Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Integrate with Live Confluence Data in MuleSoft (via CData Connect Cloud)
Use CData Connect Cloud to connect to Confluence from the MuleSoft Anypoint Platform to integrate live Confluence data into custom reports and dashboards.
The MuleSoft Anypoint Platform enables the building, deployment, and management of APIs and integrations, facilitating seamless connectivity across applications and systems. When combined with CData Connect Cloud, it provides access to Confluence data for visualizations, dashboards, and more. This article explains how to use CData Connect Cloud to create a live connection to Confluence and how to connect and access live Confluence data from the MuleSoft Anypoint Platform.
Prerequisites
Before configuring and using MuleSoft with CData Connect Cloud, you must first connect a data source to your CData Connect Cloud account. For more information, see the Connections section.
Additionally, you need to generate a Personal Access Token (PAT) on the Settings page. Be sure to copy it down, as it serves as your password during authentication.
Configure Confluence Connectivity for MuleSoft
Connectivity to Confluence from MuleSoft is made possible through CData Connect Cloud. To work with Confluence data from MuleSoft, we start by creating and configuring a Confluence connection.
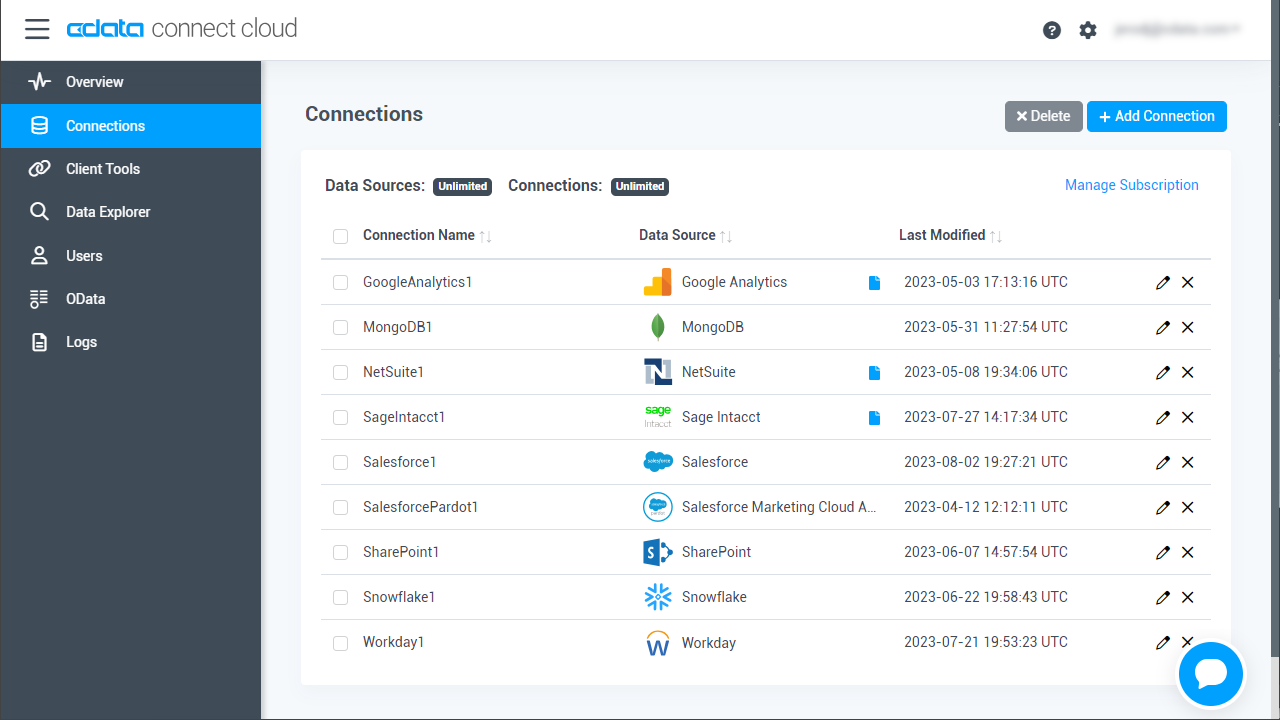
- Log into Connect Cloud, click Connections and click Add Connection
![Adding a Connection]()
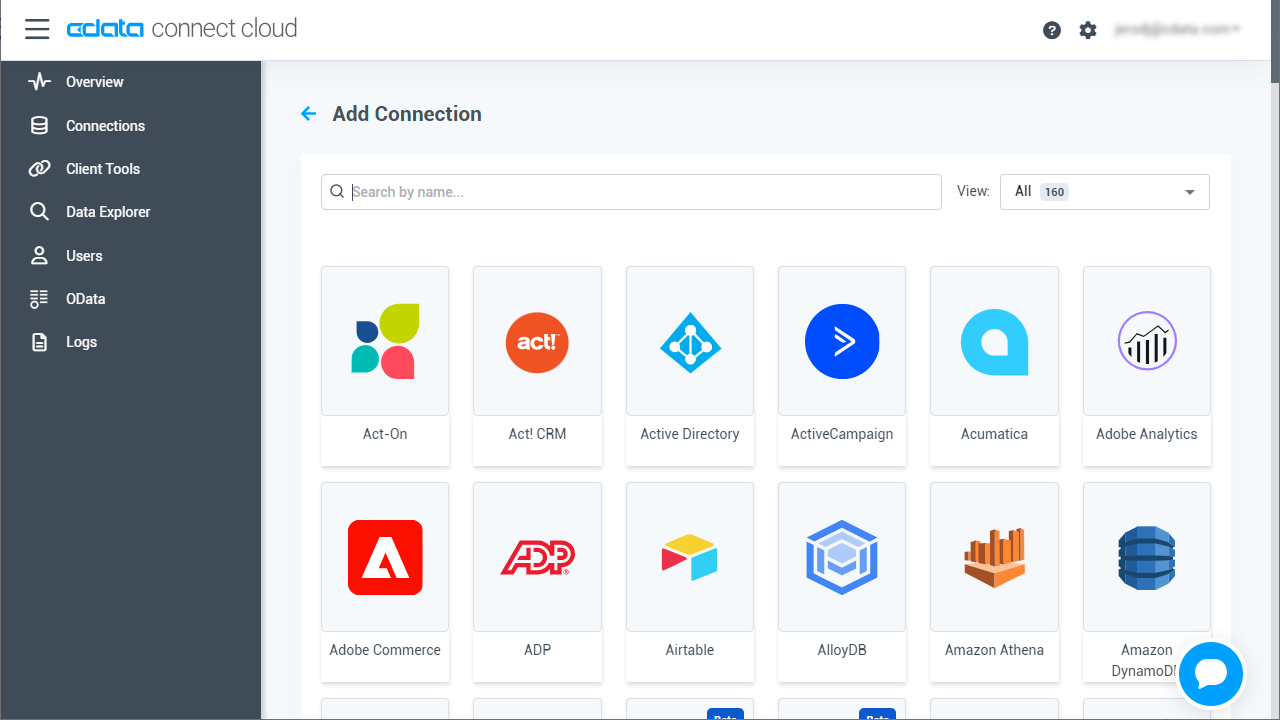
- Select "Confluence" from the Add Connection panel
![Selecting a data source]()
-
Enter the necessary authentication properties to connect to Confluence.
