Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →How to publish and share Azure Data Lake Storage Data dashboards with Tableau Server
The CData ODBC driver for Azure Data Lake Storage enables you integrate Azure Data Lake Storage data into Tableau dashboards.
Integrate connectivity to Azure Data Lake Storage data into your enterprise reporting capabilities. The CData ODBC Driver for Azure Data Lake Storage enables you to access live Azure Data Lake Storage data in business intelligence tools like Tableau Server. Connectivity to Azure Data Lake Storage APIs enables you to monitor changes to your data in real time. Other members of your organization can access your dashboards from a Web browser and get updates from their mobile phone.
This article walks through the process of configuring a DSN on the client and server machines, publishing a data source for Azure Data Lake Storage to Tableau Server, and publishing an entire Workbook to Tableau Server (including the data source). If you publish a data source, you will be able to create new, refreshable workbooks in Tableau Server.
Connect to Azure Data Lake Storage as an ODBC Data Source
To create a data source or workbook in Tableau Desktop and publish the data source or workbook to Tableau server, you will need to configure a DSN on each machine (Desktop and Server), specifying connection properties and creating DSNs using the same name on each machine. Information for connecting to Azure Data Lake Storage follows, along with different instructions for configuring a DSN in Windows and Linux environments.
Authenticating to a Gen 1 DataLakeStore Account
Gen 1 uses OAuth 2.0 in Azure AD for authentication.
For this, an Active Directory web application is required. You can create one as follows:
To authenticate against a Gen 1 DataLakeStore account, the following properties are required:
- Schema: Set this to ADLSGen1.
- Account: Set this to the name of the account.
- OAuthClientId: Set this to the application Id of the app you created.
- OAuthClientSecret: Set this to the key generated for the app you created.
- TenantId: Set this to the tenant Id. See the property for more information on how to acquire this.
- Directory: Set this to the path which will be used to store the replicated file. If not specified, the root directory will be used.
Authenticating to a Gen 2 DataLakeStore Account
To authenticate against a Gen 2 DataLakeStore account, the following properties are required:
- Schema: Set this to ADLSGen2.
- Account: Set this to the name of the account.
- FileSystem: Set this to the file system which will be used for this account.
- AccessKey: Set this to the access key which will be used to authenticate the calls to the API. See the property for more information on how to acquire this.
- Directory: Set this to the path which will be used to store the replicated file. If not specified, the root directory will be used.
When you configure the DSN, you may also want to set the Max Rows connection property. This will limit the number of rows returned, which is especially helpful for improving performance when designing reports and visualizations.
Windows
If you are installing the CData ODBC Driver for Azure Data Lake Storage on Windows, DSN configuration is the last step of the driver installation. If you already have the driver installed, or you wish to configure new DSNs, you can use the Microsoft ODBC Data Source Administrator.
Linux
If you are installing the CData ODBC Driver for Azure Data Lake Storage in a Linux environment, the driver installation predefines a system DSN. You can modify the DSN by editing the system data sources file (/etc/odbc.ini) and defining the required connection properties.
/etc/odbc.ini
[CData ADLS Source]
Driver = CData ODBC Driver for Azure Data Lake Storage
Description = My Description
Schema = ADLSGen2
Account = myAccount
FileSystem = myFileSystem
AccessKey = myAccessKey
For specific information on using these configuration files, please refer to the help documentation (installed and found online).
Publish the Azure Data Lake Storage Data Source to Tableau Server
With the connections to Azure Data Lake Storage data configured, you are ready to publish a Azure Data Lake Storage data source on Tableau, ready to be leveraged by users in your organization to create workbooks based on Azure Data Lake Storage data.
