Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Integrate with Google Cloud Storage Data in JReport Designer
Create charts and reports based on Google Cloud Storage data in JReport Designer.
The CData JDBC Driver for Google Cloud Storage data enables access to live data from dashboards and reports as if Google Cloud Storage were a relational database, allowing you to query Google Cloud Storage data using familiar SQL queries. This article shows how to connect to Google Cloud Storage data as a JDBC data source and create reports based on Google Cloud Storage data in JReport Designer.
Connect to Google Cloud Storage Data
- Edit C:\JReport\Designer\bin\setenv.bat to add the location of the JAR file to the ADDCLASSPATH variable:
... set ADDCLASSPATH=%JAVAHOME%\lib\tools.jar;C:\Program Files\CData\CData JDBC Driver for Google Cloud Storage 2016\lib\cdata.jdbc.googlecloudstorage.jar; ...
- Create a new data source by clicking File New Data Source.
- In the resulting dialog, create a name for the data source (CData JDBC Driver for Google Cloud Storage), select JDBC, and click OK.
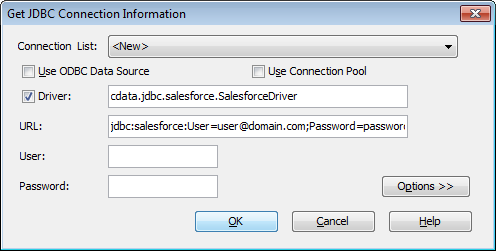
- In the Get JDBC Connection Information dialog you will configure your connection to the JDBC driver:
- Driver: Be sure that the Driver box is checked and fill in the name of the class for the driver:
cdata.jdbc.googlecloudstorage.GoogleCloudStorageDriver - URL: Enter the JDBC URL. This starts with jdbc:googlecloudstorage: and is followed by a semicolon-separated list of connection properties.
Authenticate with a User Account
You can connect without setting any connection properties for your user credentials. After setting InitiateOAuth to GETANDREFRESH, you are ready to connect.
When you connect, the Google Cloud Storage OAuth endpoint opens in your default browser. Log in and grant permissions, then the OAuth process completes
Authenticate with a Service Account
Service accounts have silent authentication, without user authentication in the browser. You can also use a service account to delegate enterprise-wide access scopes.
You need to create an OAuth application in this flow. See the Help documentation for more information. After setting the following connection properties, you are ready to connect:
- InitiateOAuth: Set this to GETANDREFRESH.
- OAuthJWTCertType: Set this to "PFXFILE".
- OAuthJWTCert: Set this to the path to the .p12 file you generated.
- OAuthJWTCertPassword: Set this to the password of the .p12 file.
- OAuthJWTCertSubject: Set this to "*" to pick the first certificate in the certificate store.
- OAuthJWTIssuer: In the service accounts section, click Manage Service Accounts and set this field to the email address displayed in the service account Id field.
- OAuthJWTSubject: Set this to your enterprise Id if your subject type is set to "enterprise" or your app user Id if your subject type is set to "user".
- ProjectId: Set this to the Id of the project you want to connect to.
The OAuth flow for a service account then completes.
Built-in Connection String Designer
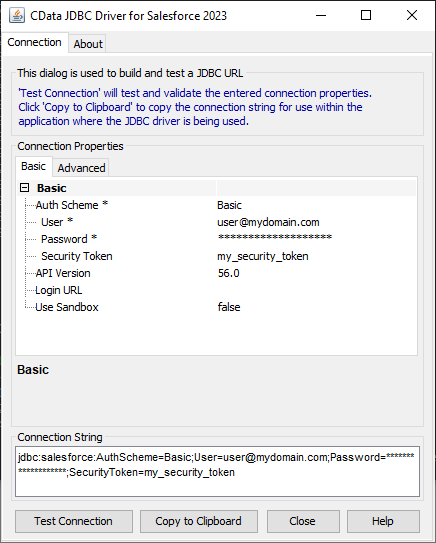
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the Google Cloud Storage JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.googlecloudstorage.jarFill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
![Using the built-in connection string designer to generate a JDBC URL (Salesforce is shown.)]()
When you configure the JDBC URL, you may also want to set the Max Rows connection property. This will limit the number of rows returned, which is especially helpful for improving performance when designing reports and visualizations.
Below is a typical JDBC URL:
jdbc:googlecloudstorage:ProjectId='project1';InitiateOAuth=GETANDREFRESH - User: The username to authenticate with; typically left blank.
