Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Build Harvest-Connected ETL Processes in Google Data Fusion
Load the CData JDBC Driver into Google Data Fusion and create ETL processes with access live Harvest data.
Google Data Fusion allows users to perform self-service data integration to consolidate disparate data. Uploading the CData API Driver for JDBC enables users to access live Harvest data from within their Google Data Fusion pipelines. While the CData JDBC Driver enables piping Harvest data to any data source natively supported in Google Data Fusion, this article walks through piping data from Harvest to Google BigQuery,
Upload the CData API Driver for JDBC to Google Data Fusion
Upload the CData API Driver for JDBC to your Google Data Fusion instance to work with live Harvest data. Due to the naming restrictions for JDBC drivers in Google Data Fusion, create a copy or rename the JAR file to match the following format driver-version.jar. For example: cdataapi-2020.jar
- Open your Google Data Fusion instance
- Click the to add an entity and upload a driver
![]()
- On the "Upload driver" tab, drag or browse to the renamed JAR file.
- On the "Driver configuration" tab:
- Name: Create a name for the driver (cdata.jdbc.api) and make note of the name
- Class name: Set the JDBC class name: (cdata.jdbc.api.APIDriver)
![Configuring the driver (Salesforce is shown.)]()
- Click "Finish"
Connect to Harvest Data in Google Data Fusion
With the JDBC Driver uploaded, you are ready to work with live Harvest data in Google Data Fusion Pipelines.
- Navigate to the Pipeline Studio to create a new Pipeline
- From the "Source" options, click "Database" to add a source for the JDBC Driver
![Adding a database source]()
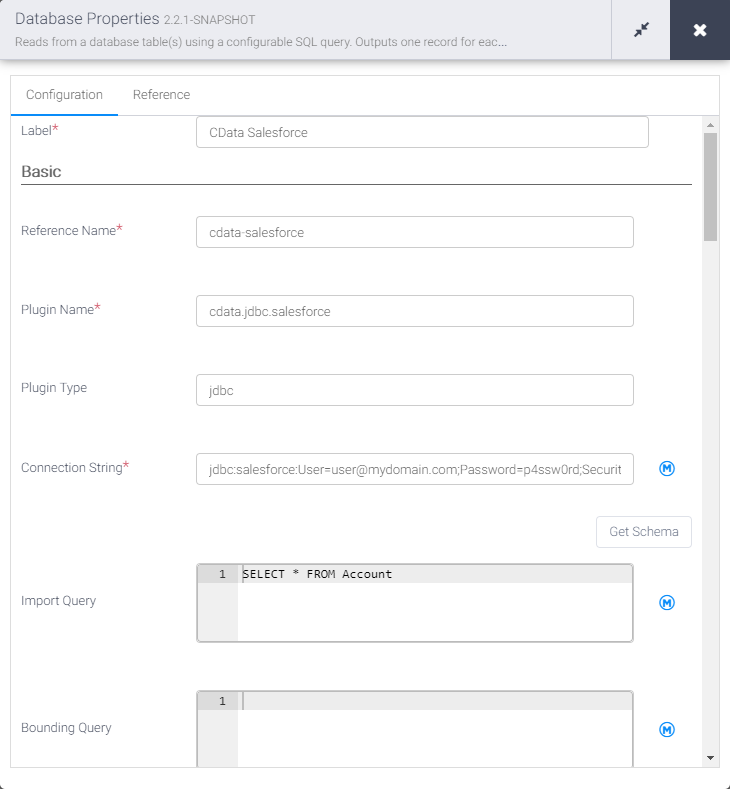
- Click "Properties" on the Database source to edit the properties
NOTE: To use the JDBC Driver in Google Data Fusion, you will need a license (full or trial) and a Runtime Key (RTK). For more information on obtaining this license (or a trial), contact our sales team.
