Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Connect to JSON Services in HULFT Integrate
Connect to JSON as a JDBC data source in HULFT Integrate
HULFT Integrate is a modern data integration platform that provides a drag-and-drop user interface to create cooperation flows, data conversion, and processing so that complex data connections are easier than ever to execute. When paired with the CData JDBC Driver for JSON, HULFT Integrate can work with live JSON services. This article walks through connecting to JSON and moving the data into a CSV file.
With built-in optimized data processing, the CData JDBC Driver offers unmatched performance for interacting with live JSON services. When you issue complex SQL queries to JSON, the driver pushes supported SQL operations, like filters and aggregations, directly to JSON and utilizes the embedded SQL engine to process unsupported operations client-side (often SQL functions and JOIN operations). Its built-in dynamic metadata querying allows you to work with and analyze JSON services using native data types.
Enable Access to JSON
To enable access to JSON services from HULFT Integrate projects:
- Copy the CData JDBC Driver JAR file (and license file if it exists), cdata.jdbc.json.jar (and cdata.jdbc.json.lic), to the jdbc_adapter subfolder for the Integrate Server
- Restart the HULFT Integrate Server and launch HULFT Integrate Studio
Build a Project with Access to JSON Services
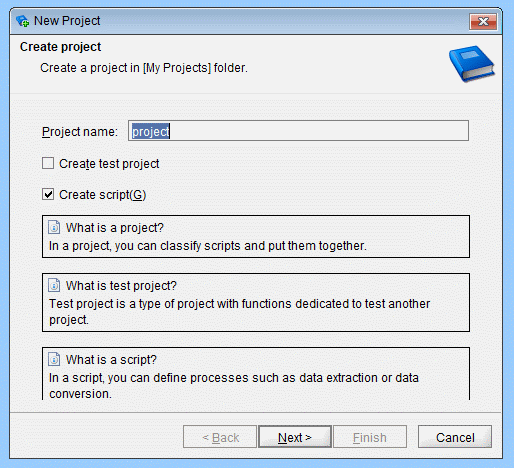
Once you copy the JAR files, you can create a project with access to JSON services. Start by opening Integrate Studio and creating a new project.
- Name the project
- Ensure the "Create script" checkbox is checked
- Click Next
![Creating a new project.]()
- Name the script (e.g.: JSONtoCSV)
Once you create the project, add components to the script to copy JSON services to a CSV file.
Configure an Execute Select SQL Component
Drag an "Execute Select SQL" component from the Tool Palette (Database -> JDBC) into the Script workspace.
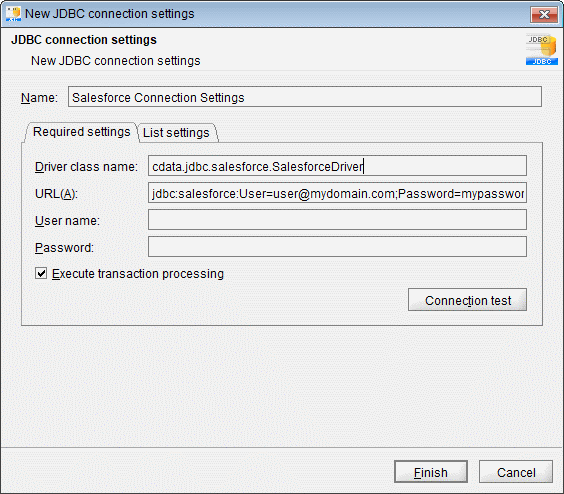
- In the "Required settings" tab for the Destination, click "Add" to create a new connection for JSON. Set the following properties:
- Name: JSON Connection Settings
- Driver class name: cdata.jdbc.json.JSONDriver
- URL: jdbc:json:URI=C:/people.json;DataModel=Relational;
![JDBC connection settings (Salesforce is shown).]()
Built-in Connection String Designer
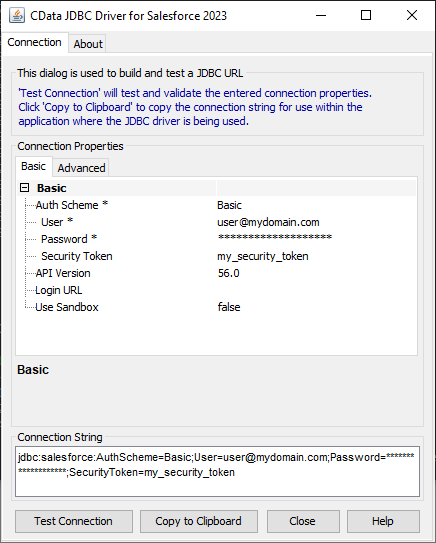
For assistance constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the JSON JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the JAR file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.json.jarFill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
See the Getting Started chapter in the data provider documentation to authenticate to your data source: The data provider models JSON APIs as bidirectional database tables and JSON files as read-only views (local files, files stored on popular cloud services, and FTP servers). The major authentication schemes are supported, including HTTP Basic, Digest, NTLM, OAuth, and FTP. See the Getting Started chapter in the data provider documentation for authentication guides.
