Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Connect to Oracle Data as an External Data Source using PolyBase
Use CData Connect Cloud and PolyBase to create an external data source in SQL Swerver with access to live Oracle data.
PolyBase for SQL Server allows you to query external data by using the same Transact-SQL syntax used to query a database table. When paired with the CData ODBC Driver for Oracle, you get access to your Oracle data directly alongside your SQL Server data. This article describes creating an external data source and external tables to grant access to live Oracle data using T-SQL queries.
NOTE: PolyBase is only available on SQL Server 19 and above, and only for Standard SQL Server.
CData Connect Cloud provides a pure SQL Server interface for Oracle, allowing you to query data from Oracle without replicating the data to a natively supported database. Using optimized data processing out of the box, CData Connect Cloud pushes all supported SQL operations (filters, JOINs, etc.) directly to Oracle, leveraging server-side processing to return the requested Oracle data quickly.
Configure Oracle Connectivity for PolyBase
Connectivity to Oracle from PolyBase is made possible through CData Connect Cloud. To work with Oracle data from PolyBase, we start by creating and configuring a Oracle connection.
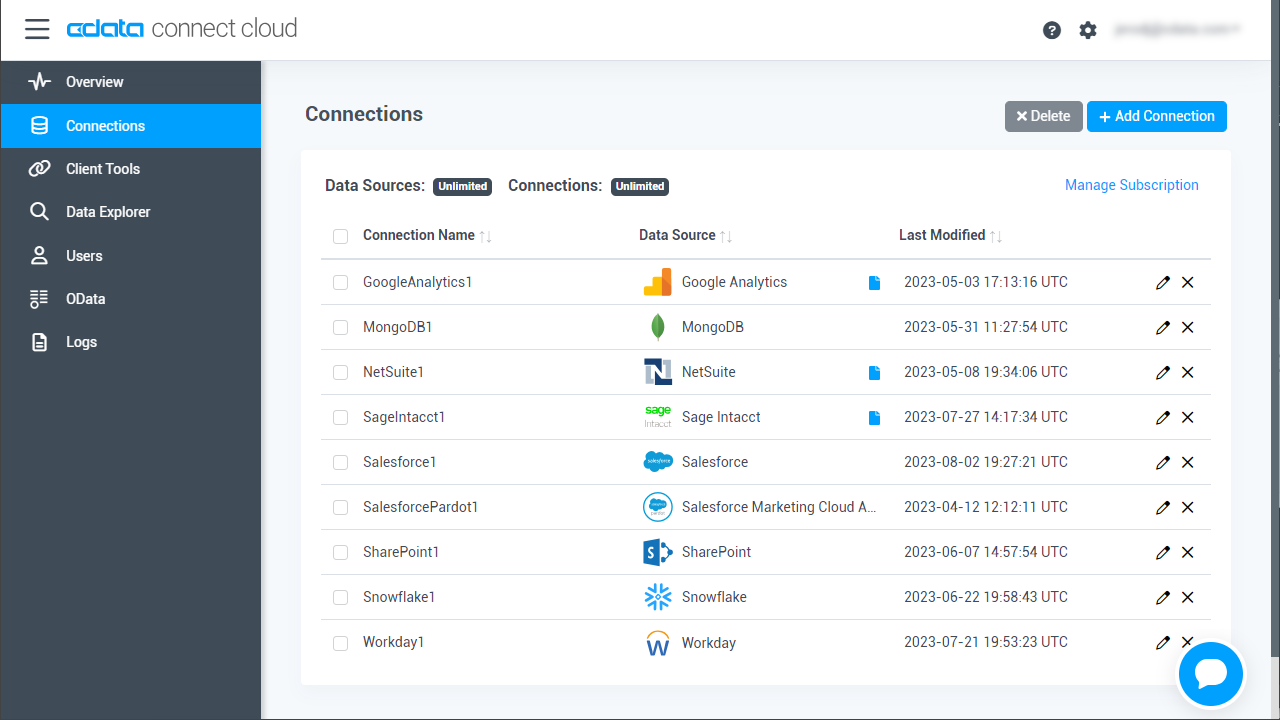
- Log into Connect Cloud, click Connections and click Add Connection
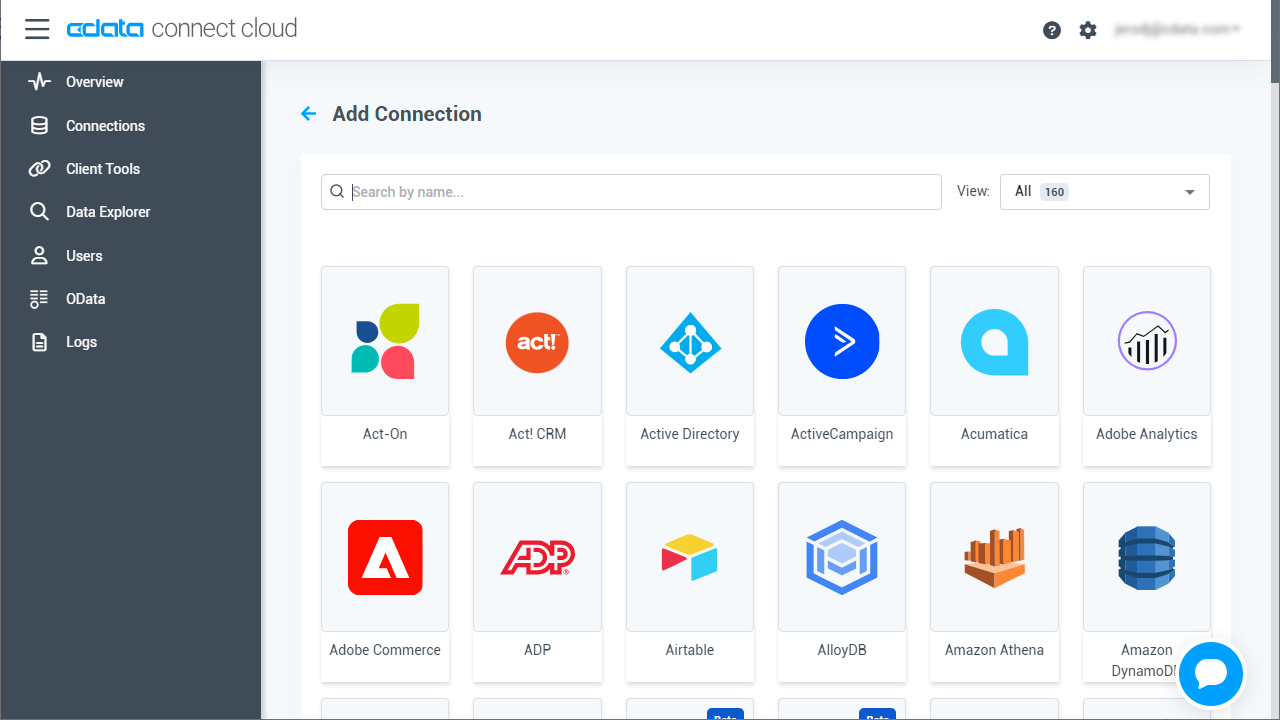
- Select "Oracle" from the Add Connection panel
-
Enter the necessary authentication properties to connect to Oracle.
To connect to Oracle, you'll first need to update your PATH variable and ensure it contains a folder location that includes the native DLLs. The native DLLs can be found in the lib folder inside the installation directory. Once you've done this, set the following to connect:
- Port: The port used to connect to the server hosting the Oracle database.
- User: The user Id provided for authentication with the Oracle database.
- Password: The password provided for authentication with the Oracle database.
- Service Name: The service name of the Oracle database.
![Configuring a connection (Salesforce is shown)]()
- Click Create & Test
-
Navigate to the Permissions tab in the Add Oracle Connection page and update the User-based permissions.
![Updating permissions]()
Add a Personal Access Token
If you are connecting from a service, application, platform, or framework that does not support OAuth authentication, you can create a Personal Access Token (PAT) to use for authentication. Best practices would dictate that you create a separate PAT for each service, to maintain granularity of access.
