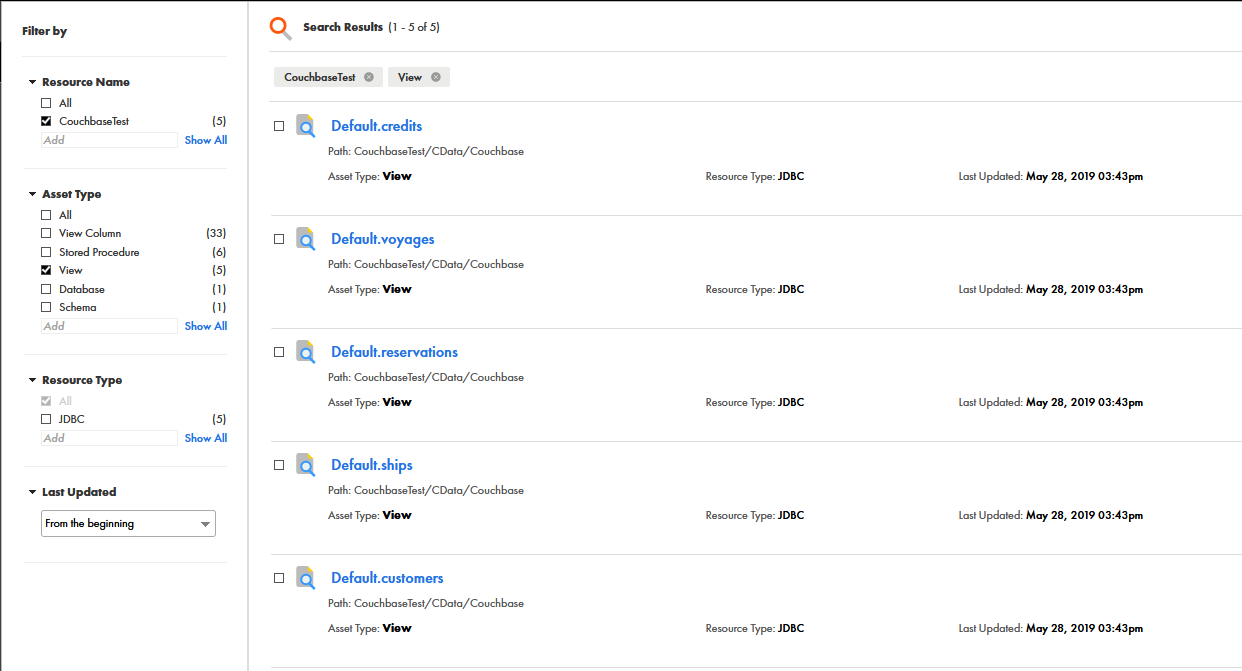
Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Add AlloyDB Data to Informatica Enterprise Data Catalog
Use the CData JDBC Driver for AlloyDB with the Informatica Enterprise Data Catalog to classify and organize data.
Informatica provides a powerful, elegant means of transporting and transforming your data. By utilizing the CData JDBC Driver for AlloyDB, you are gaining access to a driver based on industry-proven standards that integrates seamlessly with Informatica's Enterprise Data Catalog. This tutorial shows how to classify and organize AlloyDB data across any environment.
Load the JDBC Driver
To load the JDBC Driver:
- Install the JDBC Driver on the host running Informatica. For this article, it is assumed that the driver was installed into cdata.jdbc.alloydb.AlloyDBDriver.
- Navigate to the JDBC install directory and create a zip file called genericJDBC.zip containing the driver and its license file.
- Move the genericJDBC.zip file into the Catalog Service directory within Informatica. For this article, it is assumed that Informatica is installed into /opt/informatica. Working in this folder will probably require root permissions, so make sure to su or sudo to root before continuing.
- Edit the custom deployment configuration to unpack the zip file.
- Refresh the Catalog Service from the Admin console.
