Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Automate Tasks in Power Automate Using the CData API Server and SQL Server ADO.NET Provider
Automate actions like sending emails to a contact list, posting to social media, or syncing CRM and ERP.
Power Automate (Microsoft Flow) makes it easy to automate tasks that involve data from multiple systems, on premises or in the cloud. With the CData API Server and SQL Server ADO.NET Provider (or any of 200+ other ADO.NET Providers), line-of-business users have a native way to create actions based on SQL Server triggers in Power Automate; the API Server makes it possible for SaaS applications like Power Automate to integrate seamlessly with SQL Server data through data access standards like Swagger and OData. This article shows how to use wizards in Power Automate and the API Server for SQL Server to create a trigger -- entities that match search criteria -- and send an email based on the results.
Set Up the API Server
Follow the steps below to begin producing secure and Swagger-enabled SQL Server APIs:
Deploy
The API Server runs on your own server. On Windows, you can deploy using the stand-alone server or IIS. On a Java servlet container, drop in the API Server WAR file. See the help documentation for more information and how-tos.
The API Server is also easy to deploy on Microsoft Azure, Amazon EC2, and Heroku.
Connect to SQL Server
After you deploy, provide authentication values and other connection properties by clicking Settings -> Connections in the API Server administration console. You can then choose the entities you want to allow the API Server access to by clicking Settings -> Resources.
Connecting to Microsoft SQL Server
Connect to Microsoft SQL Server using the following properties:
- Server: The name of the server running SQL Server.
- User: The username provided for authentication with SQL Server.
- Password: The password associated with the authenticating user.
- Database: The name of the SQL Server database.
Connecting to Azure SQL Server and Azure Data Warehouse
You can authenticate to Azure SQL Server or Azure Data Warehouse by setting the following connection properties:
- Server: The server running Azure. You can find this by logging into the Azure portal and navigating to "SQL databases" (or "SQL data warehouses") -> "Select your database" -> "Overview" -> "Server name."
- User: The name of the user authenticating to Azure.
- Password: The password associated with the authenticating user.
- Database: The name of the database, as seen in the Azure portal on the SQL databases (or SQL warehouses) page.
You will also need to enable CORS and define the following sections on the Settings -> Server page. As an alternative, you can select the option to allow all domains without '*'.
- Access-Control-Allow-Origin: Set this to a value of '*' or specify the domains that are allowed to connect.
- Access-Control-Allow-Methods: Set this to a value of "GET,PUT,POST,OPTIONS".
- Access-Control-Allow-Headers: Set this to "x-ms-client-request-id, authorization, content-type".
Authorize API Server Users
After determining the OData services you want to produce, authorize users by clicking Settings -> Users. The API Server uses authtoken-based authentication and supports the major authentication schemes. You can authenticate as well as encrypt connections with SSL. Access can also be restricted by IP address; access is restricted to only the local machine by default.
