Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Connect to AlloyDB Data in RazorSQL
Connect to AlloyDB from wizards and query AlloyDB data from the GUI in the RazorSQL database management tool.
The CData JDBC Driver for AlloyDB enables standards-based access from third-party tools, from wizards in IDEs to data management and analysis tools. This article shows how to connect to AlloyDB using wizards in RazorSQL.
Create a JDBC Data Source for AlloyDB Data
- Open the RazorSQL application and, in the Connections menu, select Add Connection Profile -> Other -> JDBC.
- In the Connection Wizard that appears, set the following properties:
- Driver Location: Set this property to the path to the lib subfolder in the installation directory.
- Driver Class: Set the driver class to cdata.jdbc.alloydb.AlloyDBDriver.
- Username: Enter the username. (This property can also be set in the JDBC URL.)
- Password: Enter the password. (This property can also be set in the JDBC URL.)
JDBC URL: Enter connection parameters. The JDBC URL begins with jdbc:alloydb: and is followed by a semicolon-separated list of connection properties.
The following connection properties are usually required in order to connect to AlloyDB.
- Server: The host name or IP of the server hosting the AlloyDB database.
- User: The user which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
- Password: The password which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
You can also optionally set the following:
- Database: The database to connect to when connecting to the AlloyDB Server. If this is not set, the user's default database will be used.
- Port: The port of the server hosting the AlloyDB database. This property is set to 5432 by default.
Authenticating with Standard Authentication
Standard authentication (using the user/password combination supplied earlier) is the default form of authentication.
No further action is required to leverage Standard Authentication to connect.
Authenticating with pg_hba.conf Auth Schemes
There are additional methods of authentication available which must be enabled in the pg_hba.conf file on the AlloyDB server.
Find instructions about authentication setup on the AlloyDB Server here.
Authenticating with MD5 Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to md5.
Authenticating with SASL Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to scram-sha-256.
Authenticating with Kerberos
The authentication with Kerberos is initiated by AlloyDB Server when the ∏ is trying to connect to it. You should set up Kerberos on the AlloyDB Server to activate this authentication method. Once you have Kerberos authentication set up on the AlloyDB Server, see the Kerberos section of the help documentation for details on how to authenticate with Kerberos.
Built-in Connection String Designer
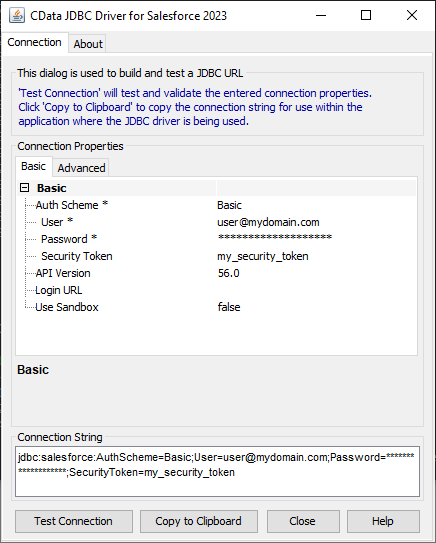
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the AlloyDB JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.alloydb.jarFill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
![Using the built-in connection string designer to generate a JDBC URL (Salesforce is shown.)]()
A typical JDBC URL is the following:
jdbc:alloydb:User=alloydb;Password=admin;Database=alloydb;Server=127.0.0.1;Port=5432
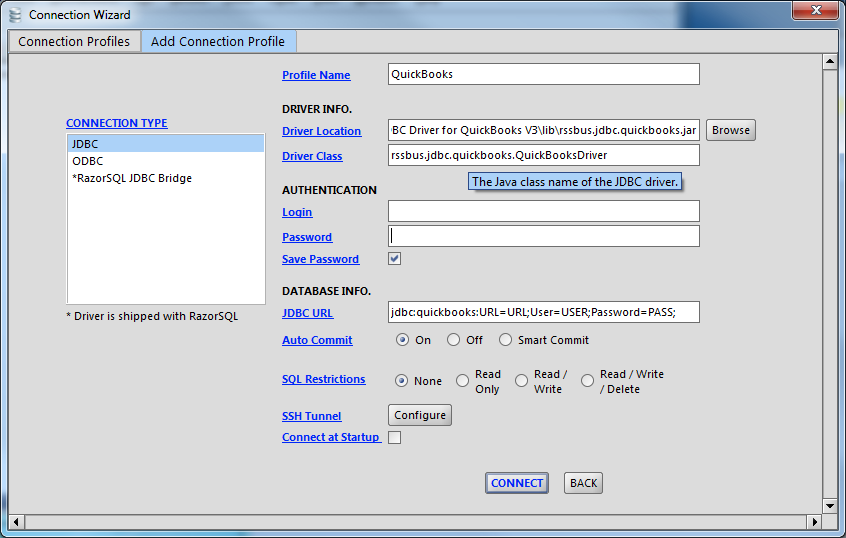
Query AlloyDB Data and Select Tables
After establishing a connection, the wizard will close and the connection will be available in the connections panel. You can then query the tables.