Create and Publish a Data Source
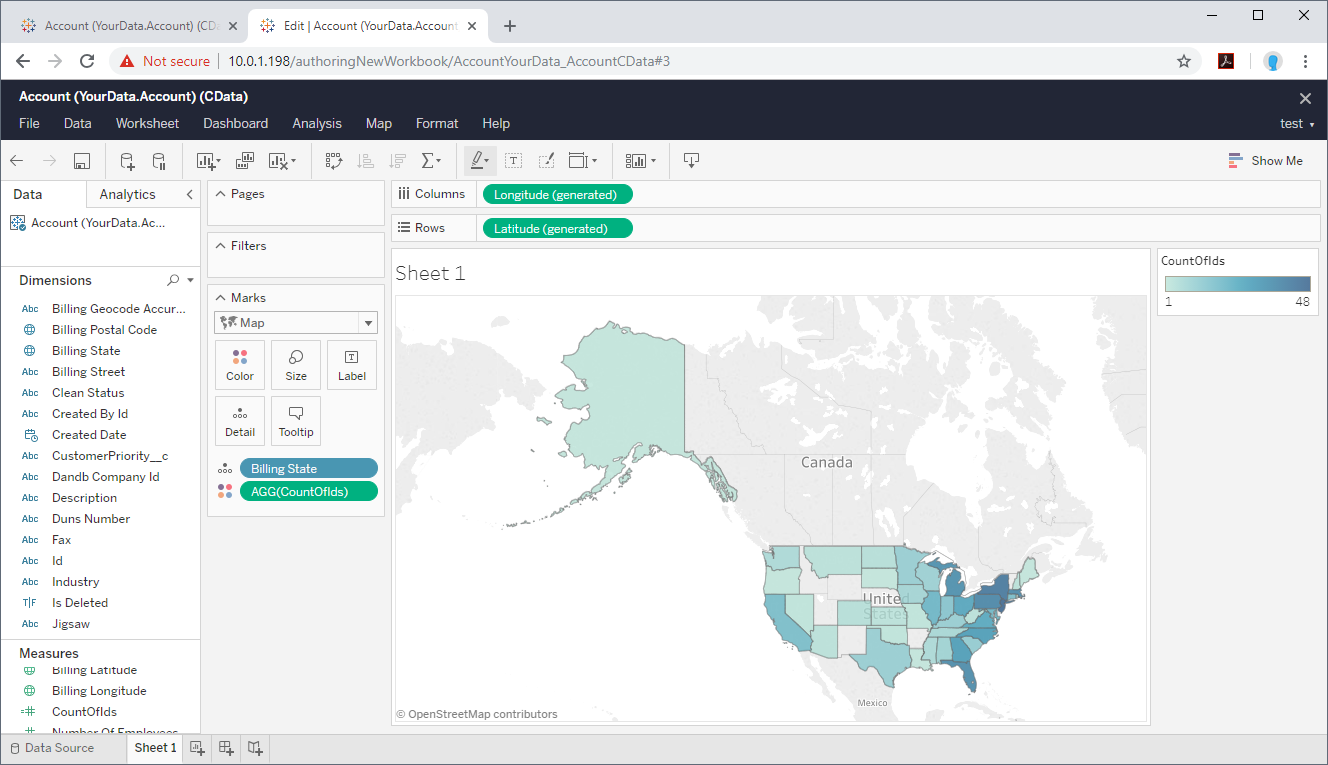
In the Connect pane, click More -> Other Databases (ODBC). Select CData ADLS Sys, the system DSN.
The driver installation automatically creates matching user and system DSNs: The system DSN is needed to connect from Tableau Server.
