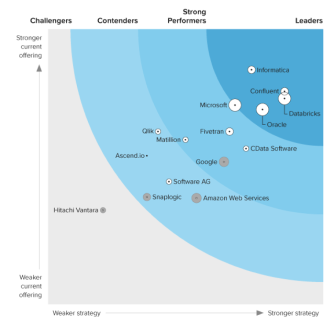
Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Replicate Multiple AlloyDB Accounts
Replicate multiple AlloyDB accounts to one or many databases.
CData Sync for AlloyDB is a stand-alone application that provides solutions for a variety of replication scenarios such as replicating sandbox and production instances into your database. Both Sync for Windows and Sync for Java include a command-line interface (CLI) that makes it easy to manage multiple AlloyDB connections. In this article we show how to use the CLI to replicate multiple AlloyDB accounts.
Configure AlloyDB Connections
You can save connection and email notification settings in an XML configuration file. To replicate multiple AlloyDB accounts, use multiple configuration files. Below is an example configuration to replicate AlloyDB to SQLite:
Windows
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<CDataSync>
<DatabaseType>SQLite</DatabaseType>
<DatabaseProvider>System.Data.SQLite</DatabaseProvider>
<ConnectionString>User=alloydb;Password=admin;Database=alloydb;Server=127.0.0.1;Port=5432</ConnectionString>
<ReplicateAll>False</ReplicateAll>
<NotificationUserName></NotificationUserName>
<DatabaseConnectionString>Data Source=C:\my.db</DatabaseConnectionString>
<TaskSchedulerStartTime>09:51</TaskSchedulerStartTime>
<TaskSchedulerInterval>Never</TaskSchedulerInterval>
</CDataSync>
Java
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<CDataSync>
<DatabaseType>SQLite</DatabaseType>
<DatabaseProvider>org.sqlite.JDBC</DatabaseProvider>
<ConnectionString>User=alloydb;Password=admin;Database=alloydb;Server=127.0.0.1;Port=5432</ConnectionString>
<ReplicateAll>False</ReplicateAll>
<NotificationUserName></NotificationUserName>
<DatabaseConnectionString>Data Source=C:\my.db</DatabaseConnectionString>
</CDataSync>
The following connection properties are usually required in order to connect to AlloyDB.
- Server: The host name or IP of the server hosting the AlloyDB database.
- User: The user which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
- Password: The password which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
You can also optionally set the following:
- Database: The database to connect to when connecting to the AlloyDB Server. If this is not set, the user's default database will be used.
- Port: The port of the server hosting the AlloyDB database. This property is set to 5432 by default.
Authenticating with Standard Authentication
Standard authentication (using the user/password combination supplied earlier) is the default form of authentication.
No further action is required to leverage Standard Authentication to connect.
Authenticating with pg_hba.conf Auth Schemes
There are additional methods of authentication available which must be enabled in the pg_hba.conf file on the AlloyDB server.
Find instructions about authentication setup on the AlloyDB Server here.
Authenticating with MD5 Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to md5.
Authenticating with SASL Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to scram-sha-256.
Authenticating with Kerberos
The authentication with Kerberos is initiated by AlloyDB Server when the ∏ is trying to connect to it. You should set up Kerberos on the AlloyDB Server to activate this authentication method. Once you have Kerberos authentication set up on the AlloyDB Server, see the Kerberos section of the help documentation for details on how to authenticate with Kerberos.
Configure Queries for Each AlloyDB Instance
Sync enables you to control replication with standard SQL. The REPLICATE statement is a high-level command that caches and maintains a table in your database. You can define any SELECT query supported by the AlloyDB API. The statement below caches and incrementally updates a table of AlloyDB data:
REPLICATE Orders;
You can specify a file containing the replication queries you want to use to update a particular database. Separate replication statements with semicolons. The following options are useful if you are replicating multiple AlloyDB accounts into the same database:
You can use a different table prefix in the REPLICATE SELECT statement:
REPLICATE PROD_Orders SELECT * FROM Orders
Alternatively, you can use a different schema:
REPLICATE PROD.Orders SELECT * FROM Orders
Run Sync
After you have configured the connection strings and replication queries, you can run Sync with the following command-line options:
Windows
AlloyDBSync.exe -g MyProductionAlloyDBConfig.xml -f MyProductionAlloyDBSync.sql
Java
java -Xbootclasspath/p:c:\sqlitejdbc.jar -jar AlloyDBSync.jar -g MyProductionAlloyDBConfig.xml -f MyProductionAlloyDBSync.sql