$ java -jar setup.jar
$ cd ~/cdata-jdbc-driver-for-alloydb/lib
$ zip genericJDBC.zip cdata.jdbc.alloydb.jar cdata.jdbc.alloydb.lic
# mv genericJDBC.zip /opt/informatica/services/CatalogService/ScannerBinaries
# cd /opt/informatica/services/CatalogService/ScannerBinaries/CustomDeployer/
# nano scannerDeployer.xml
After unpacking the existing ExecutionContextProperty nodes, add a new ExecutionContextProperty node with this content.
<ExecutionContextProperty
isLocationProperty="true"
dependencyToUnpack="genericJDBC.zip">
<PropertyName>JDBCScanner_DriverLocation</PropertyName>
<PropertyValue>scanner_miti/genericJDBC/Drivers</PropertyValue>
</ExecutionContextProperty>
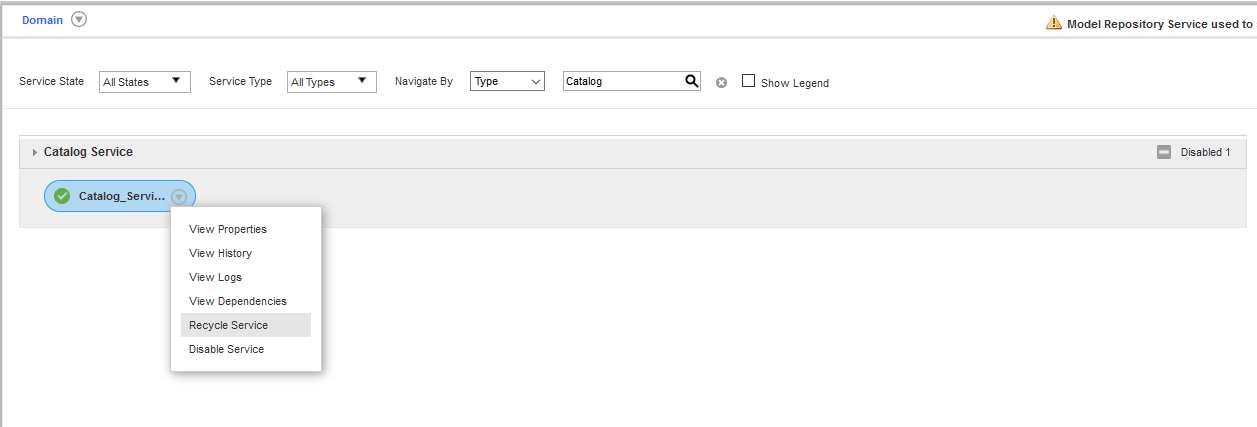
Configure the JDBC Resource
To configure the JDBC resource:
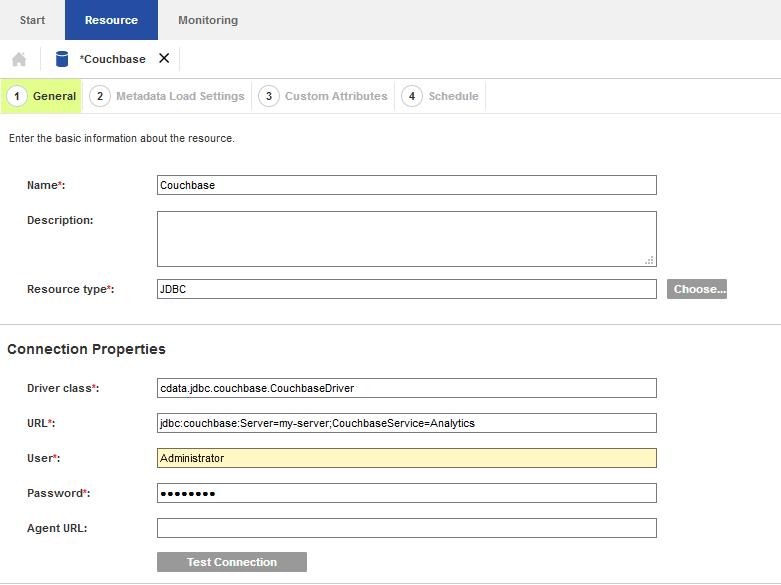
- Open the Catalog administrator and add a new JDBC resource with the following properties:
- Driver Class: cdata.jdbc.alloydb.AlloyDBDriver
- URL: jdbc.alloydb:User=alloydb;Password=admin;Database=alloydb;Server=127.0.0.1;Port=5432
- Server: The host name or IP of the server hosting the AlloyDB database.