- Set the Label
- Set Reference Name to a value for any future references (i.e.: cdata-api)
- Set Plugin Type to "jdbc"
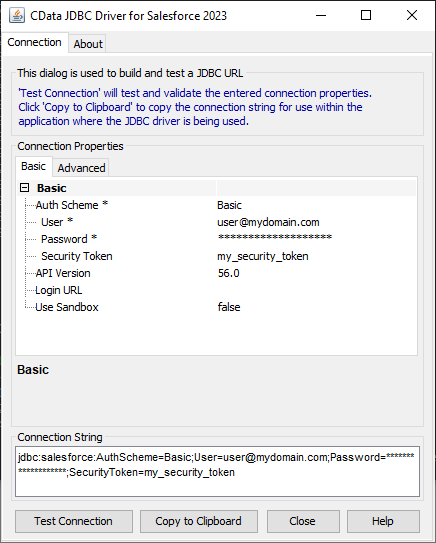
- Set Connection String to the JDBC URL for Harvest. For example:
jdbc:api:RTK=5246...;Profile=C:\profiles\Harvest.apip;ProfileSettings='APIKey=my_personal_key;AccountId=_your_account_id';Start by setting the Profile connection property to the location of the Harvest Profile on disk (e.g. C:\profiles\Harvest.apip). Next, set the ProfileSettings connection property to the connection string for Harvest (see below).
Harvest API Profile Settings
To authenticate to Harvest, you can use either Token authentication or the OAuth standard. Use Basic authentication to connect to your own data. Use OAuth to allow other users to connect to their data.
Using Token Authentication
To use Token Authentication, set the APIKey to your Harvest Personal Access Token in the ProfileSettings connection property. In addition to APIKey, set your AccountId in ProfileSettings to connect.
Using OAuth Authentication
First, register an OAuth2 application with Harvest. The application can be created from the "Developers" section of Harvest ID.
After setting the following connection properties, you are ready to connect:
- ProfileSettings: Set your AccountId in ProfileSettings.
- AuthScheme: Set this to OAuth.
- OAuthClientId: Set this to the client ID that you specified in your app settings.
- OAuthClientSecret: Set this to the client secret that you specified in your app settings.
- CallbackURL: Set this to the Redirect URI that you specified in your app settings.