![The connection to the DSN. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
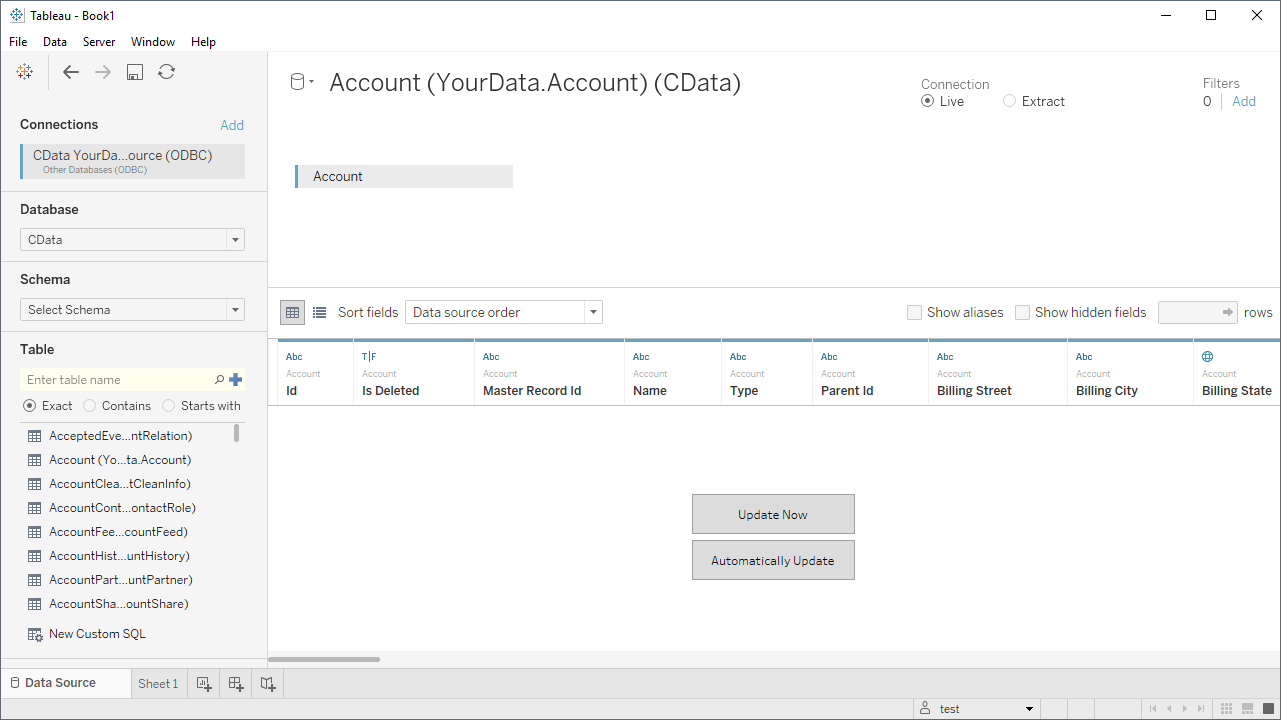
- In the Database menu, select CData.
- In the Table box, enter a table name or click New Custom SQL to enter an SQL query.
- Drag the table onto the join area.
![A connection to a single table. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
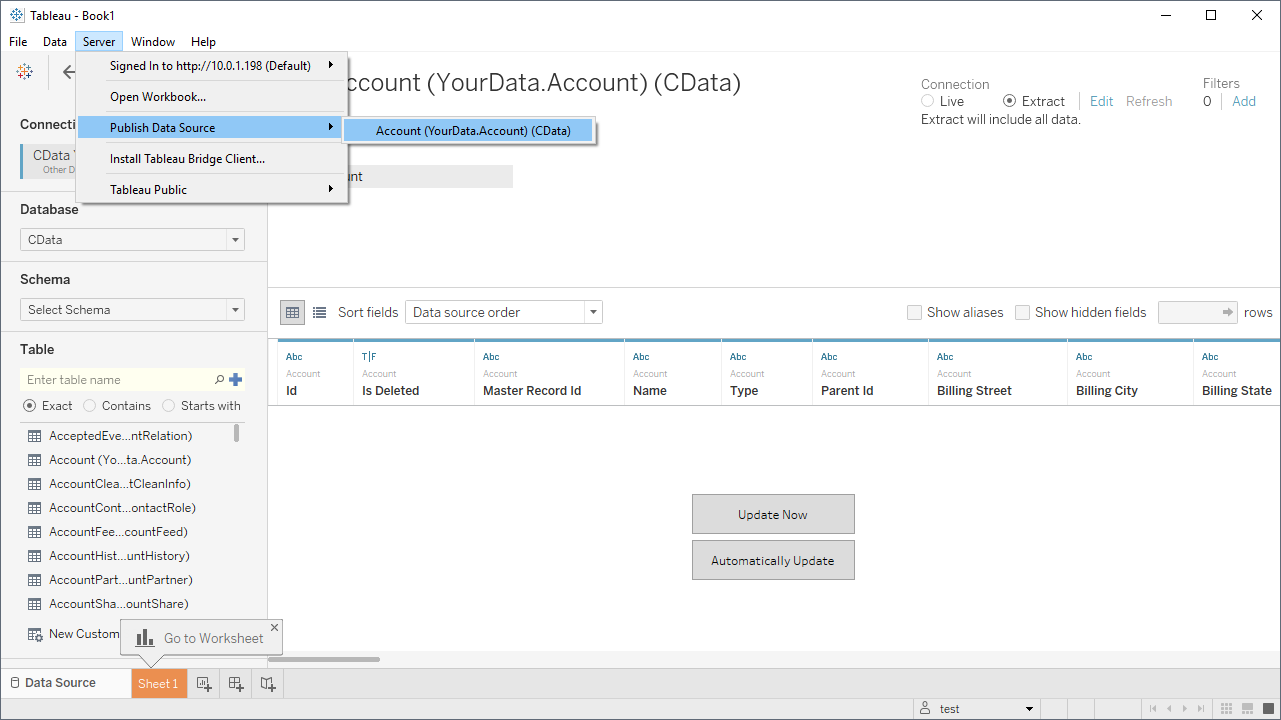
- From the Server menu, click Publish Data Source -> (YOUR DATA SOURCE).
