Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Integrate Google Cloud Storage with External Services using SnapLogic
Use CData JDBC drivers in SnapLogic to integrate Google Cloud Storage with External Services.
SnapLogic is an integration platform-as-a-service (iPaaS) that allows users to create data integration flows with no code. When paired with the CData JDBC Drivers, users get access to live data from more than 250+ SaaS, Big Data and NoSQL sources, including Google Cloud Storage, in their SnapLogic workflows.
With built-in optimized data processing, the CData JDBC Driver offers unmatched performance for interacting with live Google Cloud Storage data. When platforms issue complex SQL queries to Google Cloud Storage, the driver pushes supported SQL operations, like filters and aggregations, directly to Google Cloud Storage and utilizes the embedded SQL engine to process unsupported operations client-side (often SQL functions and JOIN operations). Its built-in dynamic metadata querying lets you work with Google Cloud Storage data using native data types.
Connect to Google Cloud Storage in SnapLogic
To connect to Google Cloud Storage data in SnapLogic, download and install the CData Google Cloud Storage JDBC Driver. Follow the installation dialog. When the installation is complete, the JAR file can be found in the installation directory (C:/Program Files/CData/CData JDBC Driver for Google Cloud Storage/lib by default).
Upload the Google Cloud Storage JDBC Driver
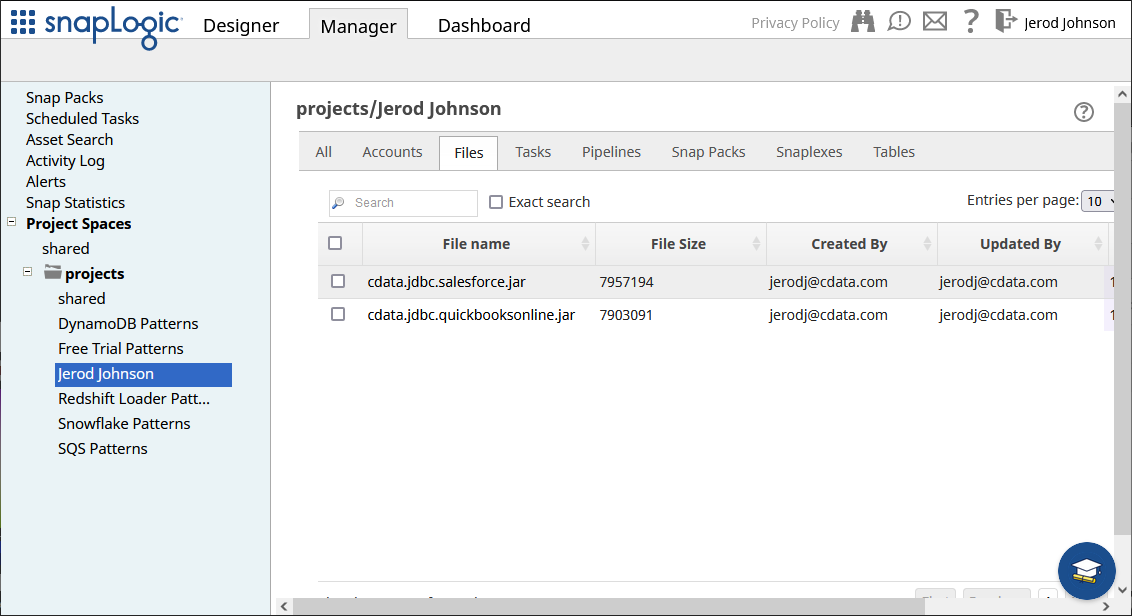
After installation, upload the JDBC JAR file to a location in SnapLogic (for example, projects/Jerod Johnson) from the Manager tab.
Configure the Connection
Once the JDBC Driver is uploaded, we can create the connection to Google Cloud Storage.
