Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →
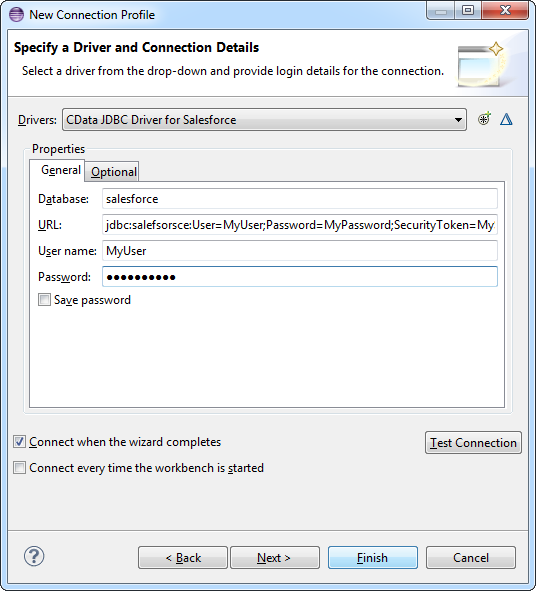
The DB2 JDBC Driver enables users to connect with live DB2 data, directly from any applications that support JDBC connectivity. Rapidly create and deploy powerful Java applications that integrate with IBM DB2.
Features
- Support for LUW and AS/400 instances of DB2. For interest in z/OS support, please contact our support team at support@cdata.com.
- Connect to live IBM DB2 data, for real-time data access
- Full support for data aggregation and complex JOINs in SQL queries
- Seamless integration with leading BI, reporting, and ETL tools and with custom applications
Specifications
- JDBC Driver for DB2 with bi-directional access.
- Write SQL, get IBM DB2 data. Access DB2 through standard Java Database Connectivity.
- Codeless integration with popular BI, Reporting, & ETL Tools.
- Integrate Java Apps with DB2 DB2Table, and more!
- Full Unicode support for data, parameter, & metadata.
- Support for 32-bit and 64-bit operating systems.
JDBC Access to IBM DB2
Full-featured and consistent SQL access to any supported data source through JDBC
-
Certified Compatibility*
Our drivers undergo extensive testing and are certified to be compatible with leading analytics and reporting applications like SAP Crystal Reports, Pentaho, Business Objects, Crystal Reports and many more.
-
Metadata Discovery
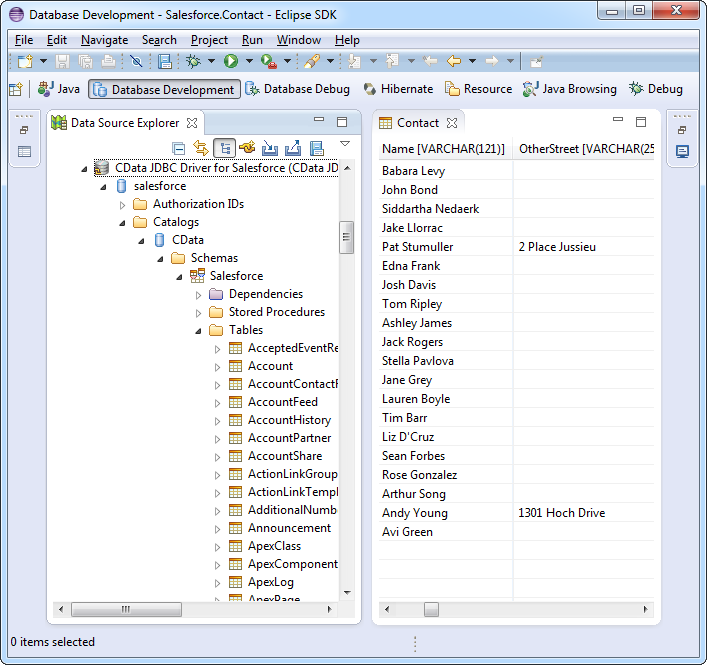
Full support for JDBC DatabaseMetaData provides extensive schema discovery capabilities. Explore tables, columns, keys, and other data constructs based on user identity.
-
Developer Friendly
Design-time support for all major Java IDEs, including Eclipse, IntelliJ, and NetBeans.
-
JDBC Remoting
Our exclusive remoting feature allows hosting the JDBC connection on a server to enable connections from various clients on any platform (Java, .NET, C++, PHP, Python), using any standards-based technology (ODBC, JDBC, etc.). JDBC Remoting is enabled using the popular MySQL wire protocol server.
-
Replication and Caching
Our replication and caching commands make it easy to copy data to local and cloud data stores such as Oracle, SQL Server, Google Cloud SQL, etc. The replication commands include many features that allow for intelligent incremental updates to cached data.
-
String, Date, Numeric SQL Functions
The driver includes a library of over 50 functions that can manipulate column values into the desired result. Popular examples include Regex, JSON, and XML processing functions.
-
Collaborative Query Processing
Our drivers enhance the data source's capabilities by additional client-side processing, when needed, to enable analytic summaries of data such as SUM, AVG, MAX, MIN, etc.
-
Easily Customizable and Configurable
The data model exposed by our JDBC Drivers can easily be customized to add or remove tables/columns, change data types, etc. without requiring a new build. These customizations are supported at runtime using human-readable schema files that are easy to edit.
-
Secure Connectivity
Includes standard Enterprise-class security features such as TLS/ SSL data encryption for all client-server communications.
JDBC Driver Performance
With traditional approaches to remote access, performance bottlenecks can spell disaster for applications. Regardless if an application is created for internal use, a commercial project, web, or mobile application, slow performance can rapidly lead to project failure. Accessing data from any remote source has the potential to create these problems. Common issues include:
- Network Connections - Slow network connections and latency issues are common in mobile applications.
