Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Connect to Google Cloud Storage Data in the Denodo Platform
Use CData driver technologies to create a virtual data source for Google Cloud Storage data in the Denodo Virtual DataPort Administrator.
Denodo Platform is a data virtualization product providing a single point of contact for enterprise database data. When paired with the CData JDBC Driver for Google Cloud Storage, Denodo users can work with live Google Cloud Storage data alongside other enterprise data sources. This article walks through creating a virtual data source for Google Cloud Storage in the Denodo Virtual DataPort Administrator.
With built-in optimized data processing, the CData JDBC Driver offers unmatched performance for interacting with live Google Cloud Storage data. When you issue complex SQL queries to Google Cloud Storage, the driver pushes supported SQL operations, like filters and aggregations, directly to Google Cloud Storage and utilizes the embedded SQL engine to process unsupported operations client-side (often SQL functions and JOIN operations). Its built-in dynamic metadata querying allows you to work with and analyze Google Cloud Storage data using native data types.
Create the Google Cloud Storage Virtual Port
To connect to live Google Cloud Storage data from Denodo, you need to copy the JDBC Driver JAR file to the external library directory for Denodo and create a new JDBC Data Source from the Virtual DataPort Administrator tool.
- Download the CData JDBC Driver for Google Cloud Storage installer, unzip the package, and run the JAR file to install the driver.
- Copy the JAR File (and license file if it exists) from the installation location (typically C:\Program Files\CData\CData JDBC Driver for Google Cloud Storage\lib\) to the Denodo external library directory (C:\Denodo\Denodo Platform\lib-external\jdbc-drivers\cdata-googlecloudstorage-19).
- Open the Denodo Virtual DataPort Administrator tool and navigate to the Server Explorer tab.
- Right-click "admin" and select New -> Data source -> JDBC.
![Creating a new JDBC data source.]()
- Configure the JDBC Connection:
- Name: your choice, e.g.: googlecloudstorage
- Database adapter: Generic
- Driver class path: C:\Denodo\Denodo Platform\lib-external\jdbc-drivers\cdata-googlecloudstorage-19
- Driver class: cdata.jdbc.googlecloudstorage.GoogleCloudStorageDriver
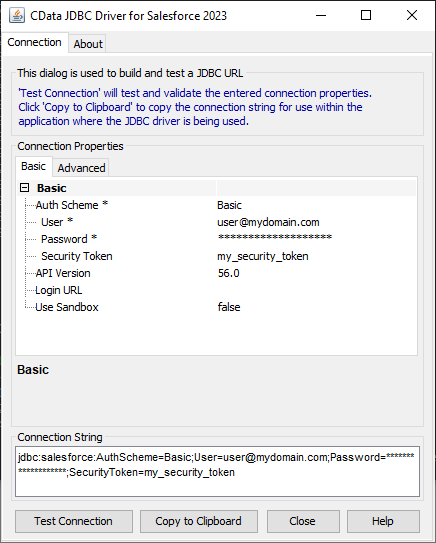
Database URI: Set this to a JDBC URL using the necessary connection properties. For example,
jdbc:googlecloudstorage:ProjectId='project1';InitiateOAuth=GETANDREFRESH
![Configuring the JDBC connection (NetSuite is shown).]()
Information on creating the Database URI follows:
Built-In Connection String Designer
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the Google Cloud Storage JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.googlecloudstorage.jarFill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
Authenticate with a User Account
You can connect without setting any connection properties for your user credentials. After setting InitiateOAuth to GETANDREFRESH, you are ready to connect.
When you connect, the Google Cloud Storage OAuth endpoint opens in your default browser. Log in and grant permissions, then the OAuth process completes
Authenticate with a Service Account
Service accounts have silent authentication, without user authentication in the browser. You can also use a service account to delegate enterprise-wide access scopes.
You need to create an OAuth application in this flow. See the Help documentation for more information. After setting the following connection properties, you are ready to connect:
- InitiateOAuth: Set this to GETANDREFRESH.
- OAuthJWTCertType: Set this to "PFXFILE".
- OAuthJWTCert: Set this to the path to the .p12 file you generated.
- OAuthJWTCertPassword: Set this to the password of the .p12 file.
- OAuthJWTCertSubject: Set this to "*" to pick the first certificate in the certificate store.
