Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Access Oracle Data in Mule Applications Using the CData JDBC Driver
Create a simple Mule Application that uses HTTP and SQL with CData JDBC drivers to create a JSON endpoint for Oracle data.
The CData JDBC Driver for Oracle connects Oracle data to Mule applications enabling read , write, update, and delete functionality with familiar SQL queries. The JDBC Driver allows users to easily create Mule applications to backup, transform, report, and analyze Oracle data.
This article demonstrates how to use the CData JDBC Driver for Oracle inside of a Mule project to create a Web interface for Oracle data. The application created allows you to request Oracle data using an HTTP request and have the results returned as JSON. The exact same procedure outlined below can be used with any CData JDBC Driver to create a Web interface for the 200+ available data sources.
- Create a new Mule Project in Anypoint Studio.
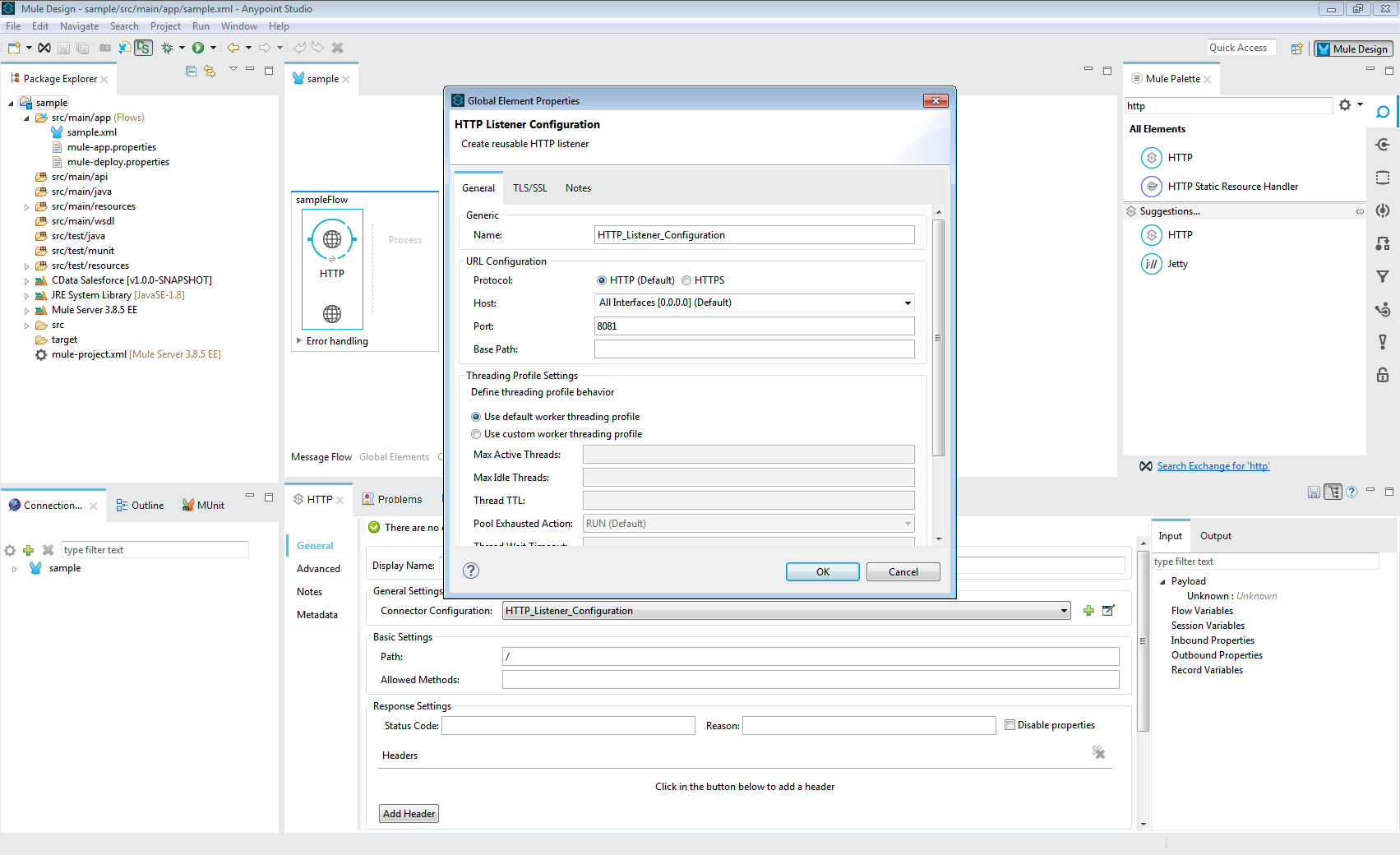
- Add an HTTP Connector to the Message Flow.