![]()
- Enter the URL to the server. For most instances, you will authenticate with the Tableau Server username and password. Other authentication scenarios can be found below:
- If Tableau is configured to use Kerberos and your computer has valid Active Directory credentials, Tableau connects to the server.
- If Tableau is configured to use SAML, a login prompt for your external identity provider is displayed.
- If Tableau is configured to use Active Directory, enter your Windows username and password.
- In the resulting dialog, set the Project, Data Source, and other properties. If you want to schedule refreshes, select Embedded Password in the Authentication menu. Click Publish.
You and other users in your organization can now create and share workbooks based on the published data source.
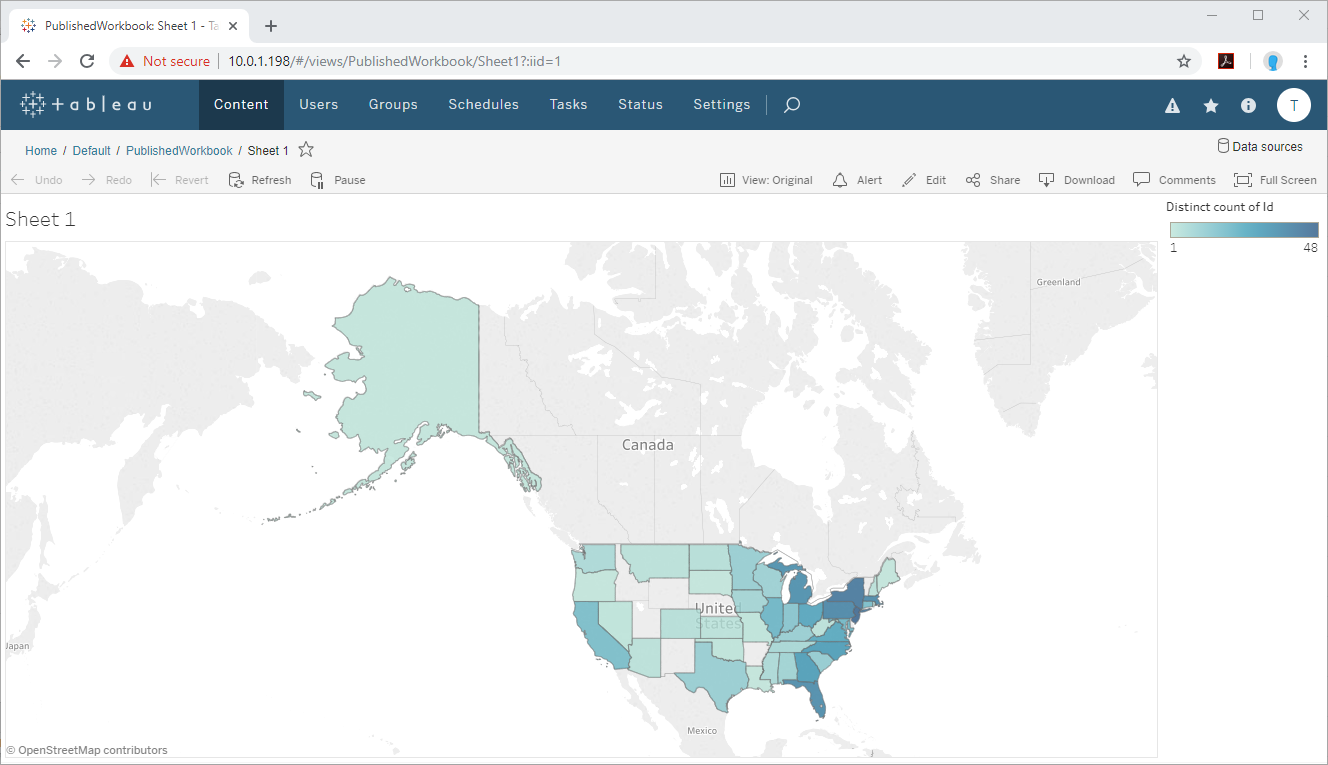
Refresh Workbooks
With a system DSN configured on the client (Tableau Desktop) machine and server (Tableau Server) machine, you can refresh workbooks connected to the Azure Data Lake Storage data source. From the Web interface for Tableau Sever, click Data -> (YOUR DATA SOURCE) -> Refresh.