For simplicity, we will allow the authtoken for API users to be passed in the URL. You will need to add a setting in the Application section of the settings.cfg file, located in the data directory. On Windows, this is the app_data subfolder in the application root. In the Java edition, the location of the data directory depends on your operation system:
- Windows: C:\ProgramData\CData
- Unix or Mac OS X: ~/cdata
[Application]
AllowAuthtokenInURL = true
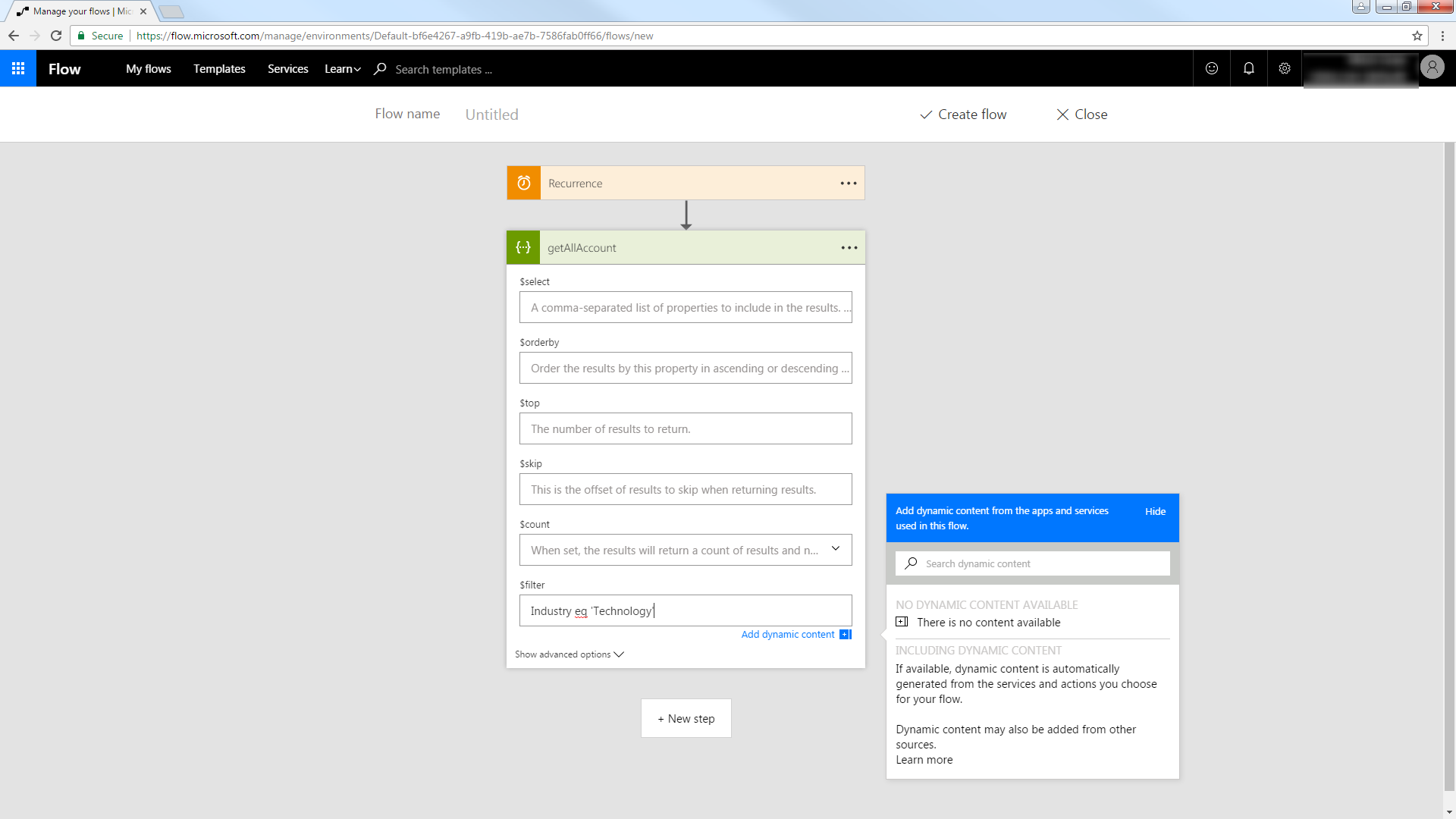
Add SQL Server Data to a Flow
You can use the built-in HTTP + Swagger connector to use a wizard to design a SQL Server process flow:
- In Power Automate, click My Flows -> Create from Blank.
- Select the Recurrence action and select a time interval for sending emails. This article uses 1 day.
- Add an HTTP + Swagger action by searching for Swagger.
- Enter the URL to the Swagger metadata document:
https://MySite:MyPort/api.rsc/@MyAuthtoken/$oas - Select the "Return Orders" operation.
Build the OData query to retrieve SQL Server data. This article defines the following OData filter expression in the $filter box:
ShipCountry eq 'USA'
See the API Server help documentation for more on filtering and examples of the supported OData.