Obtaining an API Token
An API token is necessary for account authentication. To generate one, login to your Atlassian account and navigate to API tokens > Create API token. The generated token will be displayed.
Connect Using a Confluence Cloud Account
To connect to a Cloud account, provide the following (Note: Password has been deprecated for connecting to a Cloud Account and is now used only to connect to a Server Instance.):
- User: The user which will be used to authenticate with the Confluence server.
- APIToken: The API Token associated with the currently authenticated user.
- Url: The URL associated with your JIRA endpoint. For example, https://yoursitename.atlassian.net.
Connect Using a Confluence Server Instance
To connect to a Server instance, provide the following:
- User: The user which will be used to authenticate with the Confluence instance.
- Password: The password which will be used to authenticate with the Confluence server.
- Url: The URL associated with your JIRA endpoint. For example, https://yoursitename.atlassian.net.
![Configuring a connection (Salesforce is shown)]()
- Click Create & Test
- Navigate to the Permissions tab in the Add Confluence Connection page and update the User-based permissions.
![Updating permissions]()
With the connection configured, you are ready to connect to Confluence data from MuleSoft.
Connecting to CData Connect Cloud
Follow these steps to establish a connection from Mulesoft to CData Connect Cloud through the JDBC driver:
- Download and install the CData Connect Cloud JDBC driver.
- Open the Client Tools page of CData Connect Cloud.
- Locate MuleSoft and click on Download for Mac/Windows/Linux.
- Download and run the setup file.
- When the installation is complete, the JAR file can be found in the installation directory (inside the lib folder).
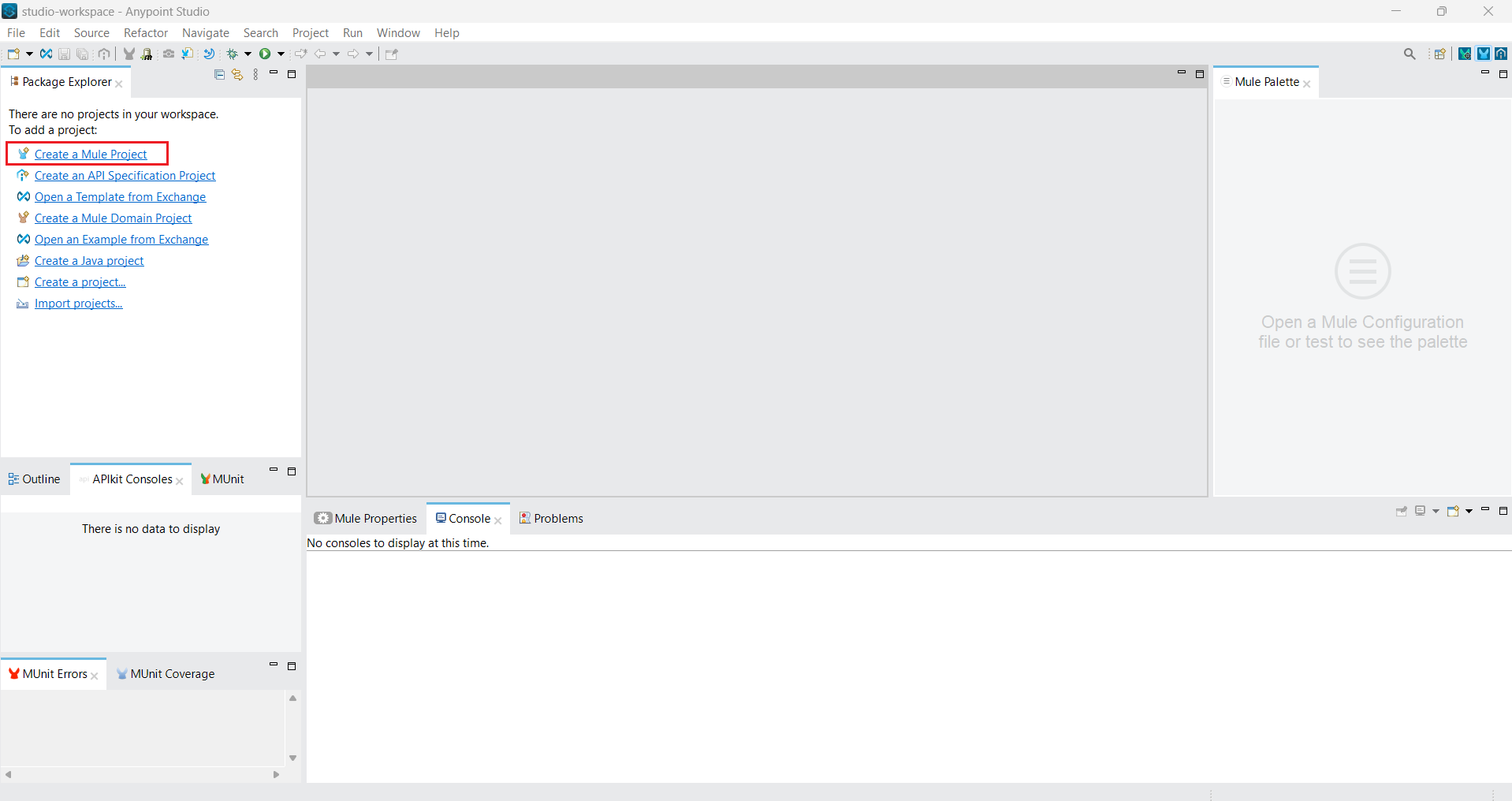
- Log into Mulesoft Anypoint Studio or launch the desktop application.