- Navigate to the Designer tab
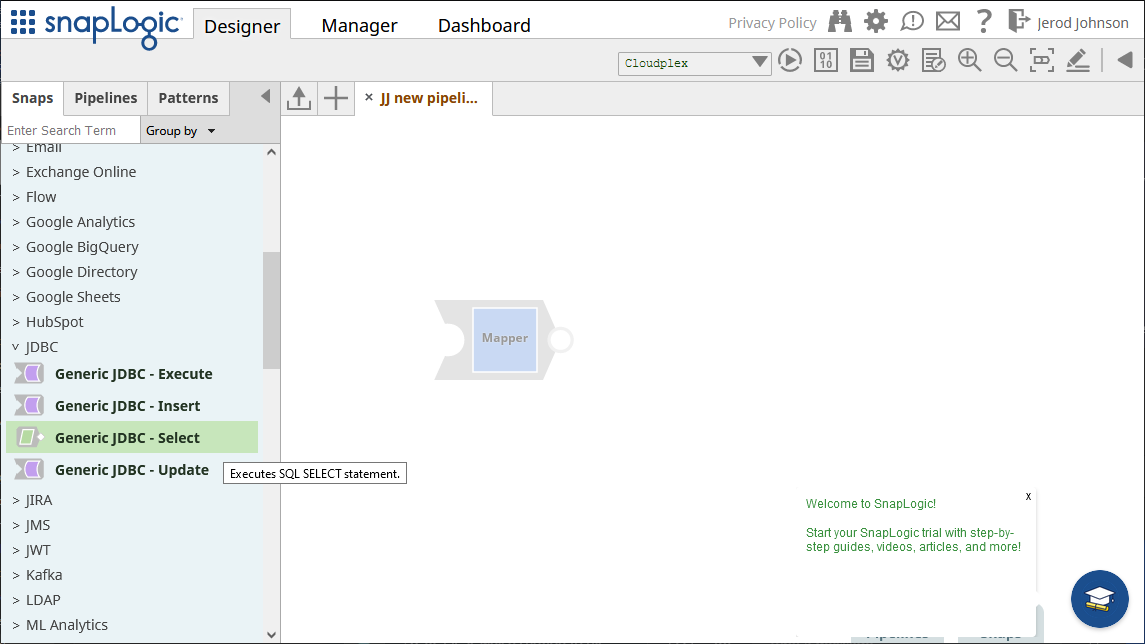
- Expand "JDBC" from Snaps and drag a "Generic JDBC - Select" snap onto the designer
![Adding a Generic JDBC snap onto the designer]()
- Click Add Account (or select an existing one) and click "Continue"
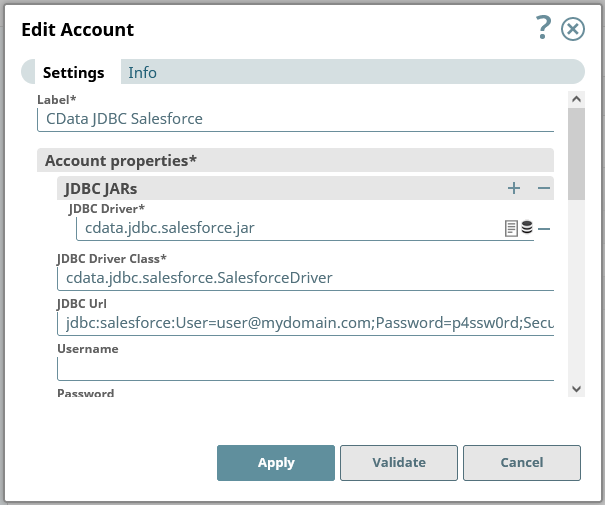
- In the next form, configure the JDBC connection properties:
- Under JDBC JARs, add the JAR file we previously uploaded
- Set JDBC Driver Class to cdata.jdbc.googlecloudstorage.GoogleCloudStorageDriver
Set JDBC URL to a JDBC connection string for the Google Cloud Storage JDBC Driver, for example:
jdbc:googlecloudstorage:ProjectId='project1';RTK=XXXXXX;InitiateOAuth=GETANDREFRESH
NOTE: RTK is a trial or full key. Contact our Support team for more information.