After setting the URI and providing any authentication values, set DataModel to more closely match the data representation to the structure of your data.
The DataModel property is the controlling property over how your data is represented into tables and toggles the following basic configurations.
- Document (default): Model a top-level, document view of your JSON data. The data provider returns nested elements as aggregates of data.
- FlattenedDocuments: Implicitly join nested documents and their parents into a single table.
- Relational: Return individual, related tables from hierarchical data. The tables contain a primary key and a foreign key that links to the parent document.
See the Modeling JSON Data chapter for more information on configuring the relational representation. You will also find the sample data used in the following examples. The data includes entries for people, the cars they own, and various maintenance services performed on those cars.
![Using the built-in connection string designer to generate a JDBC URL (Salesforce is shown.)]()
- Write your SQL statement. For example:
SELECT [ personal.name.first ], [ personal.name.last ] FROM people
- Click "Extraction test" to ensure the connection and query are configured properly
- Click "Execute SQL statement and set output schema"
- Click "Finish"
![Configuring the Execute Select SQL operation]()
Configure a Write CSV File Component
Drag a "Write CSV File" component from the Tool Palette (File -> CSV) onto the workspace.
- Set a file to write the query results to (e.g. people.csv)
- Set "Input data" to the "Select SQL" component
- Add columns for each field selected in the SQL query
- In the "Write settings" tab, check the checkbox to "Insert column names into first row"
- Click "Finish"
Map JSON Fields to the CSV Columns
Map each column from the "Select" component to the corresponding column for the "CSV" component.
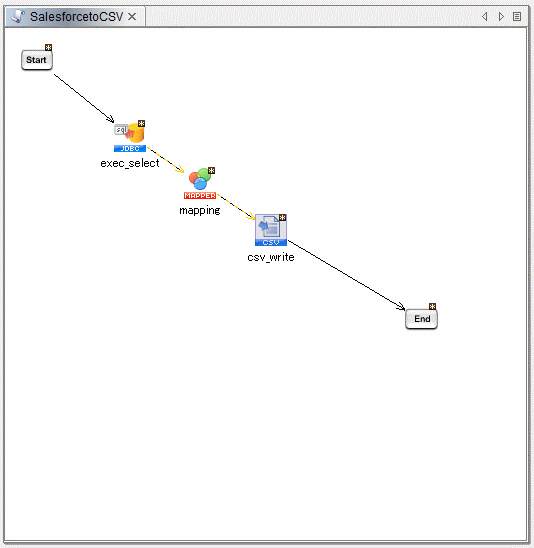
Finish the Script
Drag the "Start" component onto the "Select" component and the "CSV" component onto the "End" component. Build the script and run the script to move JSON services into a CSV file.
Download a free, 30-day trial of the CData JDBC Driver for JSON and start working with your live JSON services in HULFT Integrate. Reach out to our Support Team if you have any questions.