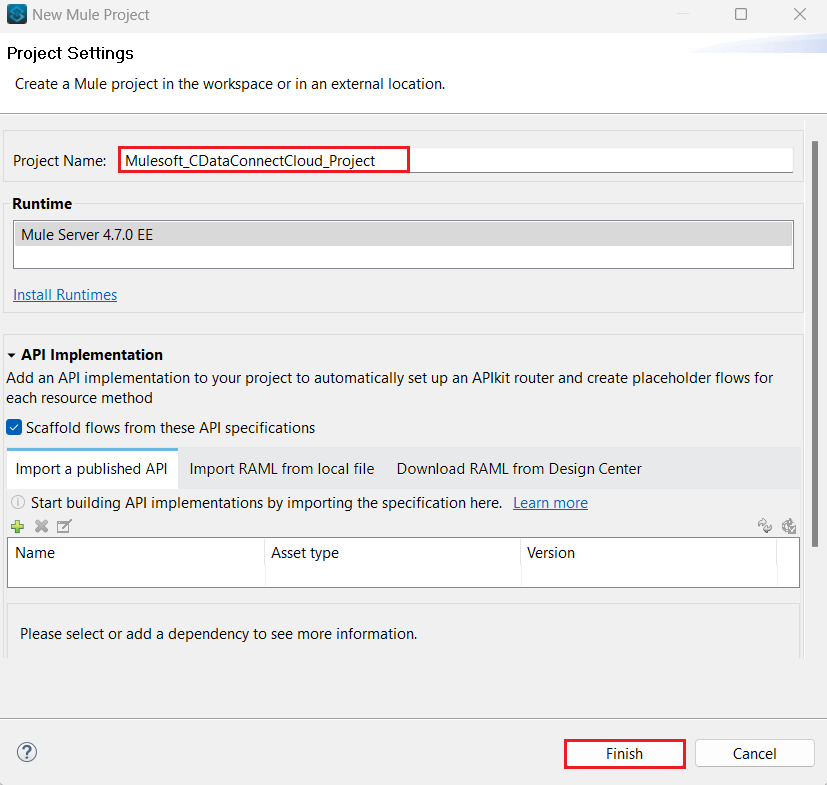
- Create a new Mulesoft project.
![Create a new MuleSoft project]()
![Add the project name]() The new project appears in a project folder.
The new project appears in a project folder.
![The new project is created]()
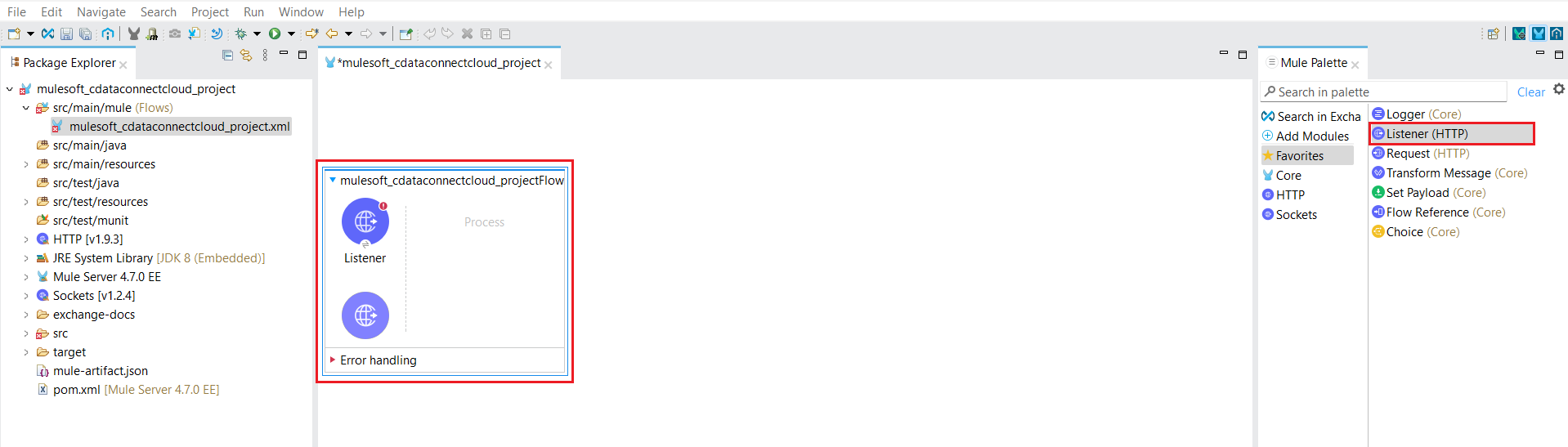
- In the Mule Palette located on the right, drag an HTTP Listener to the Message Flow area.