![Configuring a connection (Salesforce is shown)]()
Built-In Connection String Designer
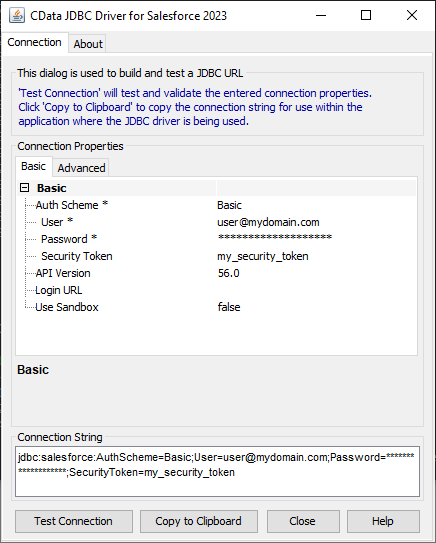
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the Google Cloud Storage JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.googlecloudstorage.jar
Fill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
Authenticate with a User Account
You can connect without setting any connection properties for your user credentials. After setting InitiateOAuth to GETANDREFRESH, you are ready to connect.
When you connect, the Google Cloud Storage OAuth endpoint opens in your default browser. Log in and grant permissions, then the OAuth process completes
Authenticate with a Service Account
Service accounts have silent authentication, without user authentication in the browser. You can also use a service account to delegate enterprise-wide access scopes.
You need to create an OAuth application in this flow. See the Help documentation for more information. After setting the following connection properties, you are ready to connect:
- InitiateOAuth: Set this to GETANDREFRESH.
- OAuthJWTCertType: Set this to "PFXFILE".
- OAuthJWTCert: Set this to the path to the .p12 file you generated.
- OAuthJWTCertPassword: Set this to the password of the .p12 file.
- OAuthJWTCertSubject: Set this to "*" to pick the first certificate in the certificate store.
- OAuthJWTIssuer: In the service accounts section, click Manage Service Accounts and set this field to the email address displayed in the service account Id field.
- OAuthJWTSubject: Set this to your enterprise Id if your subject type is set to "enterprise" or your app user Id if your subject type is set to "user".
- ProjectId: Set this to the Id of the project you want to connect to.
The OAuth flow for a service account then completes.
![Using the built-in connection string designer to generate a JDBC URL (Salesforce is shown.)]()
- After entering the connection properties, click "Validate" and "Apply"
Read Google Cloud Storage Data
In the form that opens after validating and applying the connection, configure your query.
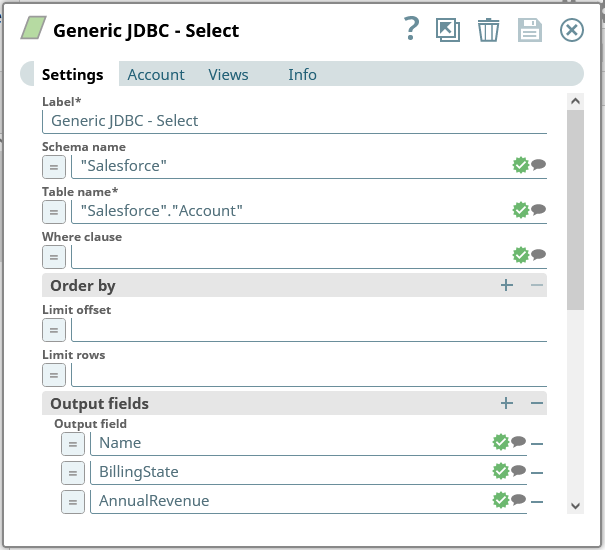
- Set Schema name to "GoogleCloudStorage"
- Set Table name to a table for Google Cloud Storage using the schema name, for example: "GoogleCloudStorage"."Buckets" (use the drop-down to see the full list of available tables)
- Add Output fields for each item you wish to work with from the table
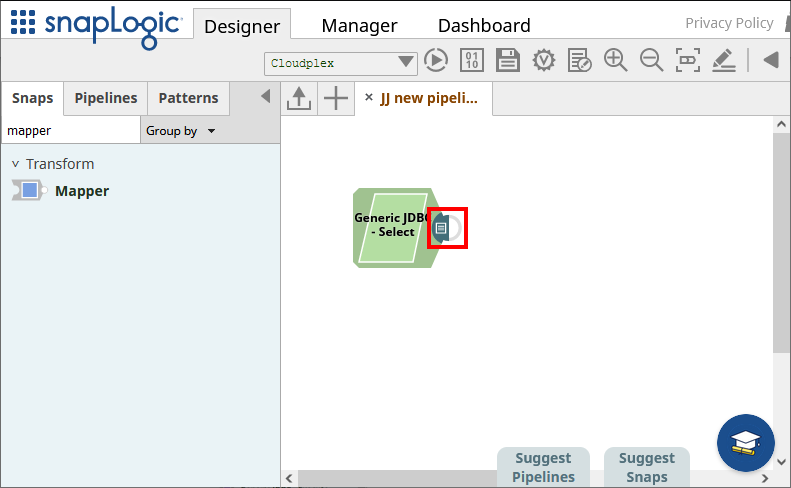
Save the Generic JDBC - Select snap.