- User: The user which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
- Password: The password which will be used to authenticate with the AlloyDB server.
- Database: The database to connect to when connecting to the AlloyDB Server. If this is not set, the user's default database will be used.
- Port: The port of the server hosting the AlloyDB database. This property is set to 5432 by default.
- Username: user
- Password: password
- Configure the metadata options to perform at least one source metadata scan. This scan uses the driver to determine what tables, views, and stored procedures are available through the service.
- Source Metadata: Enable this option.
- Catalog: Set this to the appropriate catalog for multi-catalog data sources. Otherwise, set this to CData.
- Schema: Set this to the appropriate schema for multi-schema data sources. Otherwise, set this to the name of the service (for example, Couchbase).
- Case-sensitivity: Generally this option should be disabled. Enable it only for data sources which are case-sensitive.
- Import stored procedures: Enable this if you want to import stored procedure definitions in addition to tables and views.
- Complete the driver configuration, optionally configuring custom attributes and a scanner schedule.
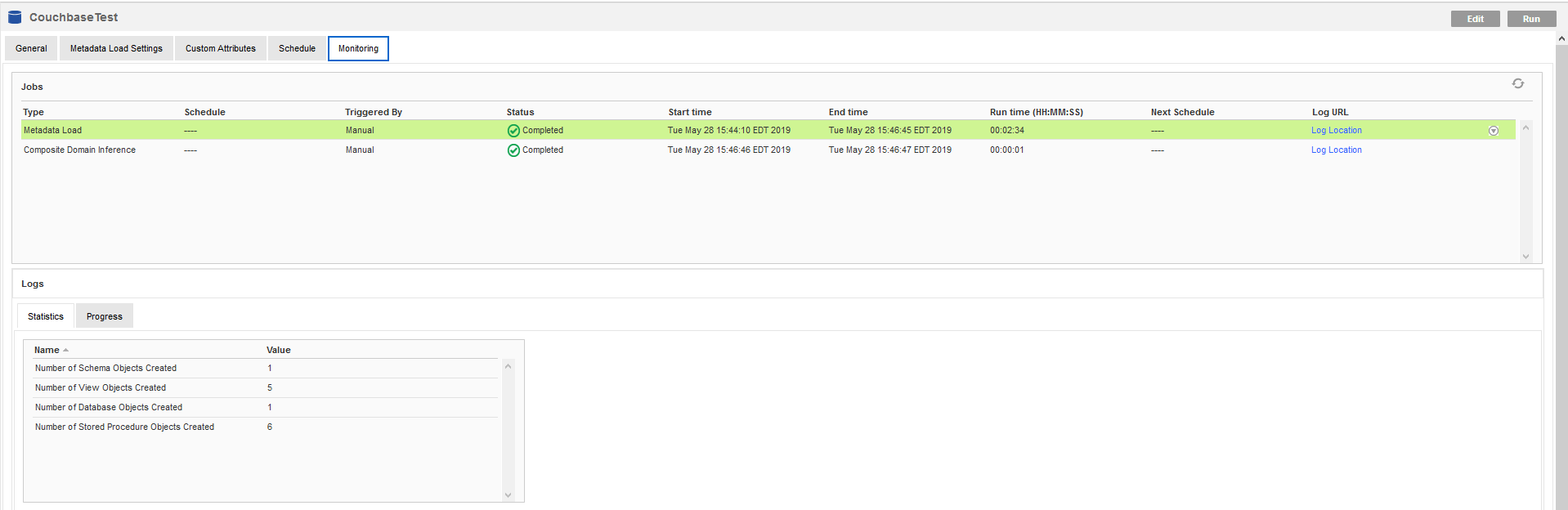
- Perform the metadata scan by navigating to the Monitoring tab and clicking Run. Depending upon the data source, this may takes a few minutes.
The following connection properties are usually required in order to connect to AlloyDB.
You can also optionally set the following:
Authenticating with Standard Authentication
Standard authentication (using the user/password combination supplied earlier) is the default form of authentication.