![Drag the HTTP Listener to the Message Flow area]()
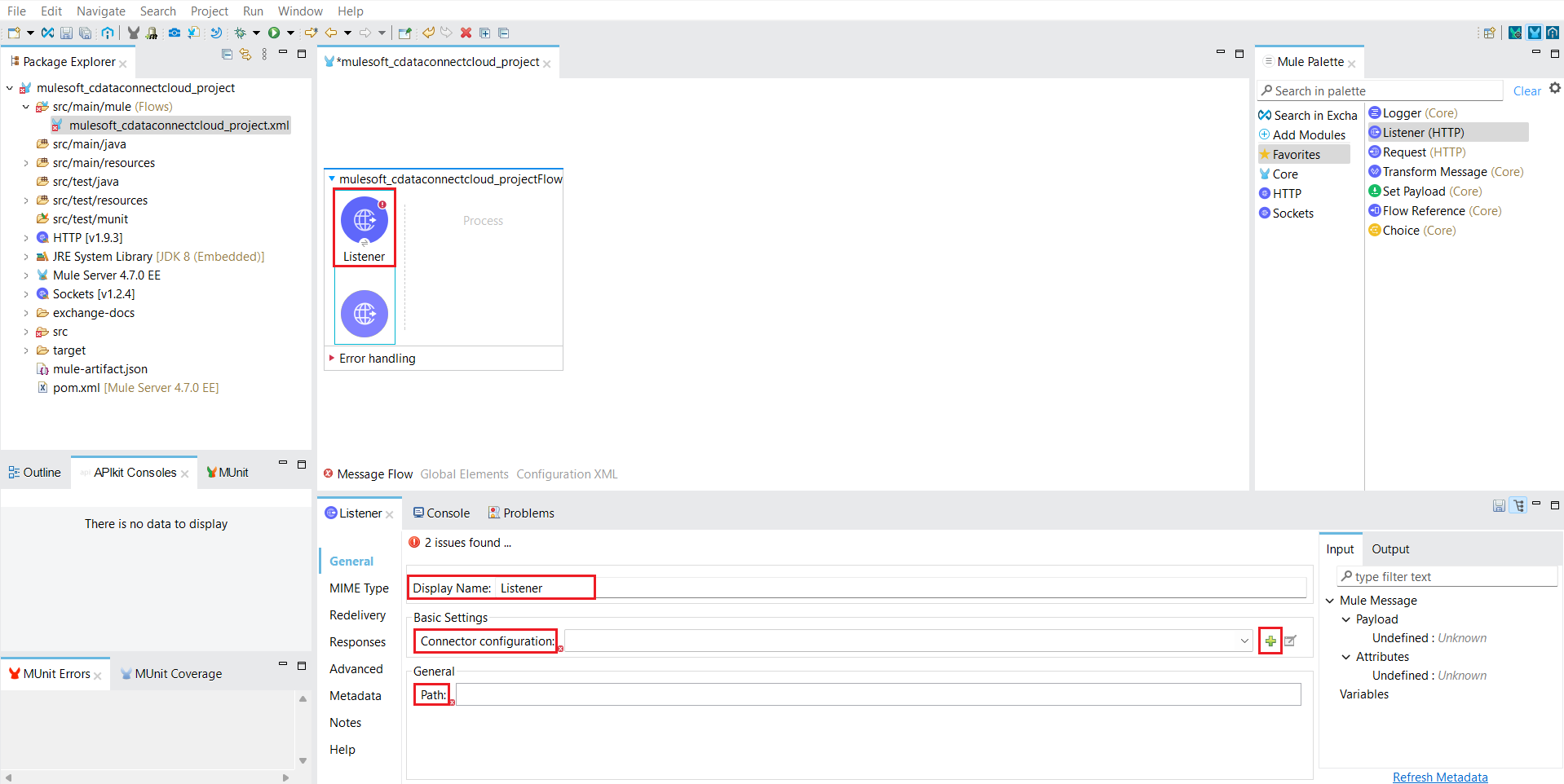
- Click on the HTTP Listener to configure it.
![Click on the HTTP Listener to configure it]()
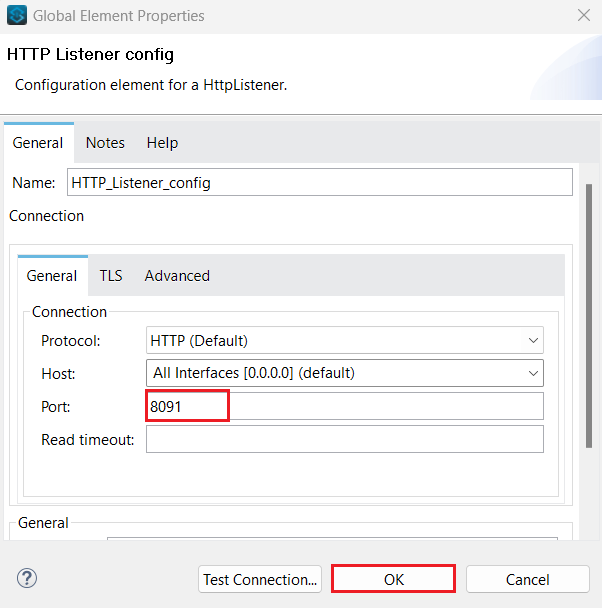
- Click the + sign on the right of Connector configuration. The HTTP Listener config dialog appears.
- Configure the HTTP Listener, providing a Port on which to query your data, and click OK.