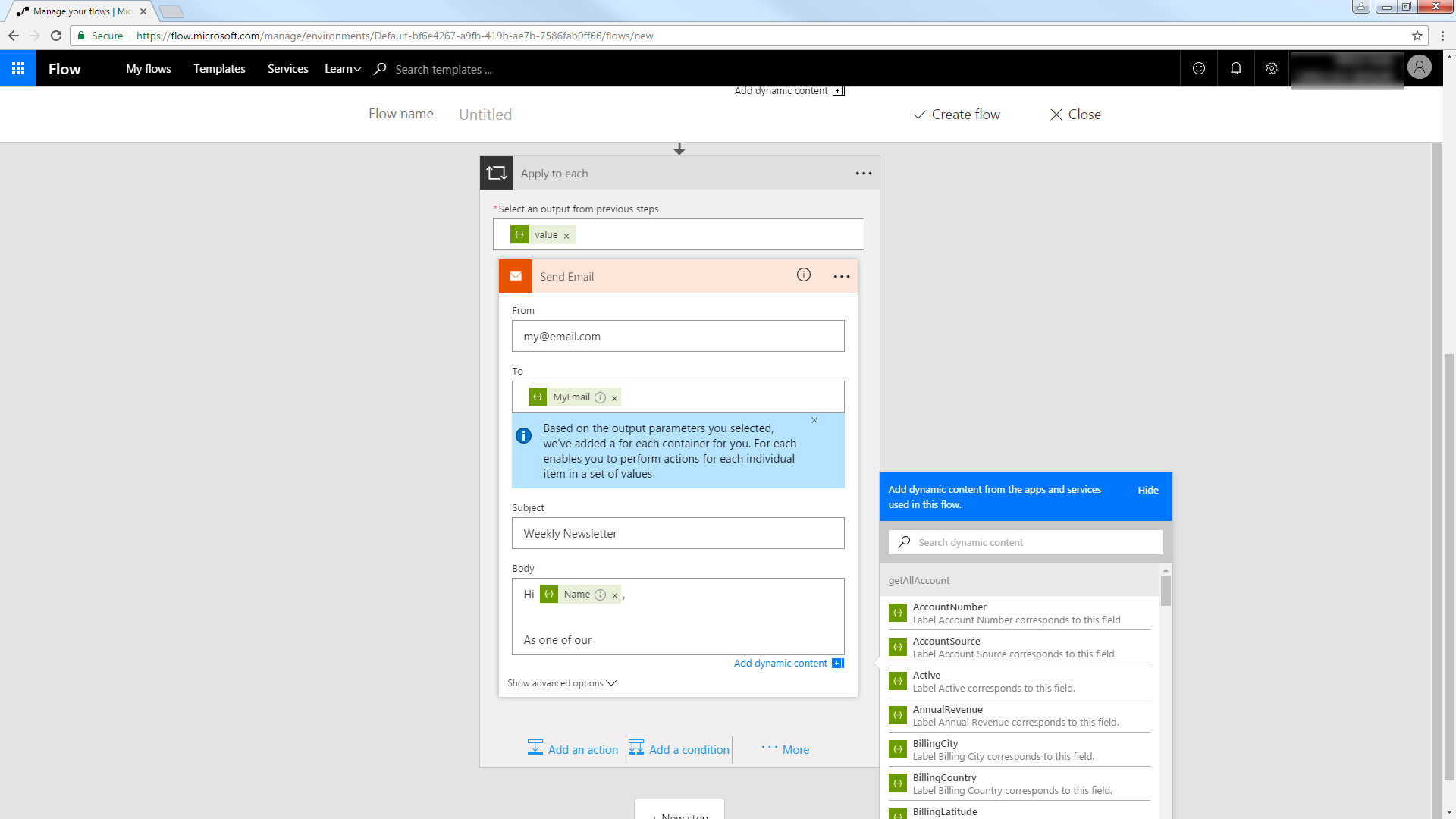
Trigger an Action
You can now work with Orders entities in your process flow. Follow the steps to send an automated email:
- Add an SMTP - Send Email action.
- Enter the address and credentials for the SMTP server and name the connection. Be sure to enable encryption if supported by your server.
- Enter the message headers and body. You can add SQL Server columns in these boxes.
![An email to be populated with results from an OData query. (Salesforce is shown.)]()