- Configure the address for the HTTP Connector.
![Add and Configure the HTTP Connector]()
- Add a Database Select Connector to the same flow, after the HTTP Connector.
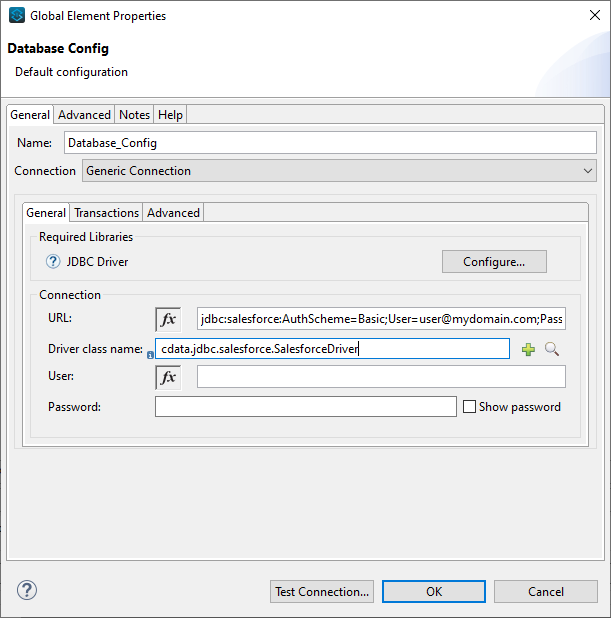
- Create a new Connection (or edit an existing one) and configure the properties.
- Set Connection to "Generic Connection"
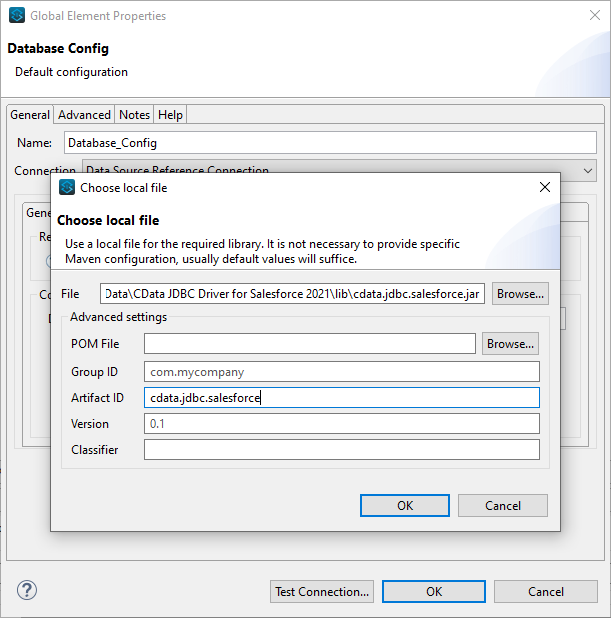
- Select the CData JDBC Driver JAR file in the Required Libraries section (e.g. cdata.jdbc.oracleoci.jar).
![Adding the JAR file (Salesforce is shown).]()
- Set the URL to the connection string for Oracle
To connect to Oracle, you'll first need to update your PATH variable and ensure it contains a folder location that includes the native DLLs. The native DLLs can be found in the lib folder inside the installation directory. Once you've done this, set the following to connect:
- Port: The port used to connect to the server hosting the Oracle database.
- User: The user Id provided for authentication with the Oracle database.
- Password: The password provided for authentication with the Oracle database.
- Service Name: The service name of the Oracle database.
Built-in Connection String Designer
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the Oracle JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.oracleoci.jarFill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
- Set the Driver class name to cdata.jdbc.oracleoci.OracleOCIDriver.
![A configured Database Connection (Salesforce is shown).]()
- Click Test Connection.