![Add the port number to configure the HTTP Listener]()
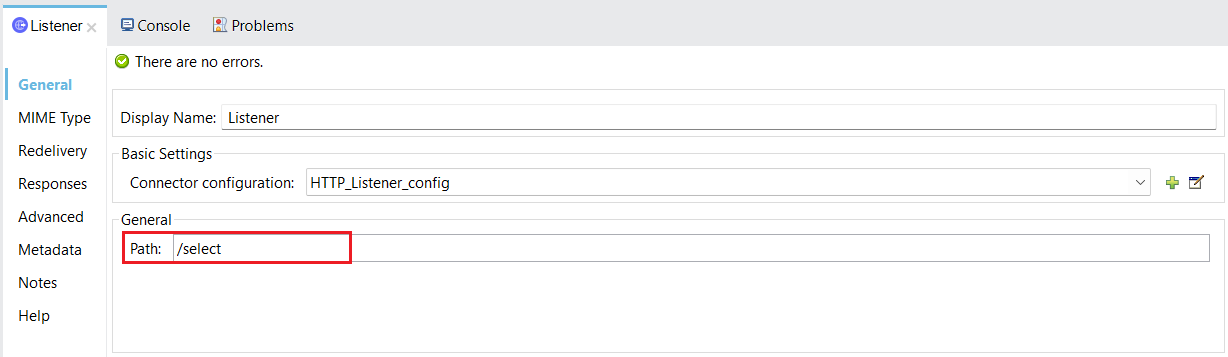
- Provide a path on which to perform the actions. The HTTP Listener is now configured.
![Provide a path to perform the actions]()
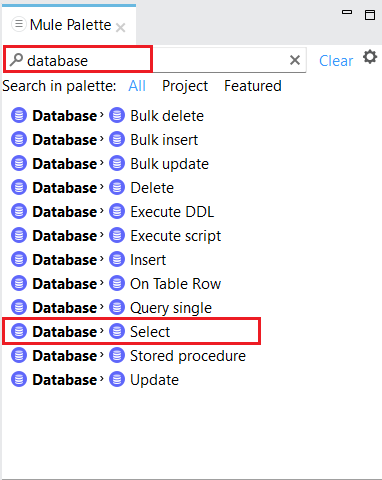
- In the Mule Palette on the right, type database in the search bar.
![Search for database in Mule Palette search bar]()
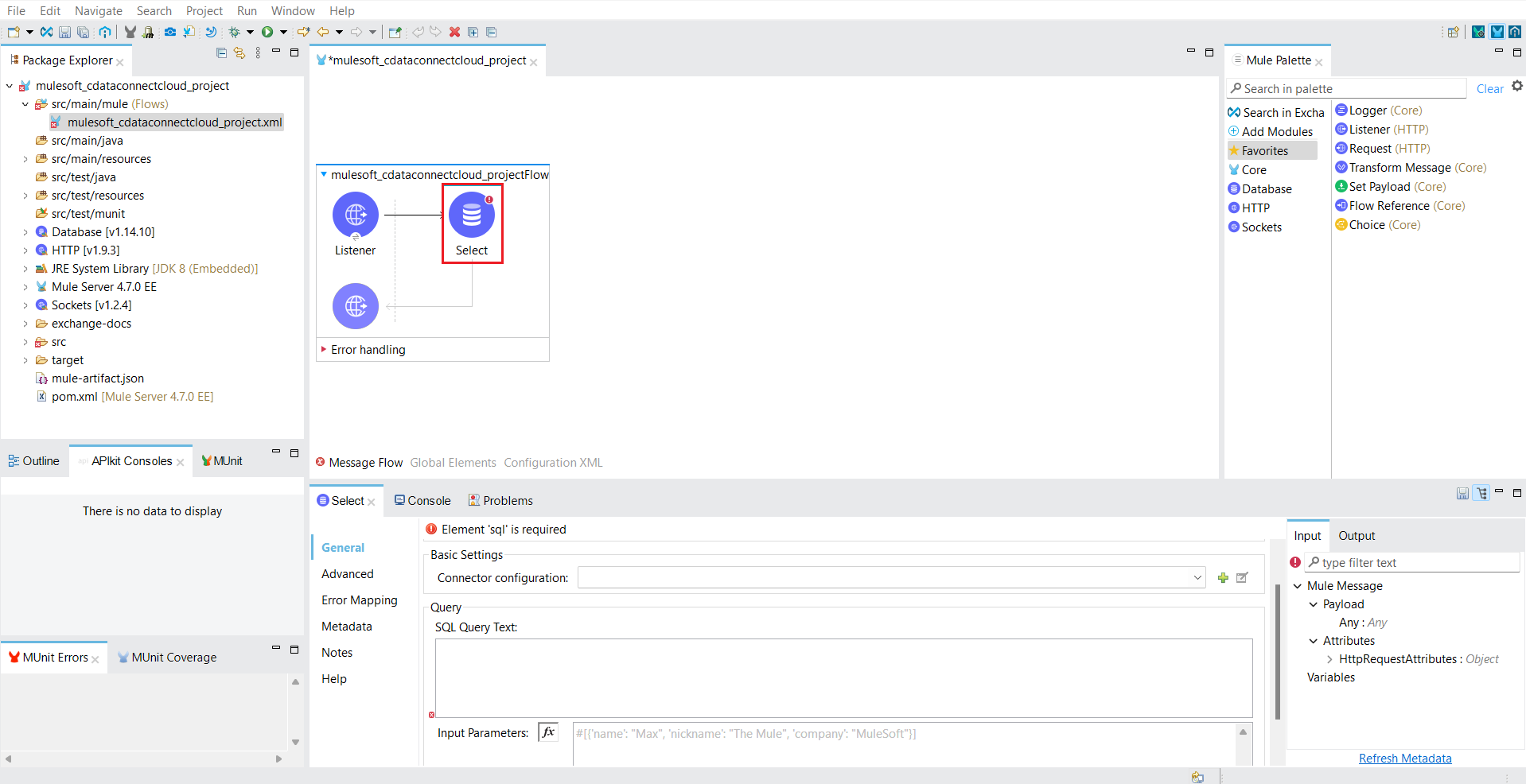
- Drag the database operation you want to perform to the Message Flow area. For this example, we choose Select.