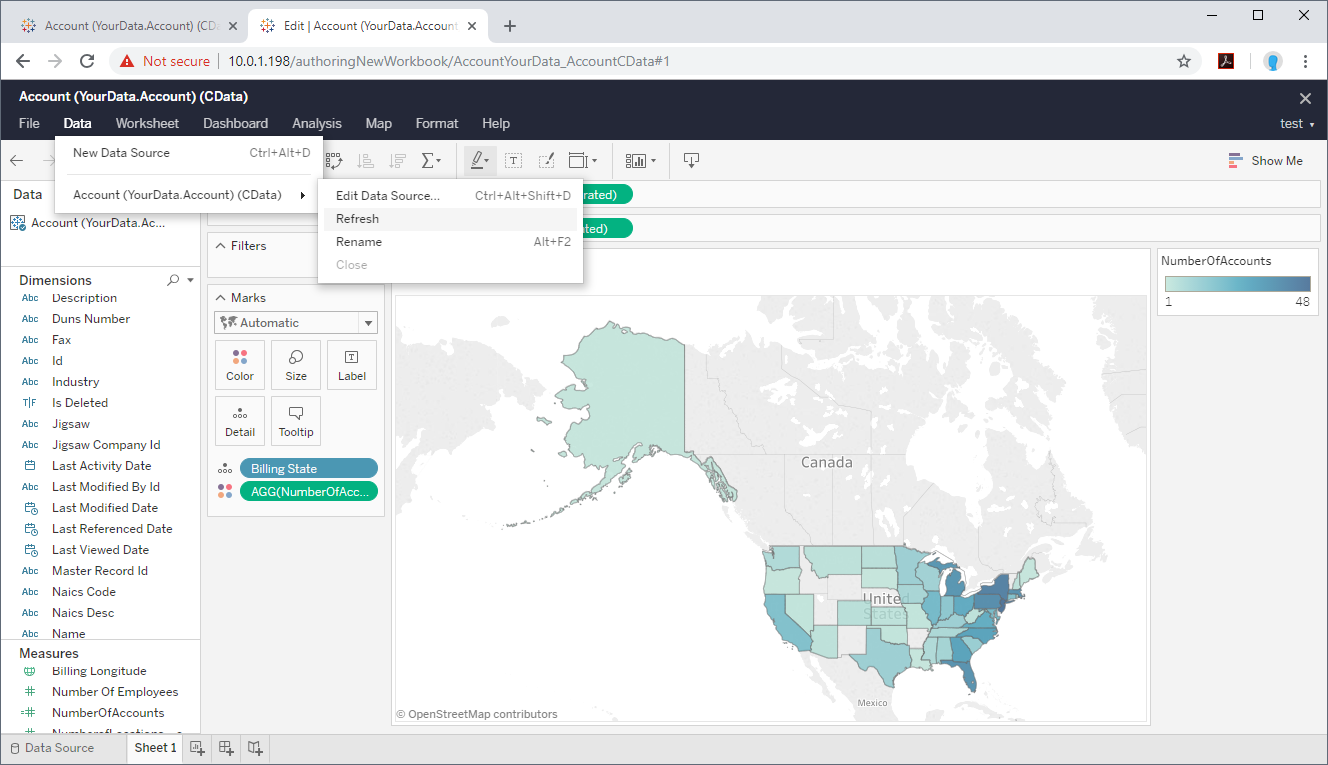
Publish a Completed Workbook with Azure Data Lake Storage Data to Tableau Server
If you have a specific Workbook that you wish to share with your organization, you can create the Workbook on Tableau Desktop and publish the Workbook directly to Tableau Server.