- Click on your username at the top right of the Connect Cloud app and click User Profile.
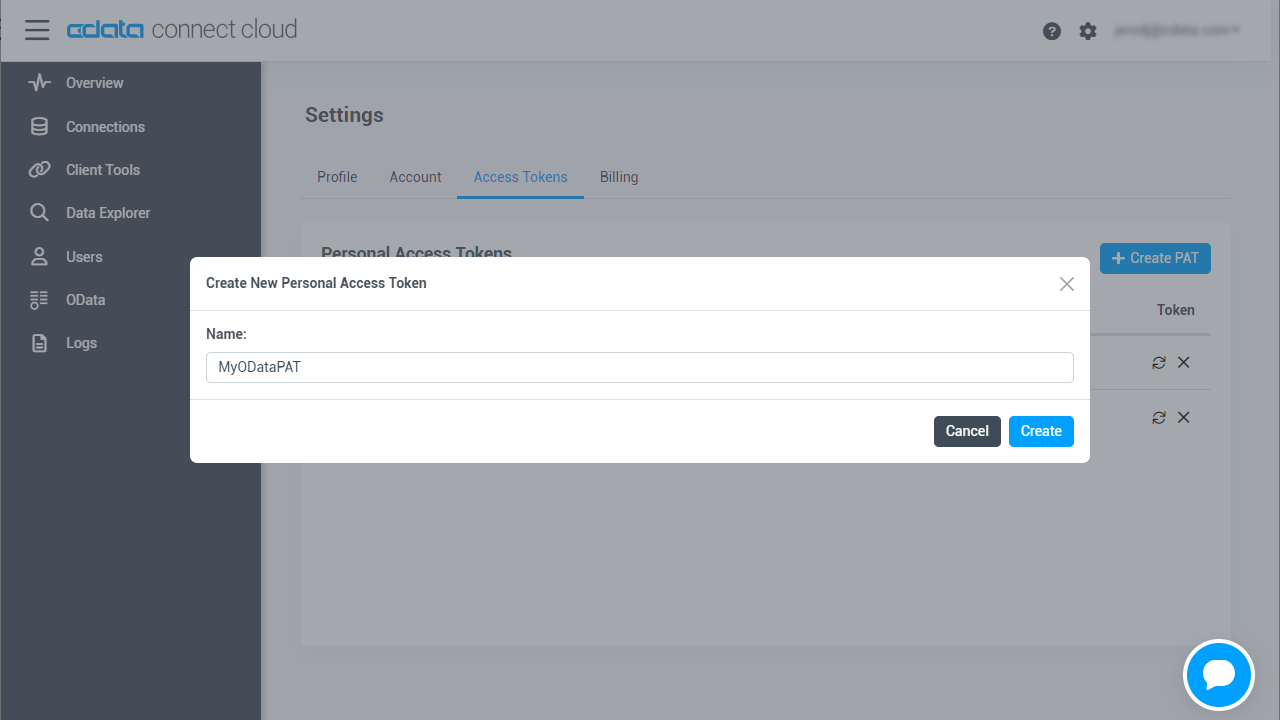
- On the User Profile page, scroll down to the Personal Access Tokens section and click Create PAT.
- Give your PAT a name and click Create.
- The personal access token is only visible at creation, so be sure to copy it and store it securely for future use.
Create an External Data Source for Oracle Data
After configuring the connection, you need to create a credential database for the external data source.
Creating a Credential Database
Execute the following SQL command to create credentials for the external data source connected to Oracle data.
NOTE: Set IDENTITY to your Connect Cloud username and set SECRET to your Personal Access Token.
