Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Configure the CData JDBC Driver for Confluence in a Connection Pool in Tomcat
Connect to Confluence data from a connection pool in Tomcat.
The CData JDBC Drivers support standard JDBC interfaces to integrate with Web applications running on the JVM. This article details how to connect to Confluence data from a connection pool in Tomcat.
Connect to Confluence Data through a Connection Pool in Tomcat
- Copy the CData JAR and CData .lic file to $CATALINA_HOME/lib. The CData JAR is located in the lib subfolder of the installation directory.
- Add a definition of the resource to the context. Specify the JDBC URL here.
Obtaining an API Token
An API token is necessary for account authentication. To generate one, login to your Atlassian account and navigate to API tokens > Create API token. The generated token will be displayed.
Connect Using a Confluence Cloud Account
To connect to a Cloud account, provide the following (Note: Password has been deprecated for connecting to a Cloud Account and is now used only to connect to a Server Instance.):
- User: The user which will be used to authenticate with the Confluence server.
- APIToken: The API Token associated with the currently authenticated user.
- Url: The URL associated with your JIRA endpoint. For example, https://yoursitename.atlassian.net.
Connect Using a Confluence Server Instance
To connect to a Server instance, provide the following:
- User: The user which will be used to authenticate with the Confluence instance.
- Password: The password which will be used to authenticate with the Confluence server.
- Url: The URL associated with your JIRA endpoint. For example, https://yoursitename.atlassian.net.
Built-in Connection String Designer
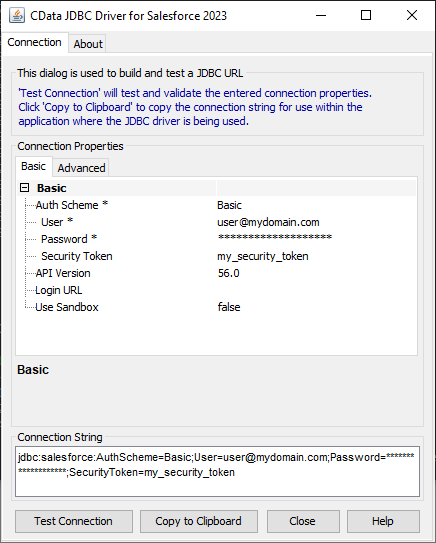
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the Confluence JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.confluence.jarFill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
![Using the built-in connection string designer to generate a JDBC URL (Salesforce is shown.)]()
You can see the JDBC URL specified in the resource definition below.
<Resource name="jdbc/confluence" auth="Container" type="javax.sql.DataSource" driverClassName="cdata.jdbc.confluence.ConfluenceDriver" factory="org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSourceFactory" url="jdbc:confluence:User=admin;APIToken=myApiToken;Url=https://yoursitename.atlassian.net;Timezone=America/New_York;" maxActive="20" maxIdle="10" maxWait="-1" />To allow a single application to access Confluence data, add the code above to the context.xml in the application's META-INF directory.
For a shared resource configuration, add the code above to the context.xml located in $CATALINA_BASE/conf. A shared resource configuration provides connectivity to Confluence for all applications.
- Add a reference to the resource to the web.xml for the application.
Confluence data JSP jdbc/Confluence javax.sql.DataSource Container -
Initialize connections from the connection pool:
Context initContext = new InitialContext(); Context envContext = (Context)initContext.lookup("java:/comp/env"); DataSource ds = (DataSource)envContext.lookup("jdbc/Confluence"); Connection conn = ds.getConnection();
More Tomcat Integration
The steps above show how to connect to Confluence data in a simple connection pooling scenario. For more use cases and information, see the JNDI Datasource How-To in the Tomcat documentation.