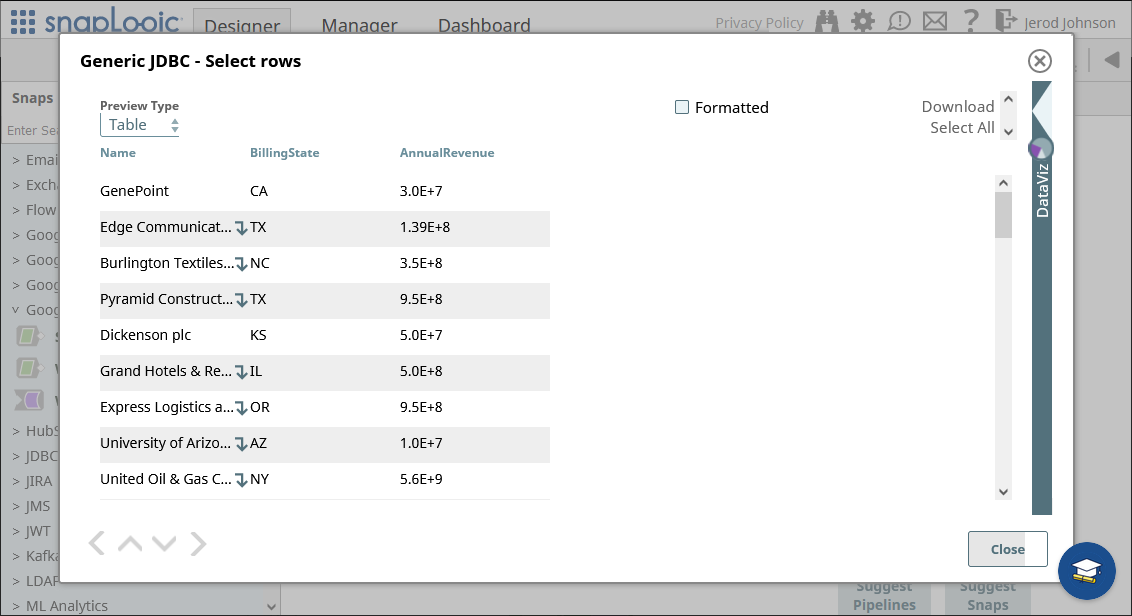
With connection and query configured, click the end of the snap to preview the data (highlighted below).
Once you confirm the results are what you expect, you can add additional snaps to funnel your Google Cloud Storage data to another endpoint.
Piping Google Cloud Storage Data to External Services
For this article, we will load data in a Google Spreadsheet. You can use any of the supported snaps, or even use a Generic JDBC snap with another CData JDBC Driver, to move data into an external service.
- Start by dropping a "Worksheet Writer" snap onto the end of the "Generic JDBC - Select" snap.