- To connect to Azure Data Lake Storage and select data, follow steps 1-5 above.
![A connection to a single table. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
- Click Server -> Sign in and configure the connection to the server. For most instances, you will authenticate with the Tableau Server username and password. Other authentication scenarios can be found below:
- If Tableau is configured to use Kerberos and your computer has valid Active Directory credentials, Tableau connects to the server.
- If Tableau is configured to use SAML, a login prompt for your external identity provider is displayed.
- If Tableau is configured to use Active Directory, enter your Windows username and password.
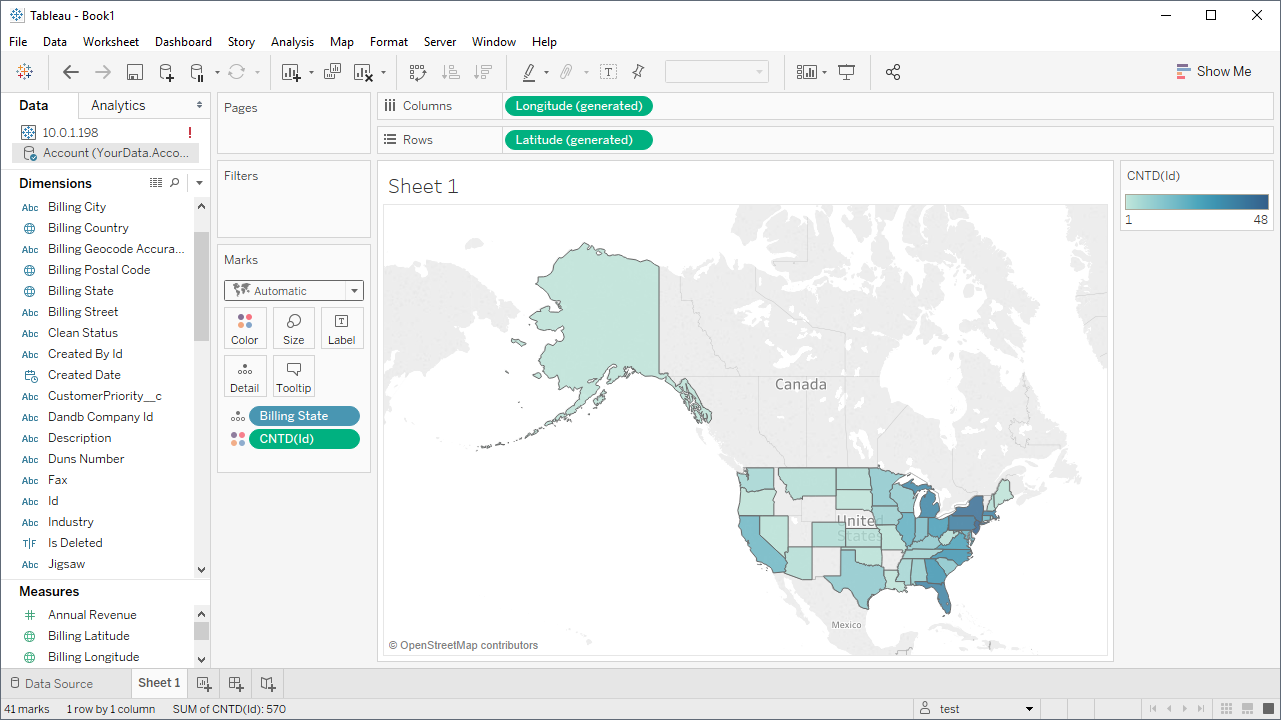
- With the data selected, select dimensions and measures to visualize and select a type of chart or graph to build your visualization(s).
![]()
- Once the Workbook is complete, click Server -> Publish Workbook to publish the Workbook to Tableau Server.
![]()
- In the resulting dialog, set the Project, Name, Description and other properties. If you want to schedule refreshes, click Edit under Data Sources and change the Authentication option to Embedded Password. Click Publish.
![]()
You and other users in your organization can now review the published workbook from Tableau Server.