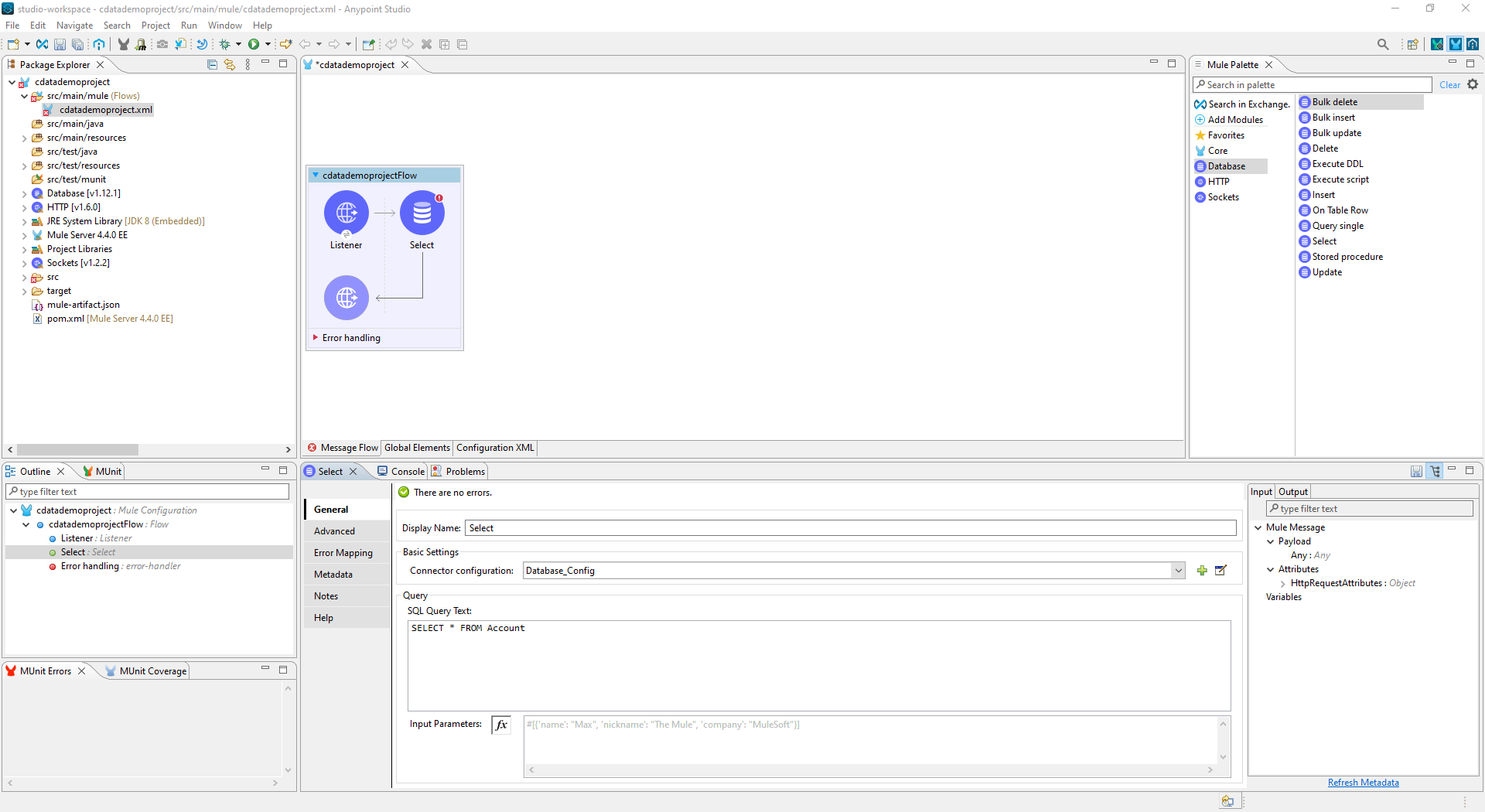
- Set the SQL Query Text to a SQL query to request Oracle data. For example:
SELECT CompanyName, City FROM Customers WHERE Country = US![Configure the Select object (Salesforce is Shown)]()
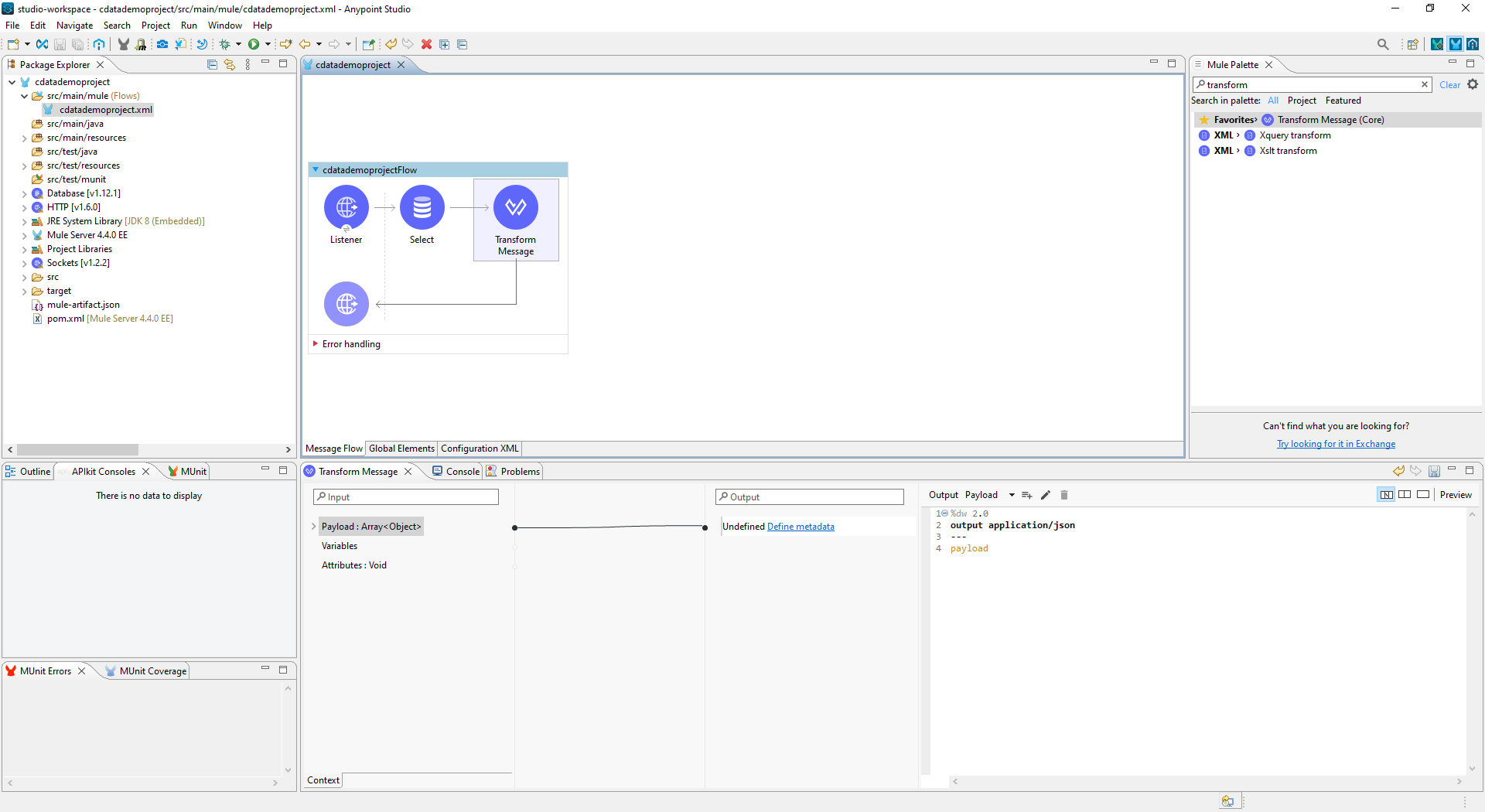
- Add a Transform Message Component to the flow.
- Set the Output script to the following to convert the payload to JSON:
%dw 2.0 output application/json --- payload![Add the Transform Message Component to the Flow]()
- To view your Oracle data, navigate to the address you configured for the HTTP Connector (localhost:8081 by default): http://localhost:8081. The Oracle data is available as JSON in your Web browser and any other tools capable of consuming JSON endpoints.
At this point, you have a simple Web interface for working with Oracle data (as JSON data) in custom apps and a wide variety of BI, reporting, and ETL tools. Download a free, 30 day trial of the JDBC Driver for Oracle and see the CData difference in your Mule Applications today.