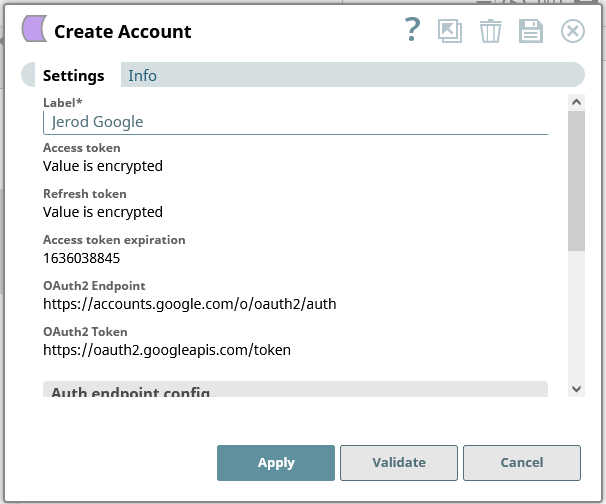
- Add an account to connect to Google Sheets
![Connecting to Google]()
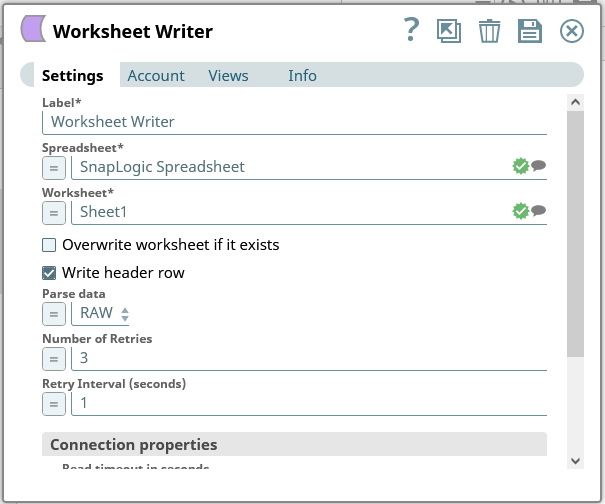
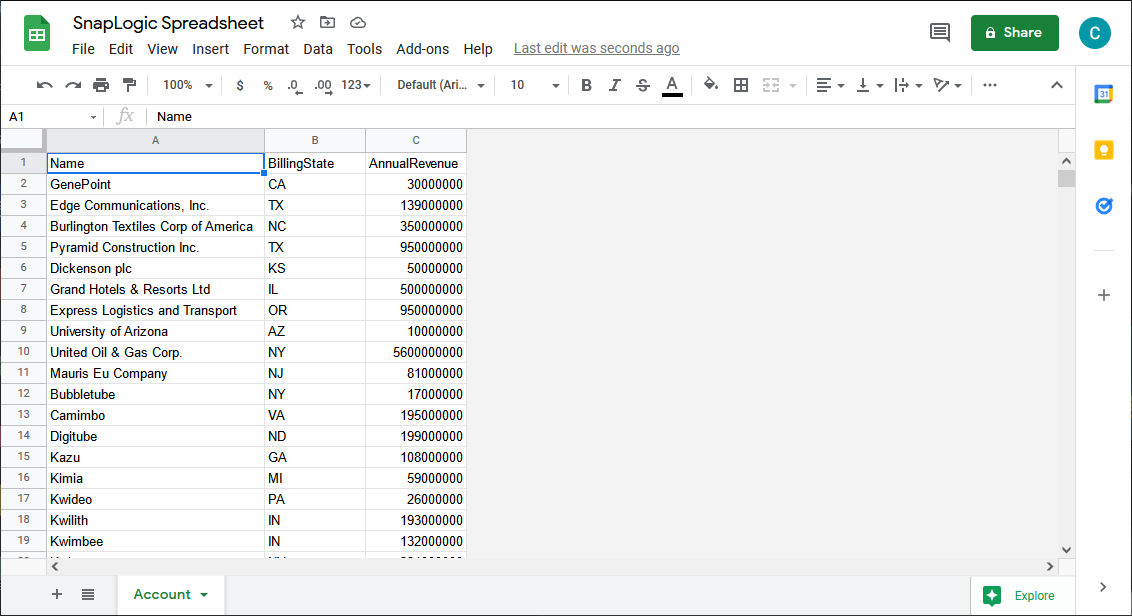
- Configure the Worksheet Writer snap to write your Google Cloud Storage data to a Google Spreadsheet
![Writing to a Google Spreadsheet]()
You can now execute the fully configured pipeline to extract data from Google Cloud Storage and push it into a Google Spreadsheet.
More Information & Free Trial
Using the CData JDBC Driver for Google Cloud Storage you can create a pipeline in SnapLogic for integrating Google Cloud Storage data with external services. For more information about connecting to Google Cloud Storage, check at our CData JDBC Driver for Google Cloud Storage page. Download a free, 30 day trial of the CData JDBC Driver for Google Cloud Storage and get started today.