilizing the CData SQL Gateway with the CData ODBC Driver for Salesforce, you can treat Salesforce data as a linked server within SQL Server. While the data isn't physically stored in SQL Server, you can query Salesforce data using SQL through the SQL Server interface.
Required CData Product: CData ODBC Drivers
Learn More: Connect to Salesforce data as a Linked Server
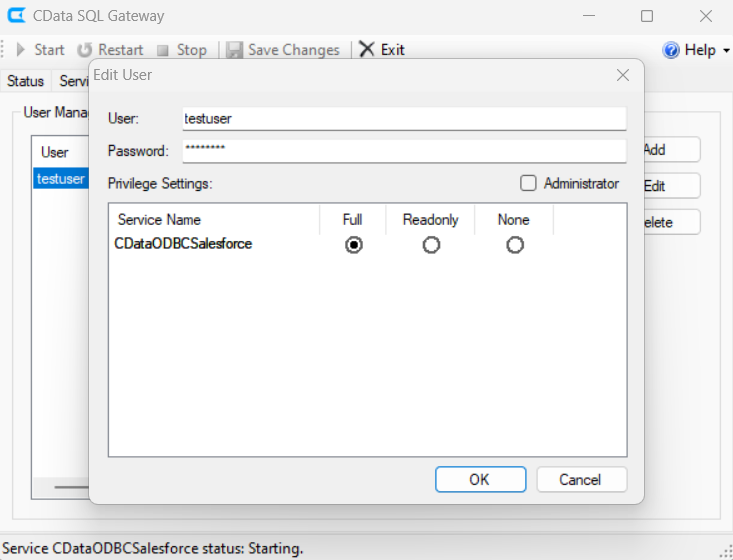
After configuring the standard ODBC Driver for the Salesforce DSN, launch SQL Gateway and set up the Salesforce DSN as an SQL Server service. By registering this service as a linked server in SSMS, you can query Salesforce data directly in SQL, making it ideal for referencing Salesforce data across multiple .NET client applications and performing JOINs with SQL Server data.
SELECT * FROM [linked server name].[CData Salesforce Sys].[Salesforce].[Account]
For those familiar with SQL Server linked servers, this is the easiest method to use. It offers the advantage of querying real-time Salesforce data and allows bi-directional linking, including writing, directly from SQL Server.
However, the only drawback is that the SQL Gateway must be hosted and managed on a server, which can incur high server hosting costs.
For SSIS users: Import Salesforce data into SQL Server with SSIS
Many SQL Server users rely on SSIS (SQL Server Integration Services) for data integration and workflow automation. CData provides an SSIS Component for Salesforce, enabling seamless connectivity between SSIS and Salesforce.
If you're an SSIS user, you can easily set up an import flow to SQL Server using the Salesforce Component. Priced similarly to the driver, it offers a cost-effective solution.
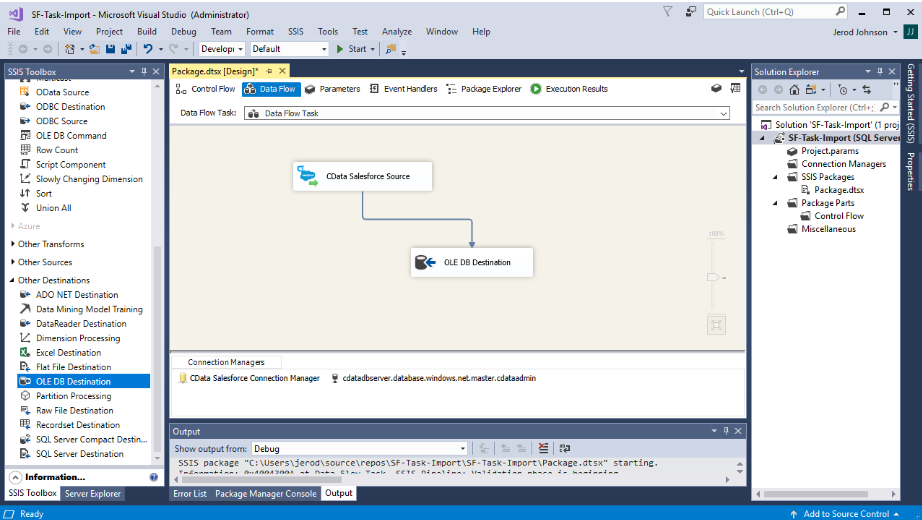
For users of ETL/EAI tools other than SSIS, CData Drivers provide a simple way to connect data. They are compatible with various ETL tools such as ASTERIA Warp, DataSpider, Informatica, and Waha! Transformer, RACCOON, Talend, and more. Salesforce and ETL integration articles listed here (including the Salesforce ETL, Replication & DWH Connection Guide), offer further guidance.
For ETL tool users, this option is cost-effective and easy to implement. You can integrate Salesforce by simply adding the driver to your existing tool.
Required CData Product: SSIS Components
Learn More: How to connect Salesforce to SQL Server with SSIS
NOTE: The demonstration and article above features Salesforce, but the same principles apply consistently across all SSIS Components.
Integrate into your data analytics infrastructure: Replicate Salesforce to SQL Server with CData Sync
If you're looking to connect Salesforce and SQL Server without coding, integrate data and use SQL Server as an analytical platform, we recommend CData Sync. This server-based ETL/ELT tool allows you to easily set up a replication job in just three steps after installation. You can also schedule tasks and customize replication settings, all through an intuitive GUI.
Required CData Product: CData Sync
Learn More: Automated Continuous Salesforce Replication to SQL Server
CData Sync is a no-code tool designed specifically for database synchronization, known for its ease of use and high scalability compared to other options. However, it comes at a higher cost than alternative methods.
Conclusion
CData offers a variety of products to integrate Salesforce with SQL Server. Here's a summary:
- CData Arc is ideal for automating business processes by connecting Salesforce to systems beyond SQL Server, such as cloud storage, accounting, and ERP.
- CData Connect Cloud is ideal for users whose business applications are cloud-based and need integration with SQL Server.
- SQL Gateway is perfect for users familiar with SQL Server who need real-time data, as it enables working with Salesforce data as a linked server to SQL Server.
- SSIS Components are recommended for those experienced with SSIS, allowing easy creation of SSIS import flows at a low cost.
- CData Sync is ideal for replicating Salesforce data to SQL Server without coding, making it perfect for building a data analysis platform on SQL Server.
Get Started Today
CData Software provides the best-in-the-segment products to meet a variety of business integration needs and use cases, as you've seen. All our products come with a 30-day free trial, allowing you to explore their features without any commitment.
Reach out to our Support Team if you have any questions.