![Drag the database operation in the Message Flow area]()
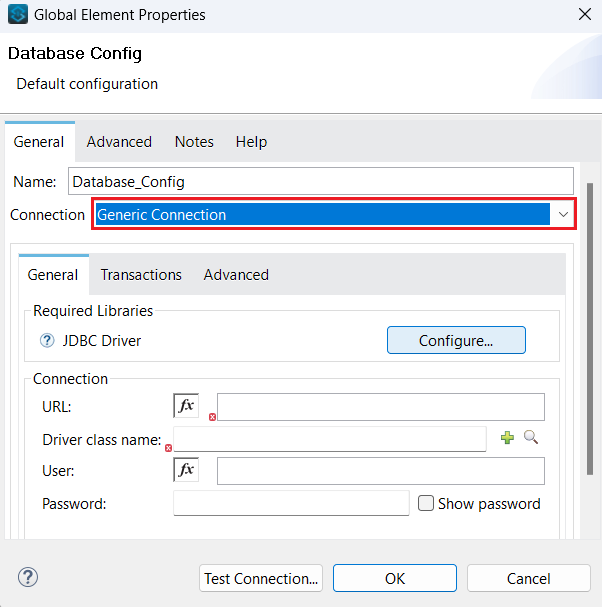
- Select Generic Connection from the Connection dropdown in the Database Config dialog.
![Select Generic Connection from the Connection dropdown]()
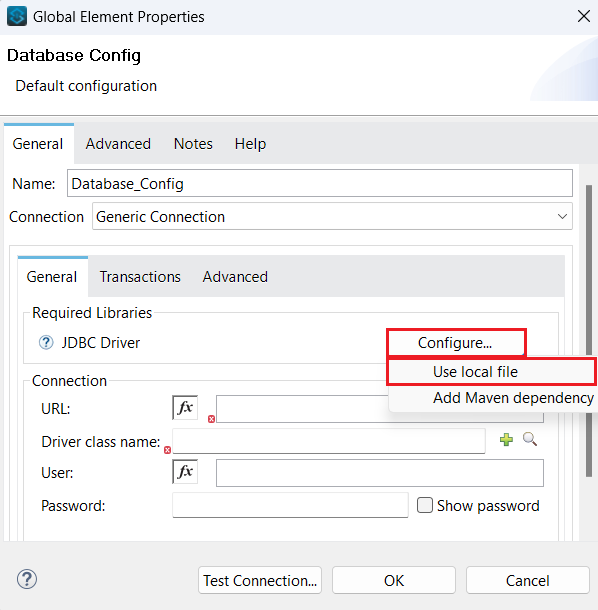
- Click the Configure button to configure the JDBC driver. Select Use local file from the drop-down list.
![Select Use local file from the dropdown]()
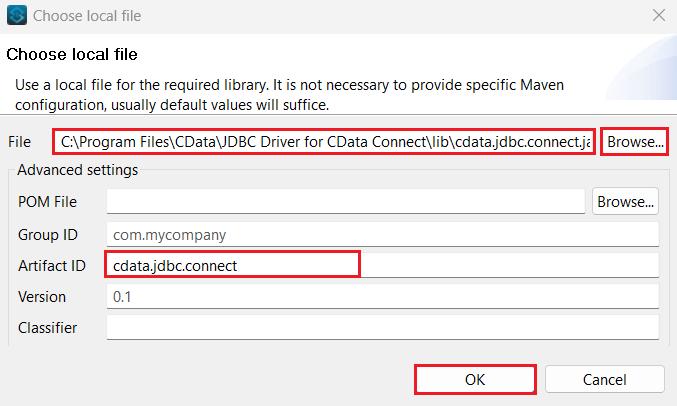
- Locate the CData Connect Cloud JAR file from the JDBC driver installation and click OK.
![Add the CData Connect Cloud JAR file path]()
- Provide the following information:
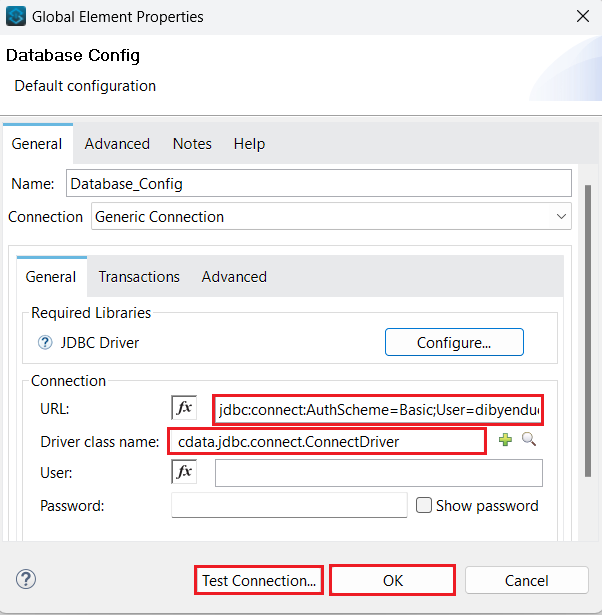
- URL: the URL for the connection, for example:
jdbc:connect:Authscheme=Basic;user=username;password=passwordNote: the password is the PAT created in the Prerequisites section. - Driver class name: Enter the Driver class name as:
cdata.jdbc.connect.ConnectDriver![Add the URL and the Driver class name]()
- URL: the URL for the connection, for example:
- Click Test Connection.