CREATE DATABASE SCOPED CREDENTIAL ConnectCloudCredentials WITH IDENTITY = 'yourusername', SECRET = 'yourPAT';
Create an External Data Source for Oracle
Execute a CREATE EXTERNAL DATA SOURCE SQL command to create an external data source for Oracle with PolyBase:
CREATE EXTERNAL DATA SOURCE ConnectCloudInstance WITH ( LOCATION = 'sqlserver://tds.cdata.com:14333', PUSHDOWN = ON, CREDENTIAL = ConnectCloudCredentials );
Create External Tables for Oracle
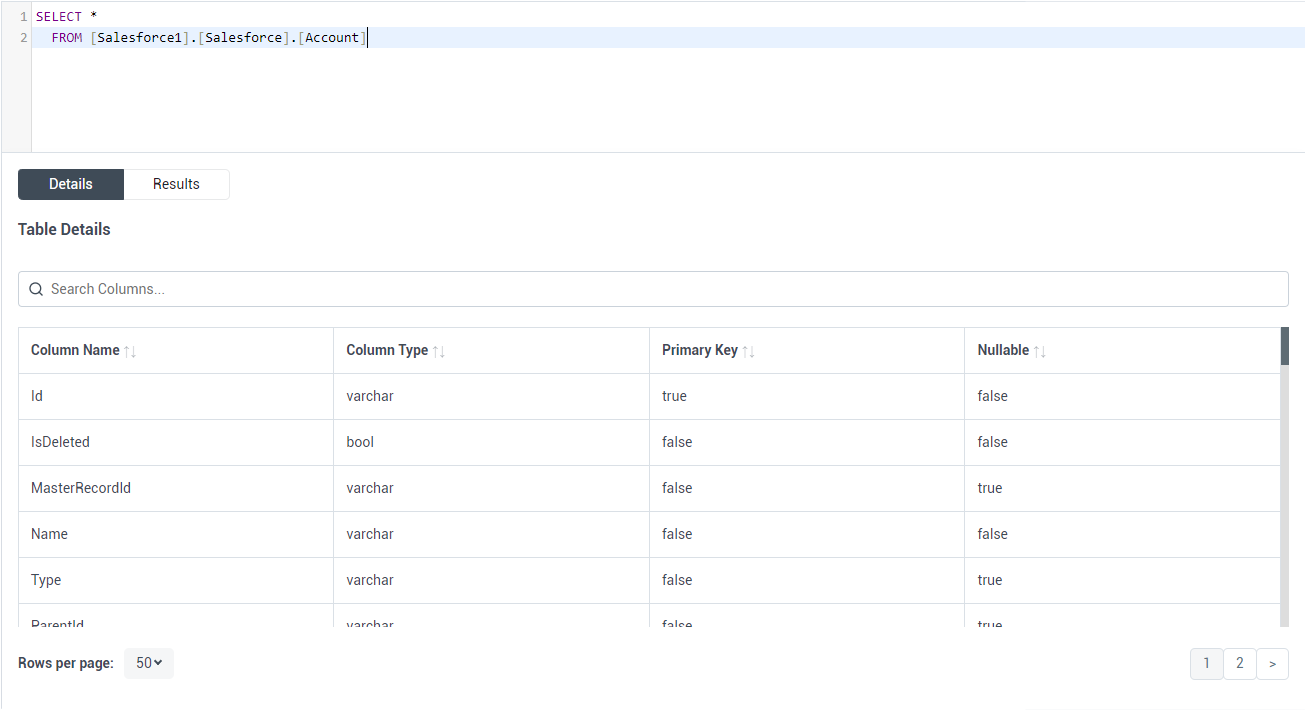
After creating the external data source, use CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE statements to link to Oracle data from your SQL Server instance. The table column definitions must match those exposed by CData Connect Cloud. You can use the Data Explorer in Connect Cloud to see the table definition.
Sample CREATE TABLE Statement
Execute a CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE SQL command to create the external table(s), using the collation and setting the LOCATION to three-part notation for the connection, catalog, and table. The statement to create an external table based on a Oracle Customers would look similar to the following.
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE Customers( CompanyName COLLATE [nvarchar](255) NULL, City COLLATE [nvarchar](255) NULL, ... ) WITH ( LOCATION='OracleOCI1.OracleOCI.Customers', DATA_SOURCE=ConnectCloudInstance );
Having created external tables for Oracle in your SQL Server instance, you are now able to query local and remote data simultaneously. To get live data access to 100+ SaaS, Big Data, and NoSQL sources directly from your SQL Server database, try CData Connect Cloud today!