No further action is required to leverage Standard Authentication to connect.
Authenticating with pg_hba.conf Auth Schemes
There are additional methods of authentication available which must be enabled in the pg_hba.conf file on the AlloyDB server.
Find instructions about authentication setup on the AlloyDB Server here.
Authenticating with MD5 Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to md5.
Authenticating with SASL Authentication
This authentication method must be enabled by setting the auth-method in the pg_hba.conf file to scram-sha-256.
Authenticating with Kerberos
The authentication with Kerberos is initiated by AlloyDB Server when the ∏ is trying to connect to it. You should set up Kerberos on the AlloyDB Server to activate this authentication method. Once you have Kerberos authentication set up on the AlloyDB Server, see the Kerberos section of the help documentation for details on how to authenticate with Kerberos.
Built-In Connection String Designer
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the AlloyDB JDBC Driver. Either double-click the .jar file or execute the .jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.alloydb.jar
Fill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
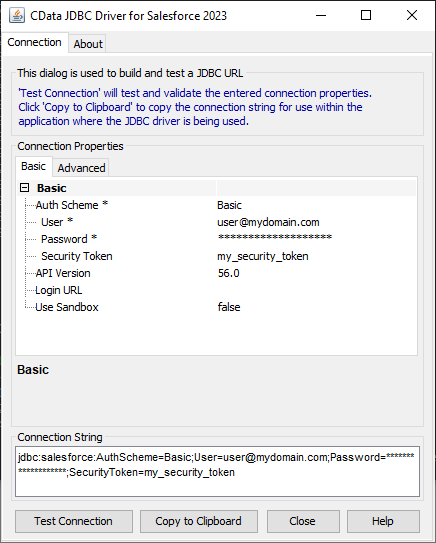
When you configure the JDBC URL, you may also want to set the Max Rows connection property. This will limit the number of rows returned, which is especially helpful for improving performance when designing reports and visualizations.
Typical additional connection string properties follow:
JDBC;MSTR_JDBC_JAR_FOLDER=PATH\TO\JAR\;DRIVER=cdata.jdbc.alloydb.AlloyDBDriver;URL={jdbc:alloydb:User=alloydb;Password=admin;Database=alloydb;Server=127.0.0.1;Port=5432};
Note that the Username and Password properties are required, even if the driver you are using does not require them. In those cases, you can enter a placeholder value instead.
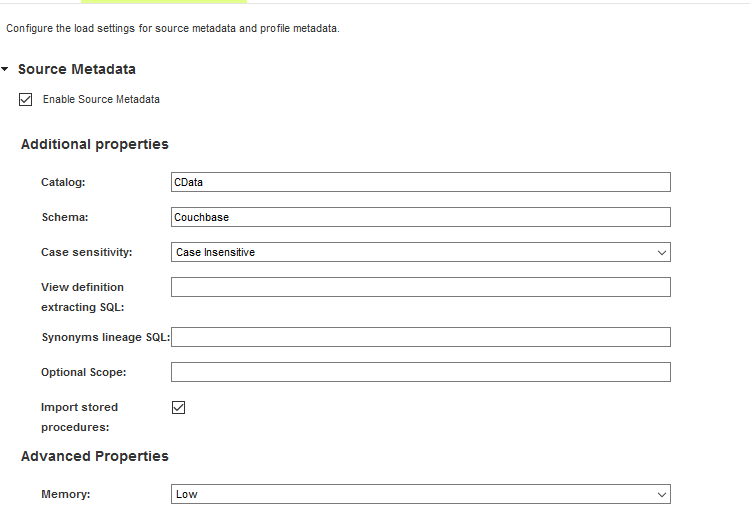
Other metadata scanners may be enabled as desired.
When the scan is complete, a summary of all of the metadata objects is displayed along with the status of the Metadata Load job. If any errors occur, you can open the Log Location link for the job to see the errors reported by Informatica or the driver.
Validate the Discovered Metadata
Open the Catalog Service browser to view the metadata extracted from the data source. Depending upon the options you selected when configuring the metadata scanner, you may see any combination of tables, views, and stored procedures for the resource you defined.