![Click on Test Connection]()
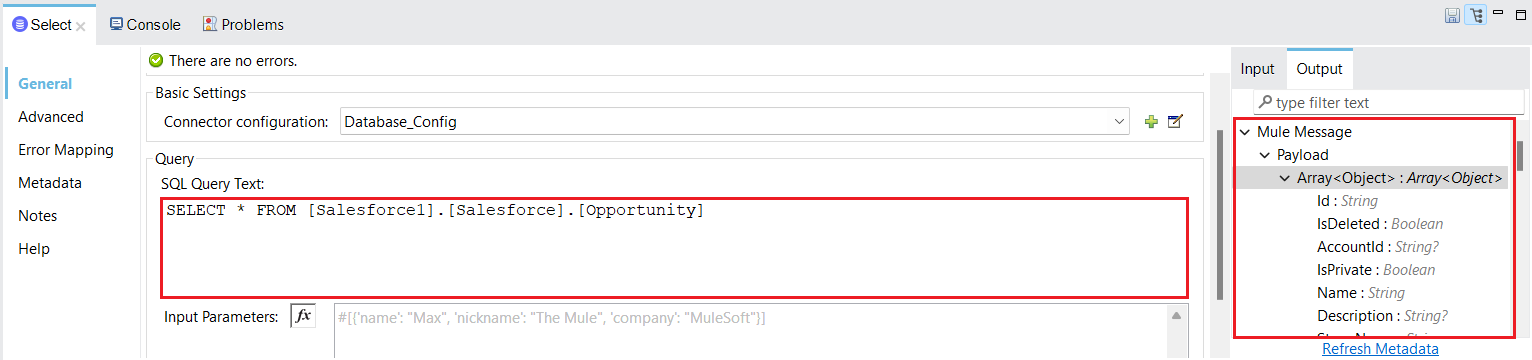
- If the connection is successful, provide the SQL Query Text in the editor. You can see the table metadata on the right side in the Output tab.
![Write the SQL Query]()
- In the Mule Palette, drag Transform Message to the Message Flow area.
![Drag Transform Message to the Message Flow area]()
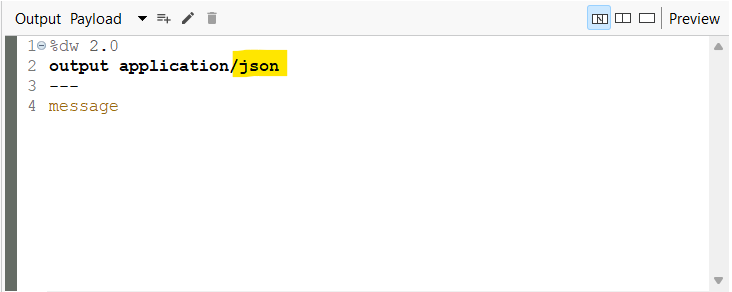
- Click Transform Message to configure it. Change the Output as follows:
![Configure Transform Message]()
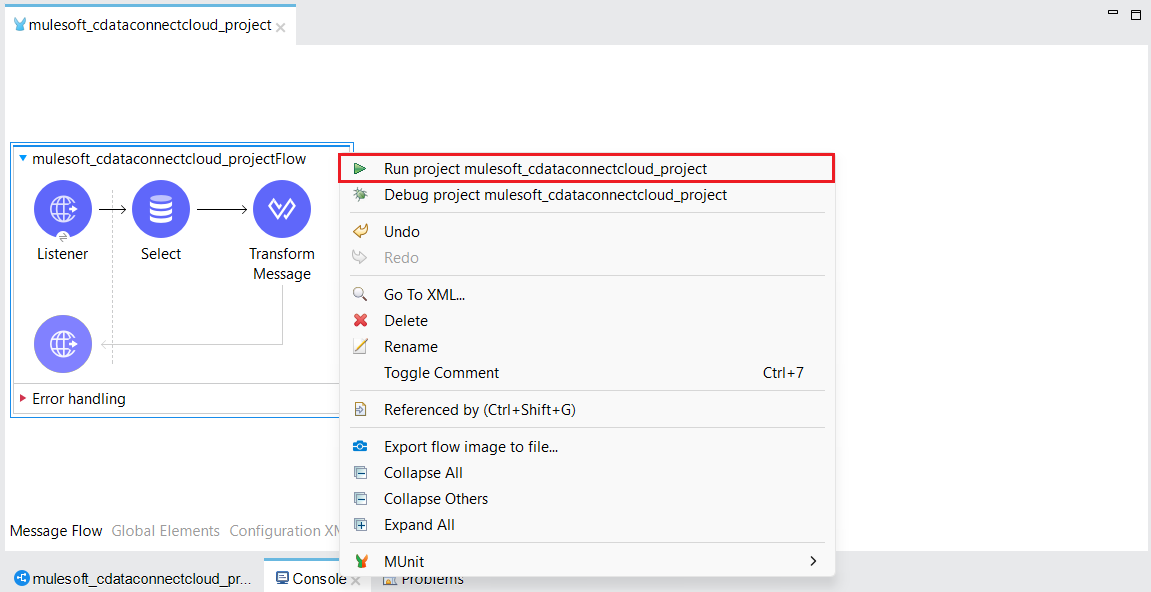
- Save your project and run it. In the console, Mulesoft starts initializing the dependencies.
