Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Connect to SingleStore Data in Google Apps Script
Use CData Connect Cloud to access SingleStore data in Google Apps Script.
Google Apps Script empowers users to build custom functionality within their Google documents, including Google Sheets and Google Docs. Apps Script natively supports SQL Server connectivity via JDBC, providing a powerful extensibility tool for connecting Google cloud applications to external data. Paired with the SQL connectivity offered by CData Connect Cloud, users can easily access live SingleStore data directly from within their Google documents.
This article shows how to connect to SingleStore in Connect Cloud and provides sample scripting for processing SingleStore data in a Google Spreadsheet.
Our script only reads data from a specified table, but you can easily extend the script to incorporate update functionality.
Configure SingleStore Connectivity for Google Apps Scripts
Connectivity to SingleStore from Google Apps Scripts is made possible through CData Connect Cloud. To work with SingleStore data from Google Apps Scripts, we start by creating and configuring a SingleStore connection.
CData Connect Cloud uses a straightforward, point-and-click interface to connect to data sources.
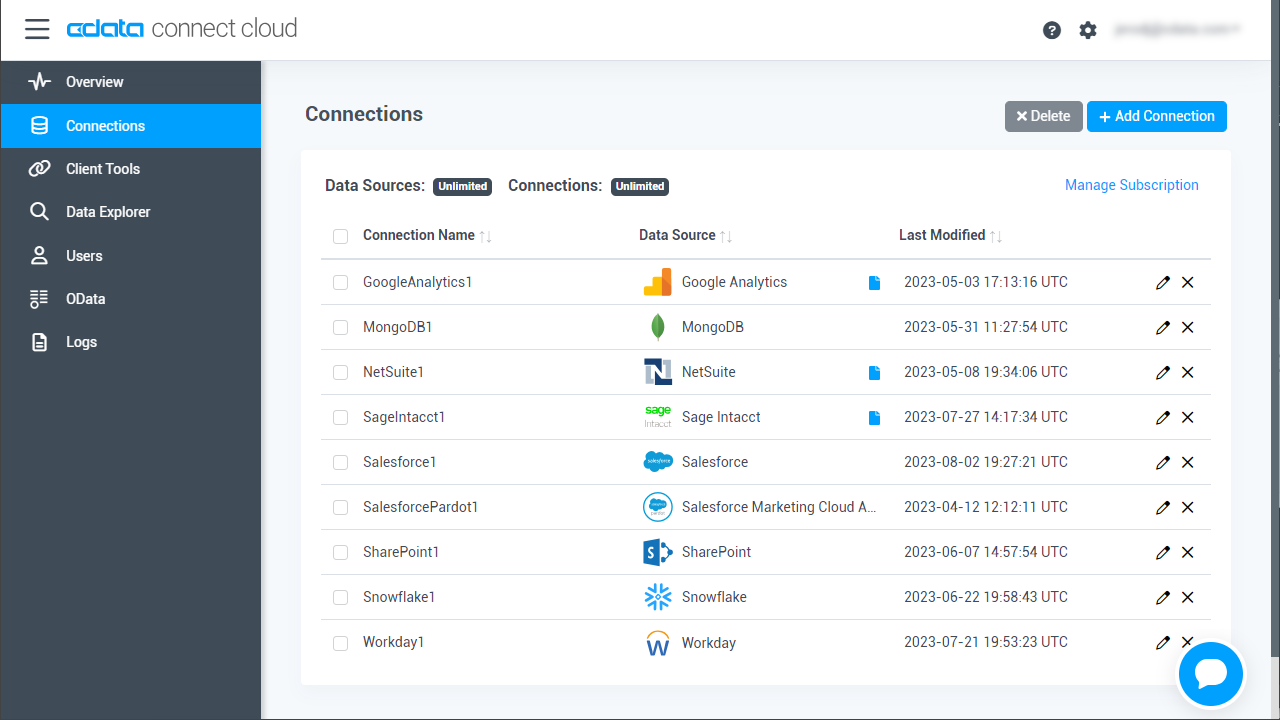
- Log into Connect Cloud, click Connections and click Add Connection
![Adding a Connection]()
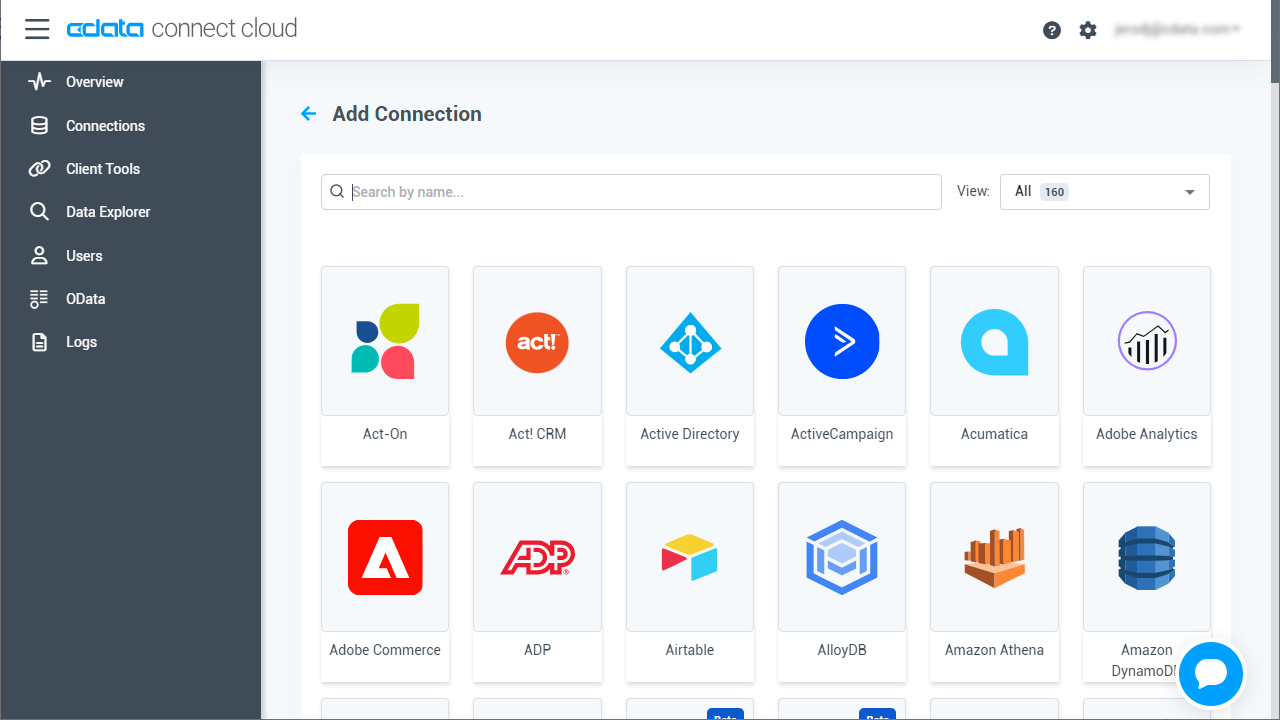
- Select "SingleStore" from the Add Connection panel
![Selecting a data source]()
-
Enter the necessary authentication properties to connect to SingleStore.
The following connection properties are required in order to connect to data.
- Server: The host name or IP of the server hosting the SingleStore database.
- Port: The port of the server hosting the SingleStore database.
- Database (Optional): The default database to connect to when connecting to the SingleStore Server. If this is not set, tables from all databases will be returned.
Connect Using Standard Authentication
To authenticate using standard authentication, set the following:
- User: The user which will be used to authenticate with the SingleStore server.
- Password: The password which will be used to authenticate with the SingleStore server.
Connect Using Integrated Security
As an alternative to providing the standard username and password, you can set IntegratedSecurity to True to authenticate trusted users to the server via Windows Authentication.
Connect Using SSL Authentication
You can leverage SSL authentication to connect to SingleStore data via a secure session. Configure the following connection properties to connect to data:
- SSLClientCert: Set this to the name of the certificate store for the client certificate. Used in the case of 2-way SSL, where truststore and keystore are kept on both the client and server machines.
- SSLClientCertPassword: If a client certificate store is password-protected, set this value to the store's password.
- SSLClientCertSubject: The subject of the TLS/SSL client certificate. Used to locate the certificate in the store.
- SSLClientCertType: The certificate type of the client store.
- SSLServerCert: The certificate to be accepted from the server.
Connect Using SSH Authentication
Using SSH, you can securely login to a remote machine. To access SingleStore data via SSH, configure the following connection properties:
- SSHClientCert: Set this to the name of the certificate store for the client certificate.
- SSHClientCertPassword: If a client certificate store is password-protected, set this value to the store's password.
- SSHClientCertSubject: The subject of the TLS/SSL client certificate. Used to locate the certificate in the store.
- SSHClientCertType: The certificate type of the client store.
- SSHPassword: The password that you use to authenticate with the SSH server.
- SSHPort: The port used for SSH operations.
- SSHServer: The SSH authentication server you are trying to authenticate against.
- SSHServerFingerPrint: The SSH Server fingerprint used for verification of the host you are connecting to.
- SSHUser: Set this to the username that you use to authenticate with the SSH server.
![Configuring a connection (Salesforce is shown)]()
- Click Create & Test
- Navigate to the Permissions tab in the Add SingleStore Connection page and update the User-based permissions.
![Updating permissions]()
Add a Personal Access Token
If you are connecting from a service, application, platform, or framework that does not support OAuth authentication, you can create a Personal Access Token (PAT) to use for authentication. Best practices would dictate that you create a separate PAT for each service, to maintain granularity of access.
- Click on your username at the top right of the Connect Cloud app and click User Profile.
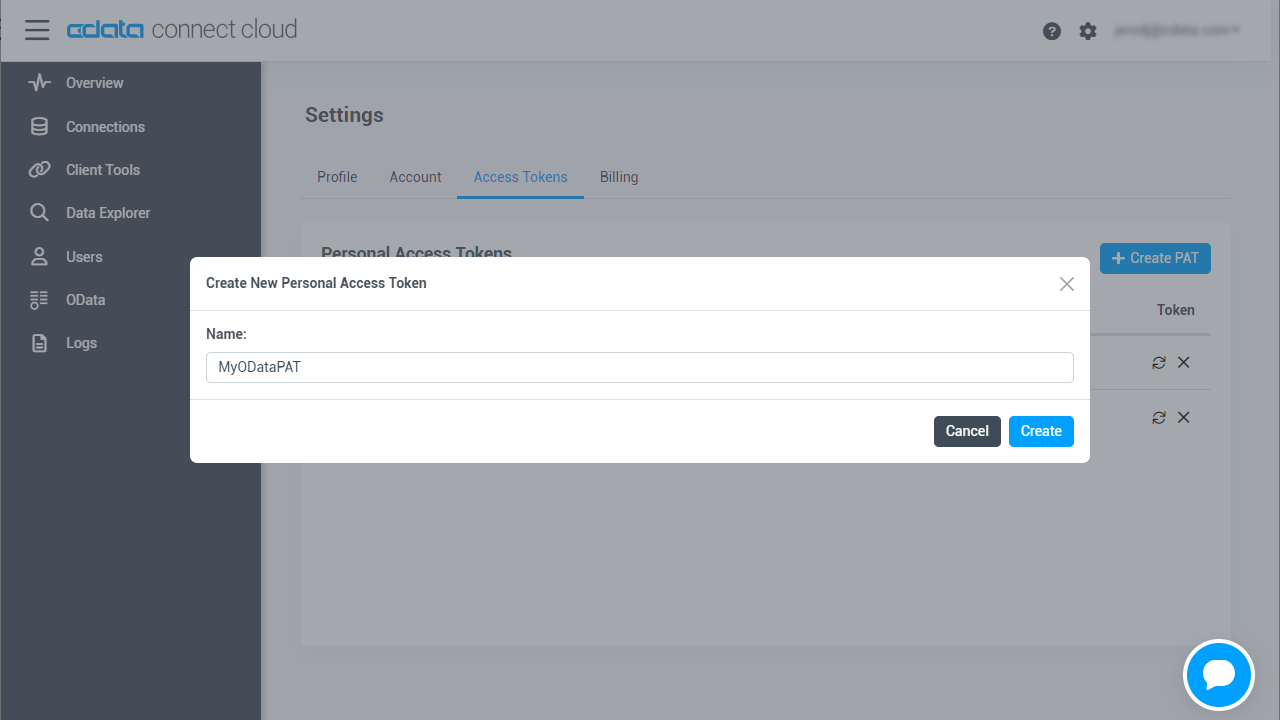
- On the User Profile page, scroll down to the Personal Access Tokens section and click Create PAT.
- Give your PAT a name and click Create.
![Creating a new PAT]()
- The personal access token is only visible at creation, so be sure to copy it and store it securely for future use.
With the connection configured, you are ready to connect to SingleStore data from Google Apps Script.
Connect to SingleStore Data from Apps Script
At this point, you should have configured a connection SingleStore in Connect Cloud. All that is left new is to use Google Apps Script to access Connect Cloud and work with your SingleStore data in Google Sheets.
In this section, you will create a script (with a menu option to call the script) to populate a spreadsheet with SingleStore data. We have created a sample script and explained the different parts. You can view the raw script at the and of the article.
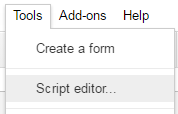
1. Create an Empty Script
To create a script for your Google Sheet, click Tools Script editor from the Google Sheets menu:
2. Declare Class Variables
Create a handful of class variables to be available for any functions created in the script.
//replace the variables in this block with real values as needed var address = 'tds.cdata.com:14333'; var user = 'CONNECT_USER'; // user@mydomain.com var userPwd = 'CONNECT_USER_PAT'; var db = 'SingleStore1'; var dbUrl = 'jdbc:sqlserver://' + address + ';databaseName=' + db;
3. Add a Menu Option
This function adds a menu option to your Google Sheet, allowing you to use the UI to call your function.
function onOpen() {
var spreadsheet = SpreadsheetApp.getActive();
var menuItems = [
{name: 'Write data to a sheet', functionName: 'connectToSingleStoreData'}
];
spreadsheet.addMenu('SingleStore Data', menuItems);
}
4. Write a Helper Function
This function is used to find the first empty row in a spreadsheet.
/*
* Finds the first empty row in a spreadsheet by scanning an array of columns
* @return The row number of the first empty row.
*/
function getFirstEmptyRowByColumnArray(spreadSheet, column) {
var column = spreadSheet.getRange(column + ":" + column);
var values = column.getValues(); // get all data in one call
var ct = 0;
while ( values[ct] && values[ct][0] != "" ) {
ct++;
}
return (ct+1);
}
5. Write a Function to Write SingleStore Data to a Spreadsheet
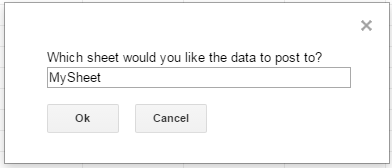
The function below writes the SingleStore data, using the Google Apps Script JDBC functionality to connect to Connect Cloud, SELECT data, and populate a spreadsheet. When the script is run, two input boxes will appear:
The first one asks the user to input the name of a sheet to hold the data (if the spreadsheet does not exist, the function creates it).
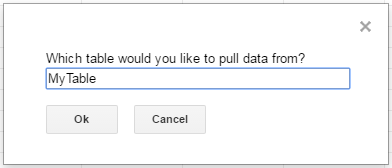
The second asks the user to input the name of a SingleStore table to read. If an invalid table is chosen, an error message appears and the function is exited.
Note, while the function is designed for use as a menu option, you can extend it for use as a spreadsheet formula.
/*
* Reads data from a specified SingleStore 'table' and writes it to the specified sheet.
* (If the specified sheet does not exist, it is created.)
*/
function connectToSingleStoreData() {
var thisWorkbook = SpreadsheetApp.getActive();
//select a sheet and create it if it does not exist
var selectedSheet = Browser.inputBox('Which sheet would you like the data to post to?',Browser.Buttons.OK_CANCEL);
if (selectedSheet == 'cancel')
return;
if (thisWorkbook.getSheetByName(selectedSheet) == null)
thisWorkbook.insertSheet(selectedSheet);
var resultSheet = thisWorkbook.getSheetByName(selectedSheet);
var rowNum = 2;
//select a SingleStore 'table'
var table = Browser.inputBox('Which table would you like to pull data from?',Browser.Buttons.OK_CANCEL);
if (table == 'cancel')
return;
var name = Jdbc.getConnection(dbUrl, {
user: user,
password: userPwd
}
);
//confirm that var table is a valid table/view
var dbMetaData = name.getMetaData();
var tableSet = dbMetaData.getTables(null, null, table, null);
var validTable = false;
while (tableSet.next()) {
var tempTable = tableSet.getString(3);
if (table.toUpperCase() == tempTable.toUpperCase()){
table = tempTable;
validTable = true;
break;
}
}
tableSet.close();
if (!validTable) {
Browser.msgBox("Invalid table name: " + table, Browser.Buttons.OK);
return;
}
var stmt = name.createStatement();
var results = stmt.executeQuery('SELECT * FROM ' + table);
var rsmd = results.getMetaData();
var numCols = rsmd.getColumnCount();
//if the sheet is empty, populate the first row with the headers
var firstEmptyRow = getFirstEmptyRowByColumnArray(resultSheet, "A");
if (firstEmptyRow == 1) {
//collect column names
var headers = new Array(new Array(numCols));
for (var col = 0; col < numCols; col++){
headers[0][col] = rsmd.getColumnName(col+1);
}
resultSheet.getRange(1, 1, headers.length, headers[0].length).setValues(headers);
} else {
rowNum = firstEmptyRow;
}
//write rows of SingleStore data to the sheet
var values = new Array(new Array(numCols));
while (results.next()) {
for (var col = 0; col < numCols; col++) {
values[0][col] = results.getString(col + 1);
}
resultSheet.getRange(rowNum, 1, 1, numCols).setValues(values);
rowNum++;
}
results.close();
stmt.close();
}
When the function is completed, you have a spreadsheet populated with your SingleStore data, and you can now leverage all of the calculating, graphing, and charting functionality of Google Sheets anywhere you have access to the Internet.
Complete Google Apps Script
//replace the variables in this block with real values as needed
var address = 'tds.cdata.com:14333';
var user = 'CONNECT_USER'; // user@mydomain.com
var userPwd = 'CONNECT_USER_PAT';
var db = 'SingleStore1';
var dbUrl = 'jdbc:sqlserver://' + address + ';databaseName=' + db;
function onOpen() {
var spreadsheet = SpreadsheetApp.getActive();
var menuItems = [
{name: 'Write table data to a sheet', functionName: 'connectToSingleStoreData'}
];
spreadsheet.addMenu('SingleStore Data', menuItems);
}
/*
* Finds the first empty row in a spreadsheet by scanning an array of columns
* @return The row number of the first empty row.
*/
function getFirstEmptyRowByColumnArray(spreadSheet, column) {
var column = spreadSheet.getRange(column + ":" + column);
var values = column.getValues(); // get all data in one call
var ct = 0;
while ( values[ct] && values[ct][0] != "" ) {
ct++;
}
return (ct+1);
}
/*
* Reads data from a specified 'table' and writes it to the specified sheet.
* (If the specified sheet does not exist, it is created.)
*/
function connectToSingleStoreData() {
var thisWorkbook = SpreadsheetApp.getActive();
//select a sheet and create it if it does not exist
var selectedSheet = Browser.inputBox('Which sheet would you like the data to post to?',Browser.Buttons.OK_CANCEL);
if (selectedSheet == 'cancel')
return;
if (thisWorkbook.getSheetByName(selectedSheet) == null)
thisWorkbook.insertSheet(selectedSheet);
var resultSheet = thisWorkbook.getSheetByName(selectedSheet);
var rowNum = 2;
//select a SingleStore 'table'
var table = Browser.inputBox('Which table would you like to pull data from?',Browser.Buttons.OK_CANCEL);
if (table == 'cancel')
return;
var name = Jdbc.getConnection(dbUrl, {
user: user,
password: userPwd
}
);
//confirm that var table is a valid table/view
var dbMetaData = name.getMetaData();
var tableSet = dbMetaData.getTables(null, null, table, null);
var validTable = false;
while (tableSet.next()) {
var tempTable = tableSet.getString(3);
if (table.toUpperCase() == tempTable.toUpperCase()){
table = tempTable;
validTable = true;
break;
}
}
tableSet.close();
if (!validTable) {
Browser.msgBox("Invalid table name: " + table, Browser.Buttons.OK);
return;
}
var stmt = name.createStatement();
var results = stmt.executeQuery('SELECT * FROM ' + table);
var rsmd = results.getMetaData();
var numCols = rsmd.getColumnCount();
//if the sheet is empty, populate the first row with the headers
var firstEmptyRow = getFirstEmptyRowByColumnArray(resultSheet, "A");
if (firstEmptyRow == 1) {
//collect column names
var headers = new Array(new Array(numCols));
for (var col = 0; col < numCols; col++){
headers[0][col] = rsmd.getColumnName(col+1);
}
resultSheet.getRange(1, 1, headers.length, headers[0].length).setValues(headers);
} else {
rowNum = firstEmptyRow;
}
//write rows of SingleStore data to the sheet
var values = new Array(new Array(numCols));
while (results.next()) {
for (var col = 0; col < numCols; col++) {
values[0][col] = results.getString(col + 1);
}
resultSheet.getRange(rowNum, 1, 1, numCols).setValues(values);
rowNum++;
}
results.close();
stmt.close();
}