- OAuthJWTIssuer: In the service accounts section, click Manage Service Accounts and set this field to the email address displayed in the service account Id field.
- OAuthJWTSubject: Set this to your enterprise Id if your subject type is set to "enterprise" or your app user Id if your subject type is set to "user".
- ProjectId: Set this to the Id of the project you want to connect to.
The OAuth flow for a service account then completes.
![Using the built-in connection string designer to generate a JDBC URL (Salesforce is shown.)]()
- Click the "Test connection" button to confirm the configuration and click Save.
View Google Cloud Storage Data in the VirtualPort Administrator Tool
After creating the data source, you can create a base view of Google Cloud Storage data for use in the Denodo Platform.
- Click the "Create base view" button in the newly created VirtualPort (admin.GoogleCloudStorage).
- Expand the object tree and select the objects (tables) you wish to import.
![Selecting objects to import (NetSuite is shown).]()
- Click the "Create selected" button to create views of the Google Cloud Storage data.
Optional: Click "Create associations from foreign keys" to define relationships between the objects. - With the view(s) created, navigate to a table (cdata_googlecloudstorage_buckets) in the Server Explorer and double-click the selected table.
- In the new tab, click "Execution panel" to open a query panel.
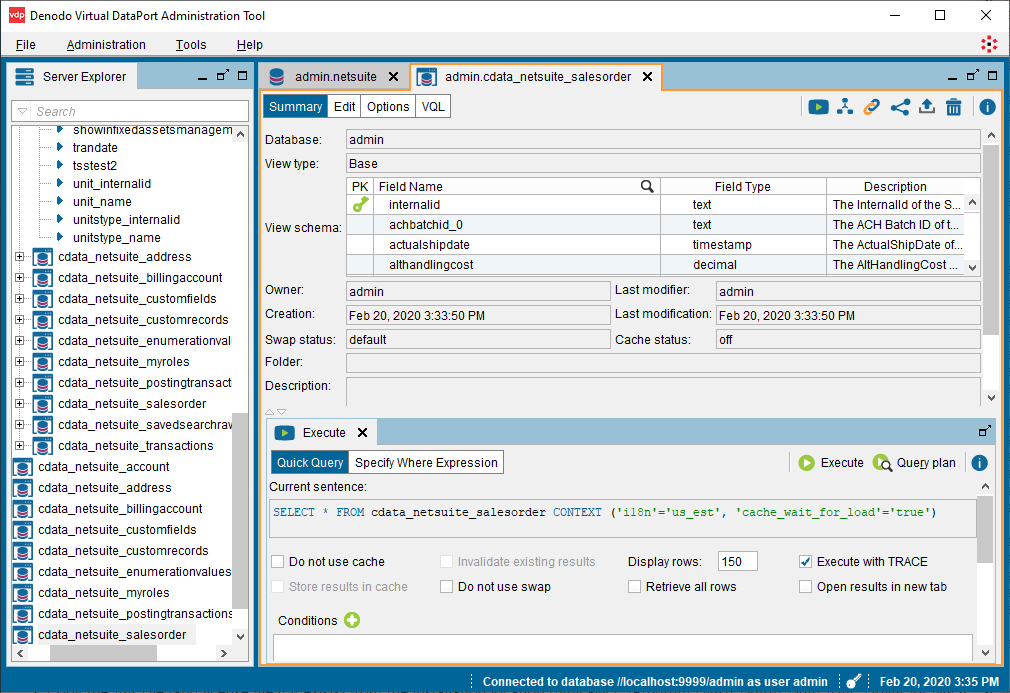
- Customize the query in the "Execute" tab or use the default:
SELECT * FROM cdata_googlecloudstorage_buckets CONTEXT ('i18n'='us_est', 'cache_wait_for_load'='true')![Configuring the query to view the data.]()
- Click Execute to view the data.
![Viewing the data.]()
With the base view created, you can now work with live Google Cloud Storage data like you would any other data source in Denodo Platform, for example, querying Google Cloud Storage in the Denodo Data Catalog.
Download a free, 30-day trial of the CData JDBC Driver for Google Cloud Storage and start working with your live Google Cloud Storage data in Denodo Platform. Reach out to our Support Team if you have any questions.