![Save and Run the project]()
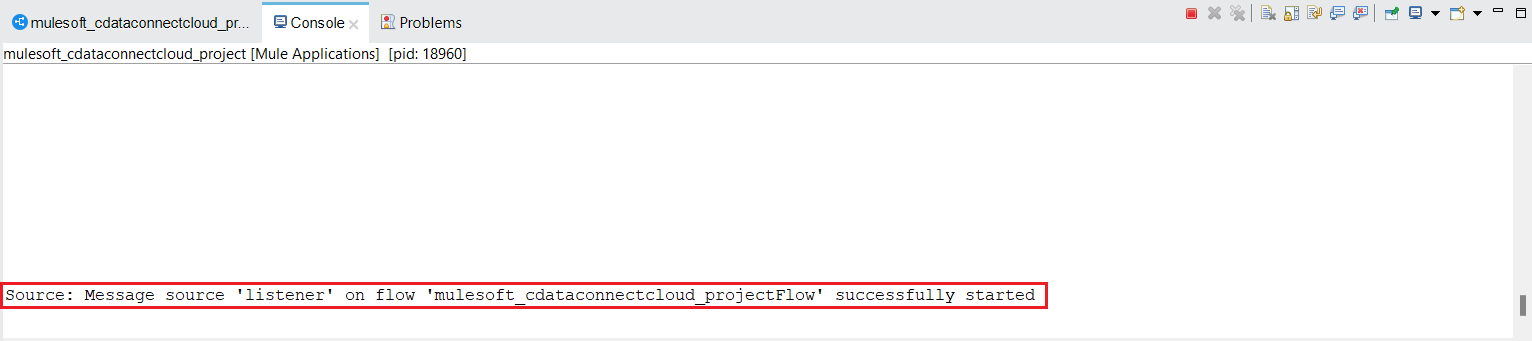
- Once you see the message, "Message source 'listener' on flow your_project_name successfully started", you can start querying your data at the endpoint you provided.
![Check for the 'Message source 'listener' on flow your_project_name successfully started' message to get started]()
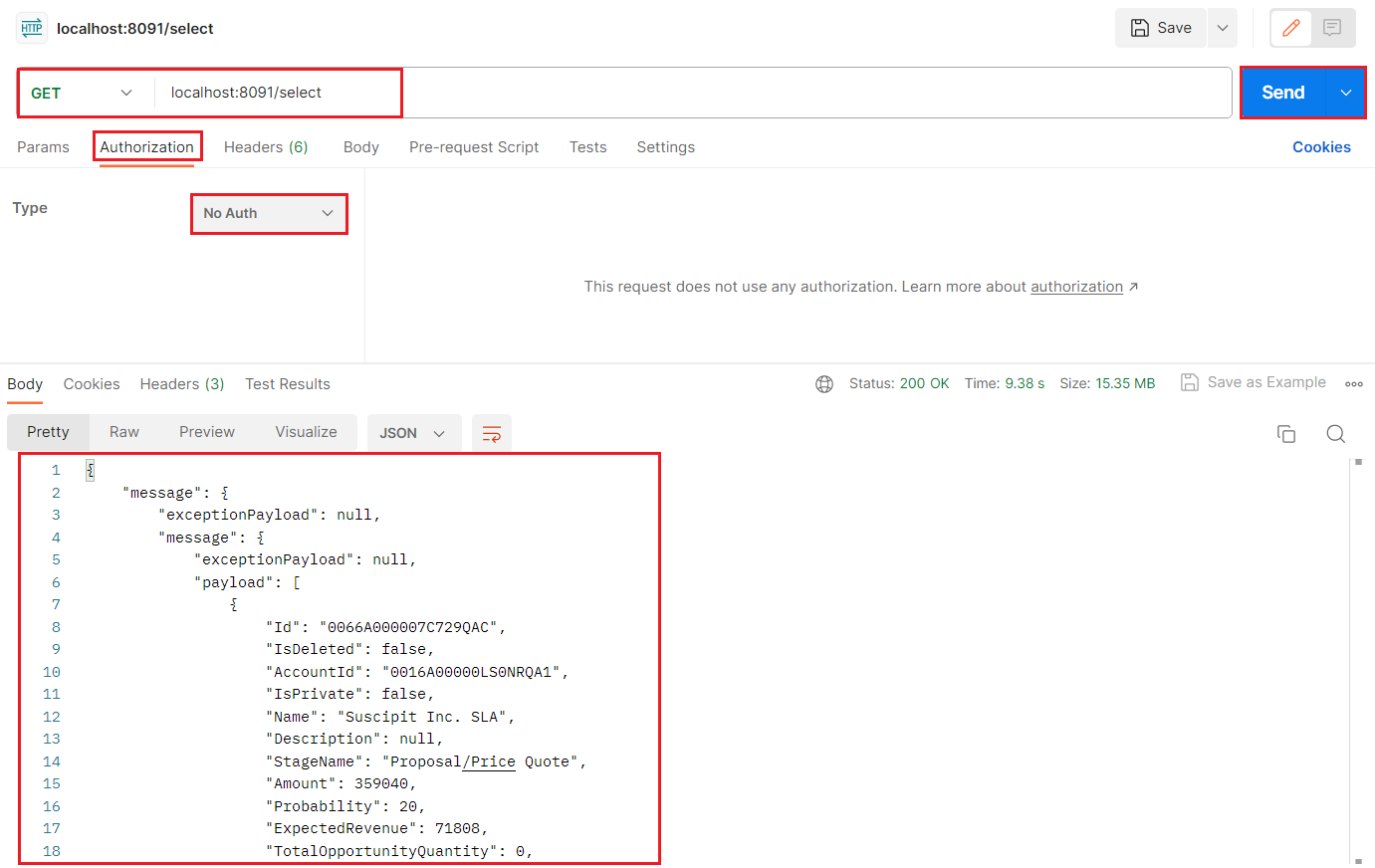
- Query to check out the data using the Postman application (as shown below).
![Send an API request from Postman to check the Confluence data]()
SQL Access to Confluence Data from Cloud Applications
Now you have a direct connection to live Confluence data from MuleSoft Anypoint Platform. You can create more connections to ensure seamless data flow, automate business processes, and manage APIs - all without replicating Confluence data.
To get real-time data access to 100+ SaaS, Big Data, and NoSQL sources (including Confluence) directly from your cloud applications, explore the CData Connect Cloud.








 The new project appears in a project folder.
The new project appears in a project folder.