Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Build Azure Data Lake Storage-Connected Dashboards in Redash
Use CData Connect Server to create a virtual SQL Server Database for Azure Data Lake Storage data and build visualizations and dashbaords from Azure Data Lake Storage data in Redash.
Redash lets you connect and query your data sources, build dashboards to visualize data and share them with your company. When paired with CData Connect Server, you get instant, cloud-to-cloud access to Azure Data Lake Storage data for visualizations, dashboards, and more. This article shows how to create a virtual database for Azure Data Lake Storage and build visualizations from Azure Data Lake Storage data in Redash.
CData Connect Server provides a pure SQL Server interface for Azure Data Lake Storage, allowing you to easily build reports from live Azure Data Lake Storage data in Redash — without replicating the data to a natively supported database. As you build visualizations, Redash generates SQL queries to gather data. Using optimized data processing out of the box, CData Connect Server pushes all supported SQL operations (filters, JOINs, etc) directly to Azure Data Lake Storage, leveraging server-side processing to quickly return the requested Azure Data Lake Storage data.
Create a Virtual SQL Server Database for Azure Data Lake Storage Data
CData Connect Server uses a straightforward, point-and-click interface to connect to data sources and generate APIs.
-
Login to Connect Server and click Connections.
![Adding a connection]()
- Select "Azure Data Lake Storage" from Available Data Sources.
-
Enter the necessary authentication properties to connect to Azure Data Lake Storage.
Authenticating to a Gen 1 DataLakeStore Account
Gen 1 uses OAuth 2.0 in Azure AD for authentication.
For this, an Active Directory web application is required. You can create one as follows:
To authenticate against a Gen 1 DataLakeStore account, the following properties are required:
- Schema: Set this to ADLSGen1.
- Account: Set this to the name of the account.
- OAuthClientId: Set this to the application Id of the app you created.
- OAuthClientSecret: Set this to the key generated for the app you created.
- TenantId: Set this to the tenant Id. See the property for more information on how to acquire this.
- Directory: Set this to the path which will be used to store the replicated file. If not specified, the root directory will be used.
Authenticating to a Gen 2 DataLakeStore Account
To authenticate against a Gen 2 DataLakeStore account, the following properties are required:
- Schema: Set this to ADLSGen2.
- Account: Set this to the name of the account.
- FileSystem: Set this to the file system which will be used for this account.
- AccessKey: Set this to the access key which will be used to authenticate the calls to the API. See the property for more information on how to acquire this.
- Directory: Set this to the path which will be used to store the replicated file. If not specified, the root directory will be used.
![Configuring a connection (SQL Server is shown).]()
- Click Save Changes
- Click Privileges -> Add and add the new user (or an existing user) with the appropriate permissions.
With the virtual database created, you are ready to connect to Azure Data Lake Storage data from Redash.
Visualize Azure Data Lake Storage Data in Redash
The steps below outline creating a new data source in Redash based on the virtual Azure Data Lake Storage database in Connect Server and building a simple visualization from the data.