- Password: The password to authenticate with; typically left blank.
![Configuring the connection to the JDBC Driver (Salesforce is shown.)]()
- Driver: Be sure that the Driver box is checked and fill in the name of the class for the driver:
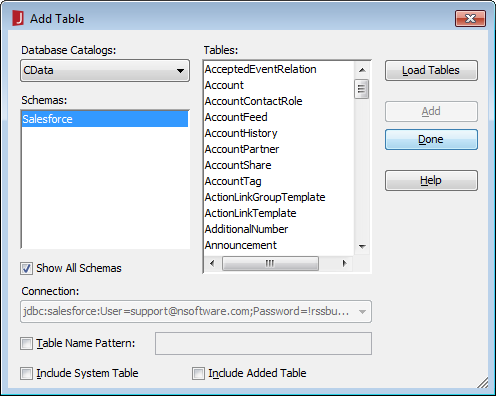
In the Add Table dialog, select the tables you wish to include in your report (or in future reports using this data source) and click Add.
![Adding Tables. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
Click Done once the dialog has completed loading the tables.
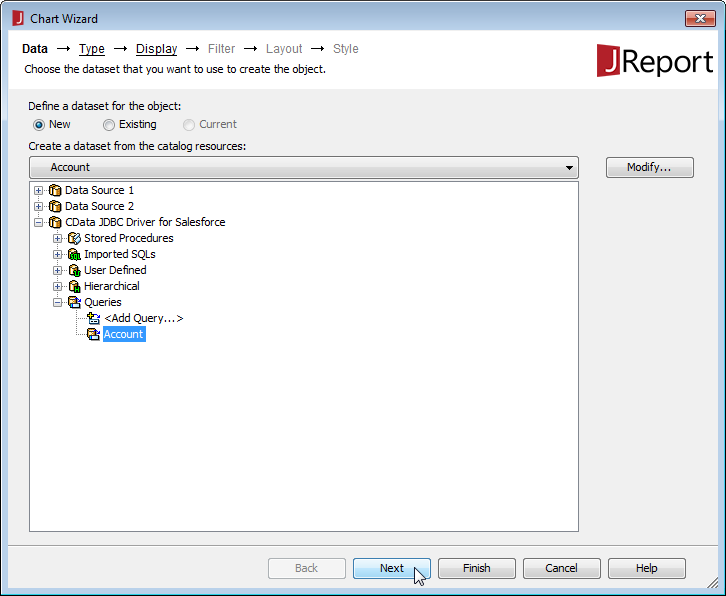
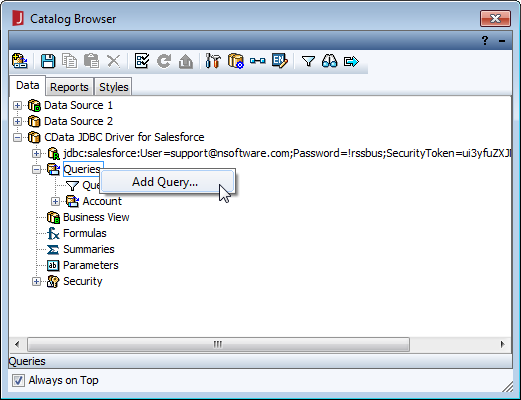
- In the Catalog Browser, you can create the queries that you will use to populate your reports. You can do this now, or after you create your report. In either case, expand () the data source (CData JDBC Driver for Google Cloud Storage), right-click on Queries, and select Add Query.
![Adding a query for data to be used in the report. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
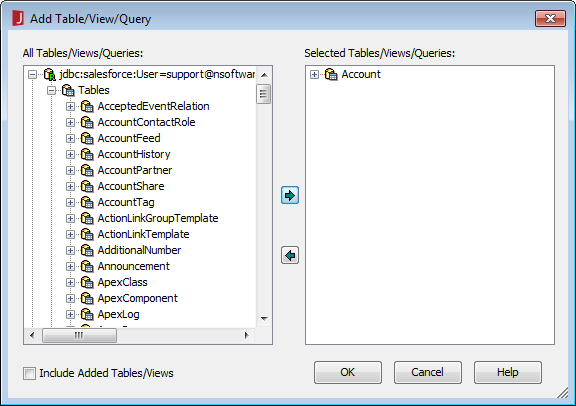
- In the Add Table/View/Query dialog, expand () the JDBC URL and Tables and select the table(s) you wish to use in the query and click OK.