- Service Delays - Delays due to service interruptions, resulting in server hardware or software updates.
- Large Data - Intentional or unintentional requests for large amounts of data.
- Disconnects - Complete loss of network connectivity.
The CData JDBC Driver for IBM DB2 solves many of these issues with support for replication queries that can be used to sync data to local databases, greatly improving the performance and dramatically reduce application bottlenecks.
More information about JDBC Driver performance capabilities are available in the included documentation.
Enterprise-Class Remoting
MySQL/SQL Database entry points for IBM DB2 Data
The CData JDBC drivers include powerful fully-integrated remoting capabilities that makes IBM DB2 data accessible from virtually anywhere. The drivers include the optional ability to accept incoming SQL and MySQL client connections and service standard database requests.
With the CData JDBC drivers, users can interact with IBM DB2 data from any client that supports SQL Server or MySQL: from web & mobile applications, to CRM and CMS systems, BI tools like SQL Server Analysis Services, and even through popular management applications like MySQL Workbench.
- Access IBM DB2 data from virtually any application that can access external data. Applications that can access SQL Server or MySQL data can now connect to IBM DB2 with this driver.
- Connect IBM DB2 data with popular BI tools like SQL Server Analysis Services.
- Enable enterprise IBM DB2 data integration through SQL Linked Server connectivity
- Includes support for the MySQL and SQL (TDS) remote access protocols - industry standards for remote database connectivity.
- Offers advanced wire-protocol SSL security for remote connectivity
Enterprise-class JDBC Connectivity
The IBM DB2 JDBC Driver offers the most natural way to access DB2 data from any Java/J2EE application. Simply use the IBM DB2 Driver to connect and access data just as you would access any traditional database. The driver is completely self-contained - no additional software installation is required!
DB2 Integration
The IBM DB2 Driver has the same JDBC architecture as the JDBC drivers for MySQL and OLEDB, including Connection, Statement and ResultSet objects. Because of this you can now access DB2 data in an easy, familiar way. You can use the IBM DB2 Driver through popular IDEs (Eclipse, IntelliJ, NetBeans, etc.), in code through familiar classes, and in data controls available through Swing, Eclipse SWT Widgets, etc.
For example:
Connection conn =
DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:db2:user=myuseraccount;password=mypassword;");
boolean ret = stat.execute("SELECT * FROM DB2Table");
ResultSet rs=stat.getResultSet();
while(rs.next()){
for(int i=1;i<=rs.getMetaData().getColumnCount();i++)
{
System.out.println(rs.getMetaData().getColumnName(i) +"="+rs.getString(i));
}
}
More Than Read-Only: Full Update/CRUD Support
IBM DB2 Driver goes beyond read-only functionality to deliver full support for Create, Read Update, and Delete operations (CRUD). Your end-users can interact with the data presented by the IBM DB2 Driver as easily as interacting with a database table.
Connection conn =
DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:db2:user=myuseraccount;password=mypassword;");
String query = "UPDATE DB2Table SET Where= ...";
PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(query);
pstmt.setString(1, "Location");
pstmt.setString(2, "UID");
pstmt.execute();
int count=pstmt.getUpdateCount();
Frequently Asked DB2 JDBC Driver Questions
Learn more about DB2 JDBC drivers for data and analytics integration
Can DB2 be used with Java?
Yes, DB2 can be used with Java . CData provides a JDBC type 4/5 driver for DB2 that allows Java applications to connect to DB2 using standard JDBC APIs. This driver enables you to execute SQL queries, manage connections, and process data stored in DB2 from Java, or any Java-based application that supports JDBC.
Does DB2 support JDBC?
Not natively. However, CData offers an JDBC driver for DB2 that allows you to connect to DB2 data from any Java-based application that supports JDBC, just like you would access a traditional database. This can be useful for tasks like:
- Accessing DB2 from applications: Connect to DB2 data in popular tools and applications including Informatica, Talend, Apache Spark, Apache NiFi, and many others.
- Real-time data: You can work with live DB2 data within these applications, enabling tasks like reporting and analysis.
- Connecting systems: Build data integrations between DB2 and other systems.
The DB2 JDBC driver is a pure Java type 4/5 driver with comprehensive ANSI SQL-92 support. This means that virtually any application that can connect to data via JDBC, can use the CData JDBC driver for real-time integration. Download a fully functional free trial of the DB2 JDBC driver today to get started.
Is there a JDBC driver for DB2?
Yes, the CData JDBC driver for DB2 provides universal JDBC data connectivity for DB2. The DB2 JDBC driver offers a simple SQL-based layer of abstraction that simplifies real-time data access for users and applications, enabling them to communicate with DB2 using a standardized set of functions. Virtually any application on any platform can use the CData JDBC driver for real-time integration.
How do I connect to DB2 via JDBC?
Connectivity to DB2 via JDBC is easy. First, download and install the DB2 JDBC driver.
Once the installation is complete, navigate to the JDBC driver documentation page. Here, you'll find a wealth of information about the installed driver. The step-by-step instructions for creating a DSN and using it to connect to DB2 via JDBC are just the beginning. The documentation also provides extensive configuration details for using the DB2 JDBC driver with all your favorite applications and development tools, ensuring you have all the support you need.
Where can I download a JDBC driver for DB2?
All of the CData JDBC drivers, including the DB2 JDBC driver are available for download online. To get started, download a fully functional free trial of the DB2 JDBC driver today.
How do I install the JDBC driver for DB2?
To install the DB2 driver, simply download one of the DB2 JDBC driver installers available online. The installers are comprehensive setup utilities that will install all the components required to use the DB2 JDBC driver on your system.
Popular JDBC Videos: