Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Connect to Redshift Data in CloverDX (formerly CloverETL)
Transfer Redshift data using the visual workflow in the CloverDX data integration tool.
The CData JDBC Driver for Redshift enables you to use the data transformation components in CloverDX (formerly CloverETL) to work with Redshift as sources and destinations. In this article, you will use the JDBC Driver for Redshift to set up a simple transfer into a flat file. The CData JDBC Driver for Redshift enables you to use the data transformation components in CloverDX (formerly CloverETL) to work with Redshift as sources and destinations. In this article, you will use the JDBC Driver for Redshift to set up a simple transfer into a flat file.
Connect to Redshift as a JDBC Data Source
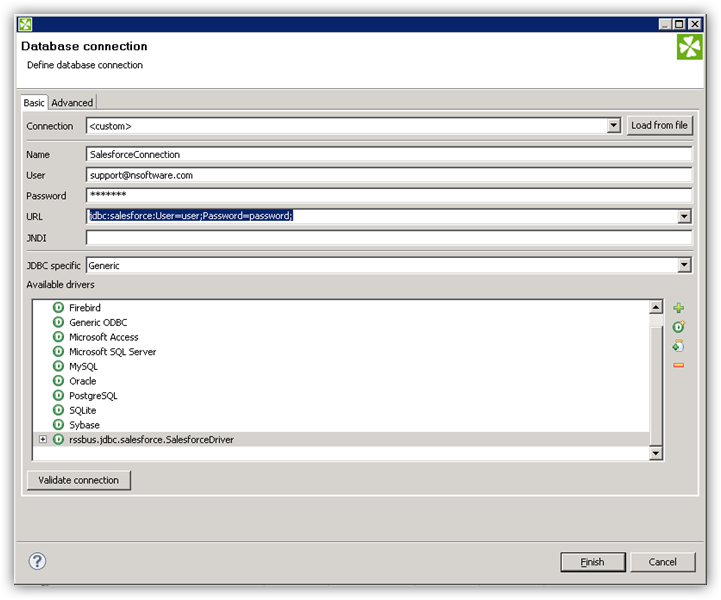
- Create the connection to Redshift data. In a new CloverDX graph, right-click the Connections node in the Outline pane and click Connections -> Create Connection. The Database Connection wizard is displayed.
- Click the plus icon to load a driver from a JAR. Browse to the lib subfolder of the installation directory and select the cdata.jdbc.redshift.jar file.
- Enter the JDBC URL.
To connect to Redshift, set the following:
- Server: Set this to the host name or IP address of the cluster hosting the Database you want to connect to.
- Port: Set this to the port of the cluster.
- Database: Set this to the name of the database. Or, leave this blank to use the default database of the authenticated user.
- User: Set this to the username you want to use to authenticate to the Server.
- Password: Set this to the password you want to use to authenticate to the Server.
You can obtain the Server and Port values in the AWS Management Console:
- Open the Amazon Redshift console (http://console.aws.amazon.com/redshift).
- On the Clusters page, click the name of the cluster.
- On the Configuration tab for the cluster, copy the cluster URL from the connection strings displayed.
Built-in Connection String Designer
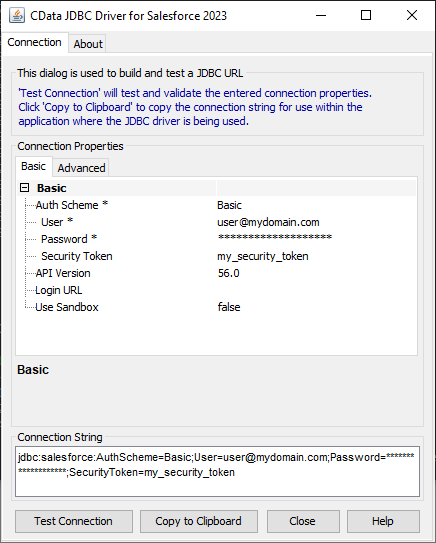
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the Redshift JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.redshift.jarFill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
![Using the built-in connection string designer to generate a JDBC URL (Salesforce is shown.)]()
A typical JDBC URL is below:
jdbc:redshift:User=admin;Password=admin;Database=dev;Server=examplecluster.my.us-west-2.redshift.amazonaws.com;Port=5439;
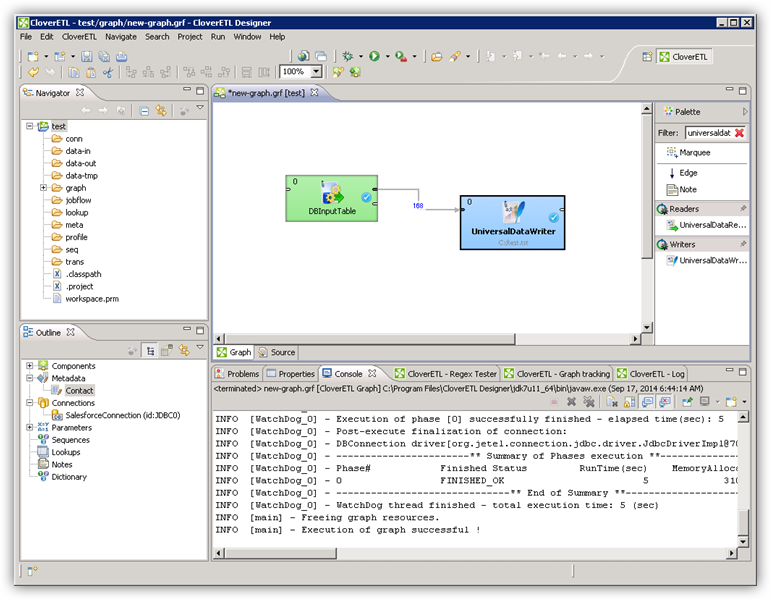
Query Redshift Data with the DBInputTable Component
- Drag a DBInputTable from the Readers selection of the Palette onto the job flow and double-click it to open the configuration editor.
- In the DB connection property, select the Redshift JDBC data source from the drop-down menu.
- Enter the SQL query. For example:
SELECT ShipName, ShipCity FROM Orders
Write the Output of the Query to a UniversalDataWriter
- Drag a UniversalDataWriter from the Writers selection onto the jobflow.
- Double-click the UniversalDataWriter to open the configuration editor and add a file URL.
- Right-click the DBInputTable and then click Extract Metadata.
- Connect the output port of the DBInputTable to the UniversalDataWriter.
- In the resulting Select Metadata menu for the UniversalDataWriter, choose the Orders table. (You can also open this menu by right-clicking the input port for the UniversalDataWriter.)
- Click Run to write to the file.