Create a New Data Source
- Log into Redash, click on your profile and click "Data Sources"
- Click the " New Data Source" button
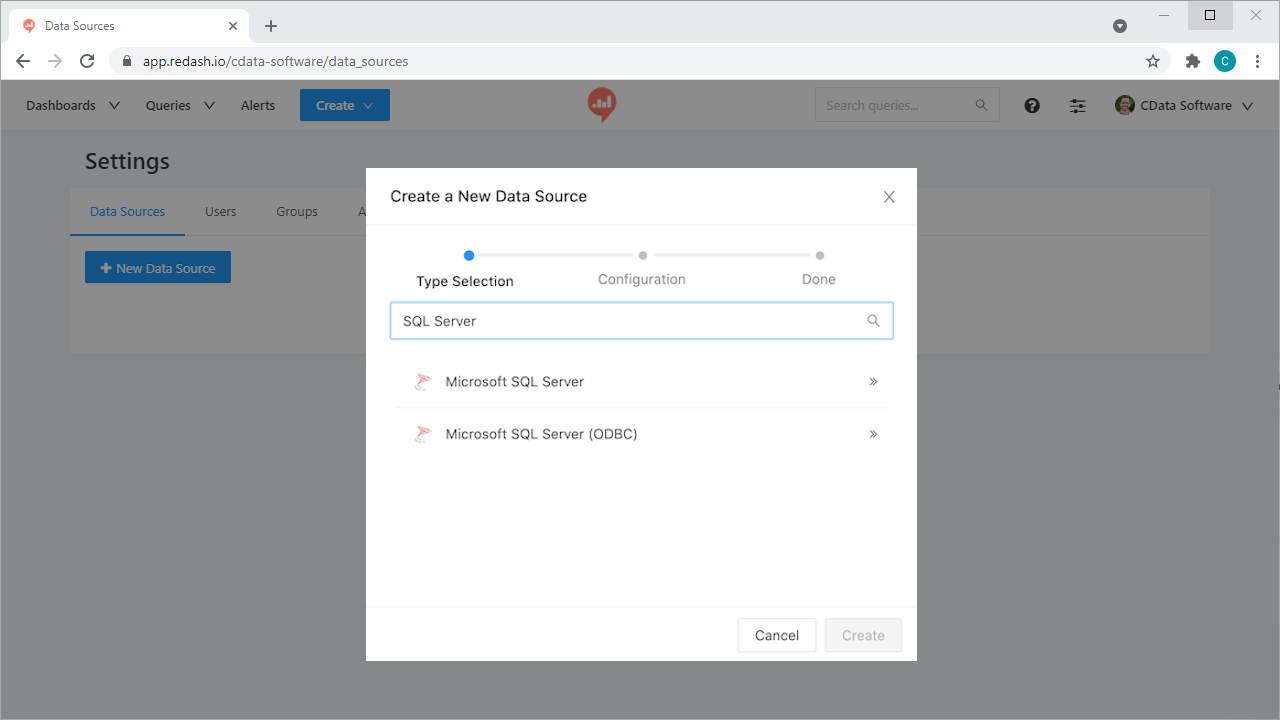
- Select "Microsoft SQL Server" as the Data Source Type
![Creating a new Data Source.]()
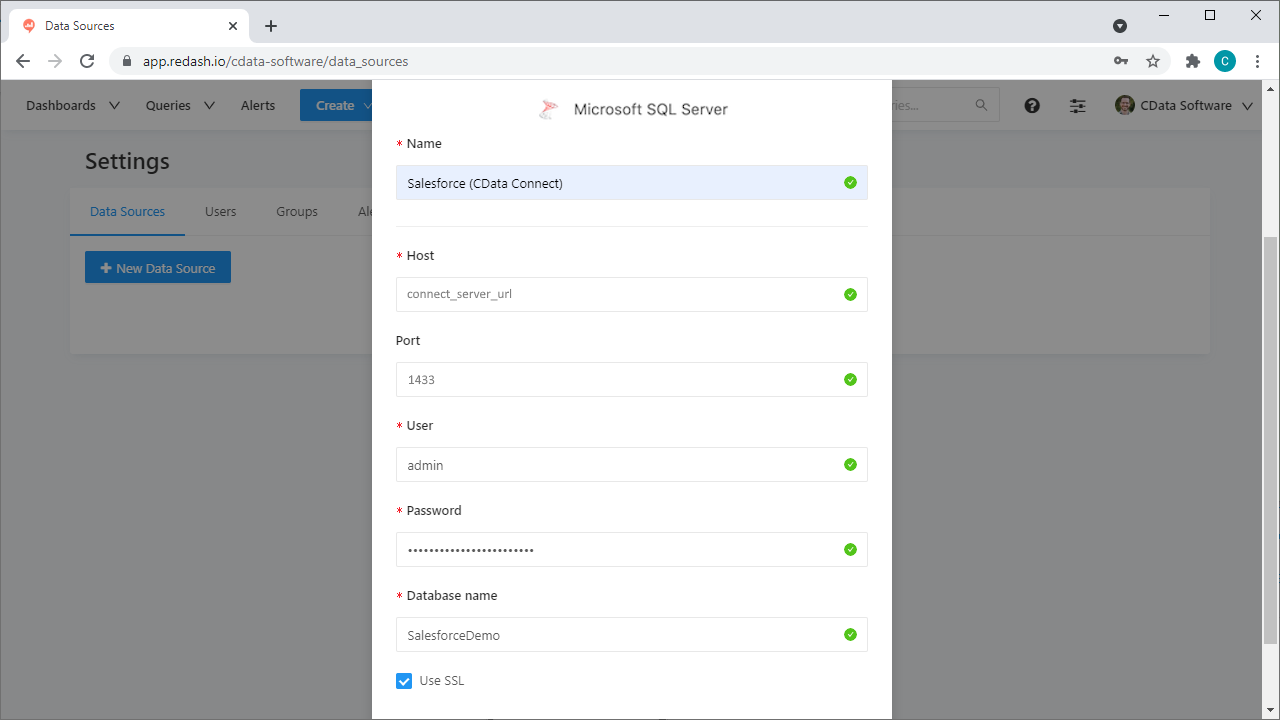
- On the configuration tab, set the following properties:
- Name: Name the data source (e.g. Azure Data Lake Storage (CData Connect))
- Host: The full URL to your CData Connect instance (e.g. https://connect_server_url)
- Port: The port of the CData Connect SQL Server endpoint (e.g. 1433)
- User: A CData Connect user
- Password: The password for the above user
- Database name: The name of the virtual database for Azure Data Lake Storage (e.g. ADLS1)