- InitiateOAuth: Set this to GETANDREFRESH. You can use InitiateOAuth to manage how the driver obtains and refreshes the OAuthAccessToken.
Built-in Connection String Designer
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the Harvest JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.api.jarFill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
![Using the built-in connection string designer to generate a JDBC URL (Salesforce is shown.)]()
- Set Import Query to a SQL query that will extract the data you want from Harvest, i.e.:
SELECT * FROM Invoices
![Configuring the database source]()
- From the "Sink" tab, click to add a destination sink (we use Google BigQuery in this example)
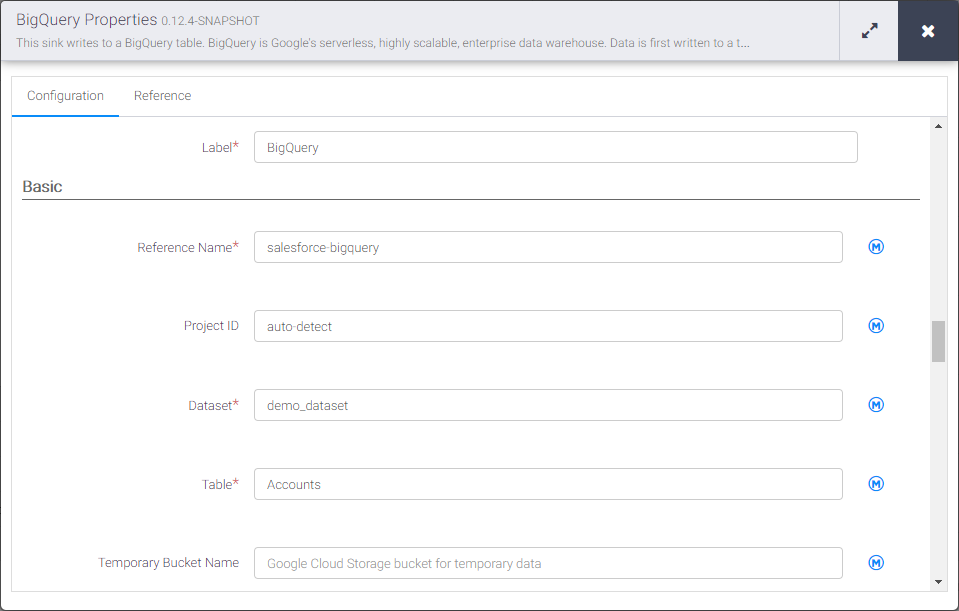
- Click "Properties" on the BigQuery sink to edit the properties
- Set the Label
- Set Reference Name to a value like api-bigquery
- Set Project ID to a specific Google BigQuery Project ID (or leave as the default, "auto-detect")
- Set Dataset to a specific Google BigQuery dataset
- Set Table to the name of the table you wish to insert Harvest data into
![Configuring the BigQuery sink]()
With the Source and Sink configured, you are ready to pipe Harvest data into Google BigQuery. Save and deploy the pipeline. When you run the pipeline, Google Data Fusion will request live data from Harvest and import it into Google BigQuery.
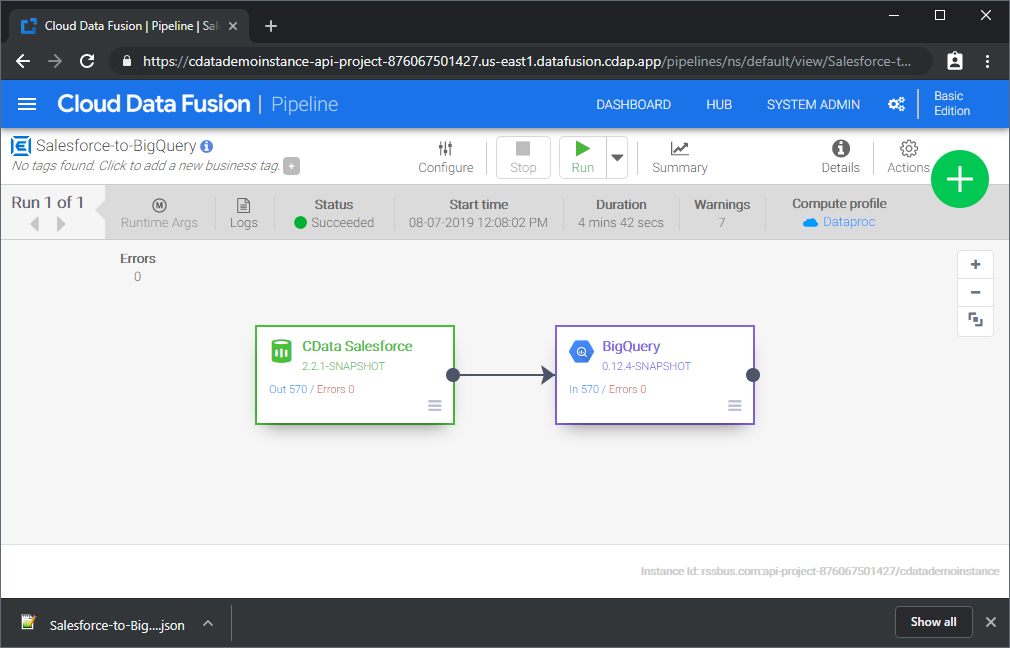
While this is a simple pipeline, you can create more complex Harvest pipelines with transforms, analytics, conditions, and more. Download a free, 30-day trial of the CData API Driver for JDBC and start working with your live Harvest data in Google Data Fusion today.