Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →A PostgreSQL Interface for Elasticsearch Data
Use the Remoting features of the Elasticsearch JDBC Driver to create a PostgreSQL entry-point for data access.
There are a vast number of PostgreSQL clients available on the Internet. From standard Drivers to BI and Analytics tools, PostgreSQL is a popular interface for data access. Using our JDBC Drivers, you can now create PostgreSQL entry-points that you can connect to from any standard client.
To access Elasticsearch data as a PostgreSQL database, use the CData JDBC Driver for Elasticsearch and a JDBC foreign data wrapper (FDW). In this article, we compile the FDW, install it, and query Elasticsearch data from PostgreSQL Server.
About Elasticsearch Data Integration
Accessing and integrating live data from Elasticsearch has never been easier with CData. Customers rely on CData connectivity to:
- Access both the SQL endpoints and REST endpoints, optimizing connectivity and offering more options when it comes to reading and writing Elasticsearch data.
- Connect to virtually every Elasticsearch instance starting with v2.2 and Open Source Elasticsearch subscriptions.
- Always receive a relevance score for the query results without explicitly requiring the SCORE() function, simplifying access from 3rd party tools and easily seeing how the query results rank in text relevance.
- Search through multiple indices, relying on Elasticsearch to manage and process the query and results instead of the client machine.
Users frequently integrate Elasticsearch data with analytics tools such as Crystal Reports, Power BI, and Excel, and leverage our tools to enable a single, federated access layer to all of their data sources, including Elasticsearch.
For more information on CData's Elasticsearch solutions, check out our Knowledge Base article: CData Elasticsearch Driver Features & Differentiators.
Getting Started
Connect to Elasticsearch Data as a JDBC Data Source
To connect to Elasticsearch as a JDBC data source, you will need the following:
- Driver JAR path: The JAR is located in the lib subfolder of the installation directory.
Driver class:
cdata.jdbc.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchDriver- JDBC URL:
The URL must start with "jdbc:elasticsearch:" and can include any of the connection properties in name-value pairs separated with semicolons.
Set the Server and Port connection properties to connect. To authenticate, set the User and Password properties, PKI (public key infrastructure) properties, or both. To use PKI, set the SSLClientCert, SSLClientCertType, SSLClientCertSubject, and SSLClientCertPassword properties.
The data provider uses X-Pack Security for TLS/SSL and authentication. To connect over TLS/SSL, prefix the Server value with 'https://'. Note: TLS/SSL and client authentication must be enabled on X-Pack to use PKI.
Once the data provider is connected, X-Pack will then perform user authentication and grant role permissions based on the realms you have configured.
Built-in Connection String Designer
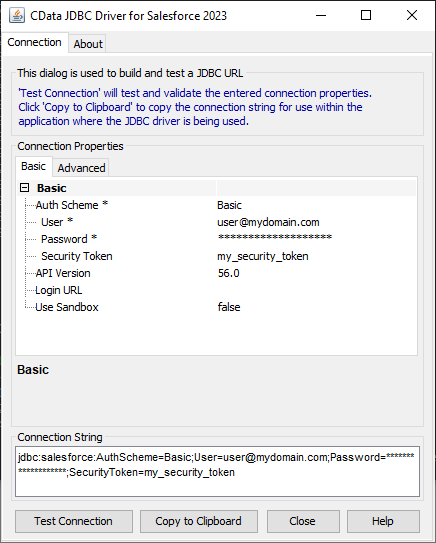
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the Elasticsearch JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.elasticsearch.jarFill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
![Using the built-in connection string designer to generate a JDBC URL (Salesforce is shown.)]()
A typical JDBC URL is below:
jdbc:elasticsearch:Server=127.0.0.1;Port=9200;User=admin;Password=123456;
Build the JDBC Foreign Data Wrapper
The Foreign Data Wrapper can be installed as an extension to PostgreSQL, without recompiling PostgreSQL. The jdbc2_fdw extension is used as an example (downloadable here).
- Add a symlink from the shared object for your version of the JRE to /usr/lib/libjvm.so. For example:
ln -s /usr/lib/jvm/java-6-openjdk/jre/lib/amd64/server/libjvm.so /usr/lib/libjvm.so - Start the build:
make install USE_PGXS=1
Query Elasticsearch Data as a PostgreSQL Database
After you have installed the extension, follow the steps below to start executing queries to Elasticsearch data:
- Log into your database.
-
Load the extension for the database:
CREATE EXTENSION jdbc2_fdw; -
Create a server object for Elasticsearch:
CREATE SERVER Elasticsearch FOREIGN DATA WRAPPER jdbc2_fdw OPTIONS ( drivername 'cdata.jdbc.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchDriver', url 'jdbc:elasticsearch:Server=127.0.0.1;Port=9200;User=admin;Password=123456;', querytimeout '15', jarfile '/home/MyUser/CData/CData\ JDBC\ Driver\ for\ Salesforce MyDriverEdition/lib/cdata.jdbc.elasticsearch.jar'); -
Create a user mapping for the username and password of a user known to the MySQL daemon.
CREATE USER MAPPING for postgres SERVER Elasticsearch OPTIONS ( username 'admin', password 'test'); -
Create a foreign table in your local database:
postgres=# CREATE FOREIGN TABLE orders ( orders_id text, orders_OrderName text, orders_Freight numeric) SERVER Elasticsearch OPTIONS ( table_name 'orders');
postgres=# SELECT * FROM orders;