- Click the checkbox to Use SSQL
![Configuring the new Data Source.]()
- Click Create
- Click the "Test Connection" button to ensure you have configured the connection properly
With the new Data Source created, we are ready to visualize our Azure Data Lake Storage data.
Create a Azure Data Lake Storage Data Visualization
- Click Create -> New Query
- Select the newly created Data Source (you can explore the data structure in the New Query wizard)
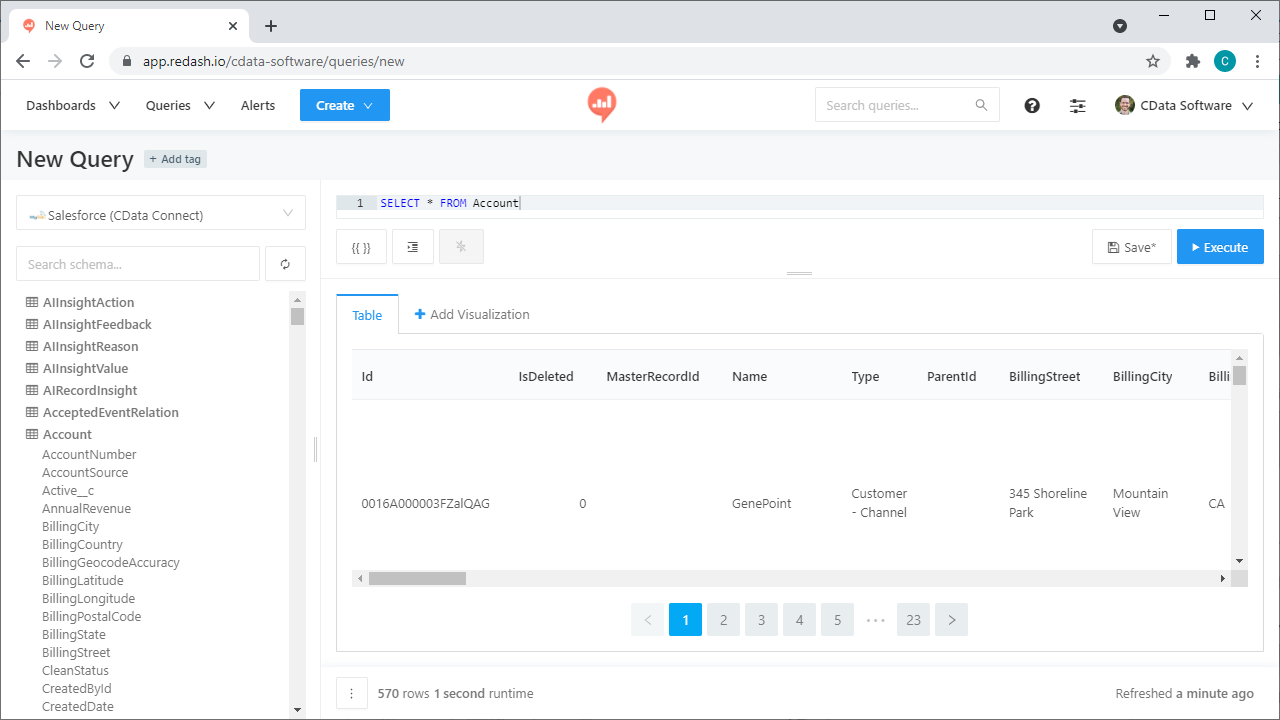
- Write a SQL statement to retrieve the data, for example:
SELECT FullPath, Permission FROM Resources WHERE Type = 'FILE' - Click the "Execute" button to load Azure Data Lake Storage data into Redash via CData Connect