![Selecting a table for the query. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
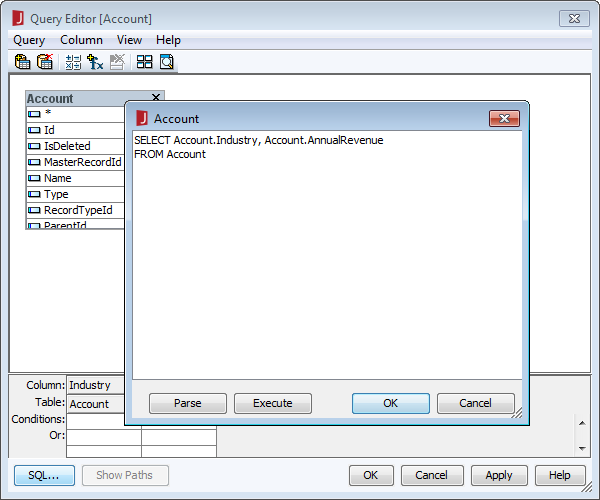
- In the Query Editor dialog, you can select the columns you wish to include or simply click the SQL button and manually input your own query. For example:
SELECT Name, OwnerId FROM Buckets WHERE Name = 'TestBucket'
![Editing the query. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
With the query built, click OK to close the Query Editor dialog. At this point you are ready to add Google Cloud Storage data to a new or existing report.
NOTE: Now that the query is built, you can create a Business View based on the query. With a Business View, you can create Web reports or library components based on the query. For more information on this, refer to the JReport tutorials.
Add Google Cloud Storage Data to a Report
You are now ready to create a report with Google Cloud Storage data.
- Create a new report (File New Page Report) or open the Chart Wizard for an existing report.
- Select the Query (or create a new one; see above).
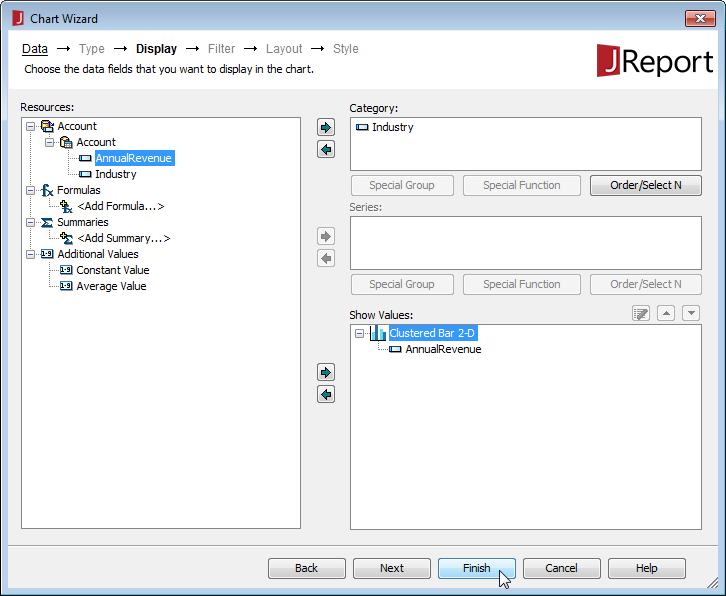
- Assign a Category and Value for the chart from the columns in your Query and click Finish.
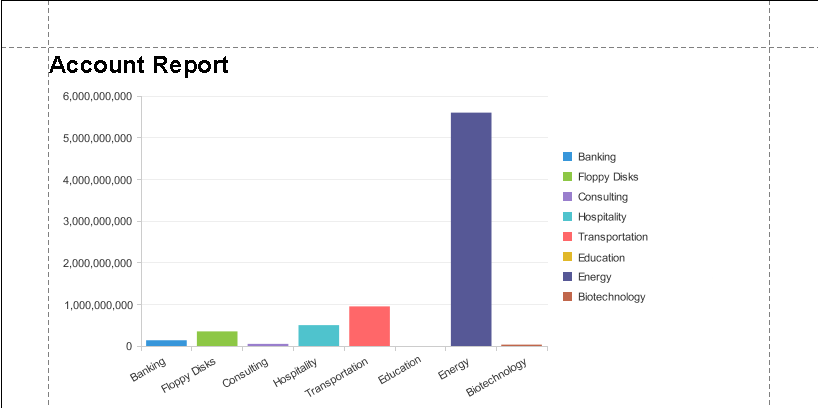
- Click the View tab for your report to see the chart.