![Loading Azure Data Lake Storage data into Redash]()
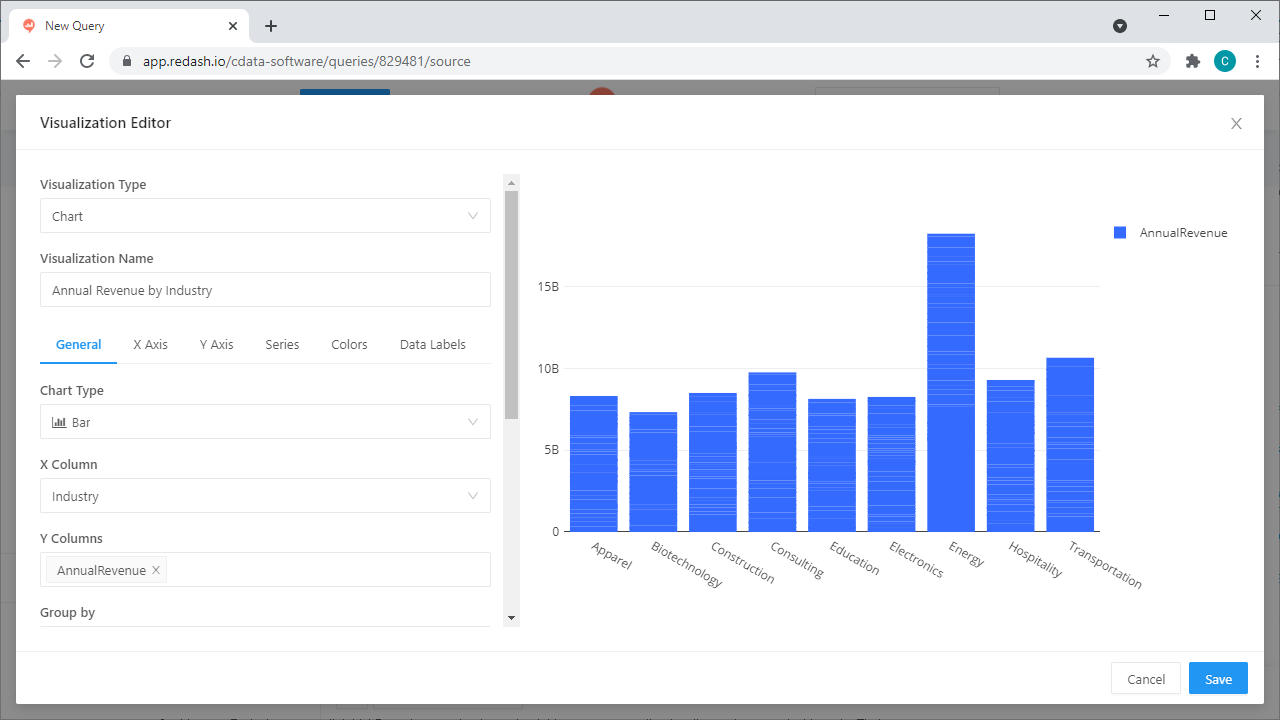
- Use the Visualization Editor to create and analyze graphs from Azure Data Lake Storage data
![Choosing a Database and Tables]()
- You can schedule the query to refresh and update the visualization periodically
SQL Access to Azure Data Lake Storage Data from Cloud Applications
At this point, you have a direct, cloud-to-cloud connection to Azure Data Lake Storage data from Redash. You can create new visualizations, build dashboards, and more. For more information on gaining SQL access to data from more than 100 SaaS, Big Data, and NoSQL sources from cloud applications like Redash, refer to our Connect Server page.