Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Build Visualizations of SQL Server Data in Birst
Use CData drivers and the Birst Cloud Agent to build real-time visualizations of SQL Server data in Birst.
Birst is a cloud business intelligence (BI) tool and analytics platform that helps organizations quickly understand and optimize complex processes. When paired with the CData JDBC Driver for SQL Server, you can connect to live SQL Server data through the Birst Cloud Agent and build real-time visualizations. In this article, we walk you through, step-by-step, how to connect to SQL Server using the Cloud Agent and create dynamic reports in Birst.
With powerful data processing capabilities, the CData JDBC Driver offers unmatched performance for live SQL Server data operations in Birst. When you issue complex SQL queries from Birst to SQL Server, the driver pushes supported SQL operations, like filters and aggregations, directly to SQL Server and utilizes the embedded SQL Engine to process unsupported operations client-side (often SQL functions and JOIN operations). With built-in dynamic metadata querying, the JDBC driver enables you to visualize and analyze SQL Server data using native Birst data types.
Configure a JDBC Connection to SQL Server Data in Birst
Before creating the Birst project, you will need to install the Birst Cloud Agent (in order to work with the installed JDBC Driver). Also, copy the JAR file for the JDBC Driver (and the LIC file, if it exists) to the /drivers/ directory in the installation location for the Cloud Agent.
With the driver and Cloud Agent installed, you are ready to begin.
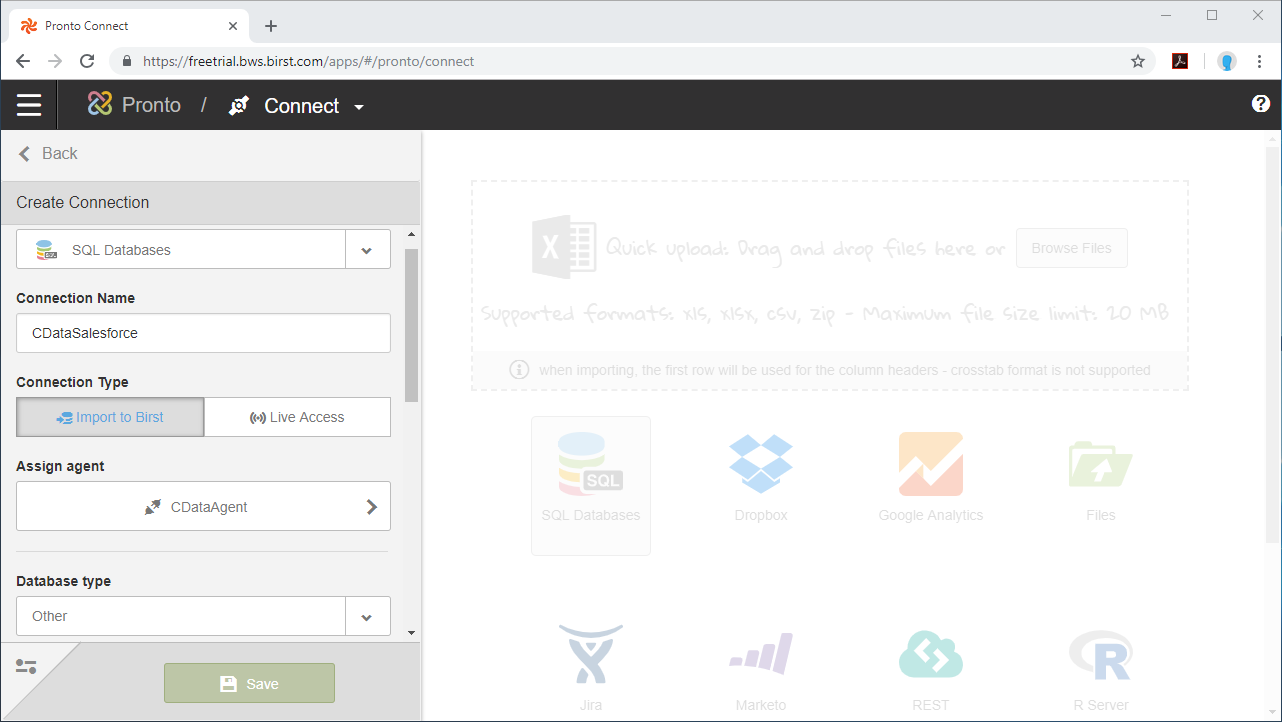
- Create a new project in Birst.
![Create a new Project in Birst]()
- Name the connection (e.g. CDataSQL).
- Choose Live Access.
- Select an agent.
- Set Database Type to Other.
- Set SQL Type to MSSQL
- Set the Connection string.
Connecting to Microsoft SQL Server
Connect to Microsoft SQL Server using the following properties:
- Server: The name of the server running SQL Server.
- User: The username provided for authentication with SQL Server.
- Password: The password associated with the authenticating user.
- Database: The name of the SQL Server database.
Connecting to Azure SQL Server and Azure Data Warehouse
You can authenticate to Azure SQL Server or Azure Data Warehouse by setting the following connection properties:
- Server: The server running Azure. You can find this by logging into the Azure portal and navigating to "SQL databases" (or "SQL data warehouses") -> "Select your database" -> "Overview" -> "Server name."
- User: The name of the user authenticating to Azure.
- Password: The password associated with the authenticating user.
- Database: The name of the database, as seen in the Azure portal on the SQL databases (or SQL warehouses) page.
Built-in Connection String Designer
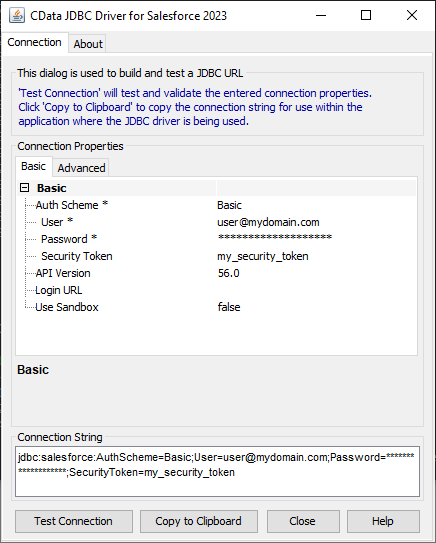
For assistance in constructing the JDBC URL, use the connection string designer built into the SQL Server JDBC Driver. Either double-click the JAR file or execute the jar file from the command-line.
java -jar cdata.jdbc.sql.jarFill in the connection properties and copy the connection string to the clipboard.
![Using the built-in connection string designer to generate a JDBC URL (Salesforce is shown.)]()
When you configure the JDBC URL, you may also want to set the Max Rows connection property. This will limit the number of rows returned, which is especially helpful for improving performance when designing reports and visualizations.
Below is a typical JDBC connection string for SQL Server:
jdbc:sql:User=myUser;Password=myPassword;Database=NorthWind;Server=myServer;Port=1433; - Set the Driver Name: cdata.jdbc.sql.SQLDriver and click Save.
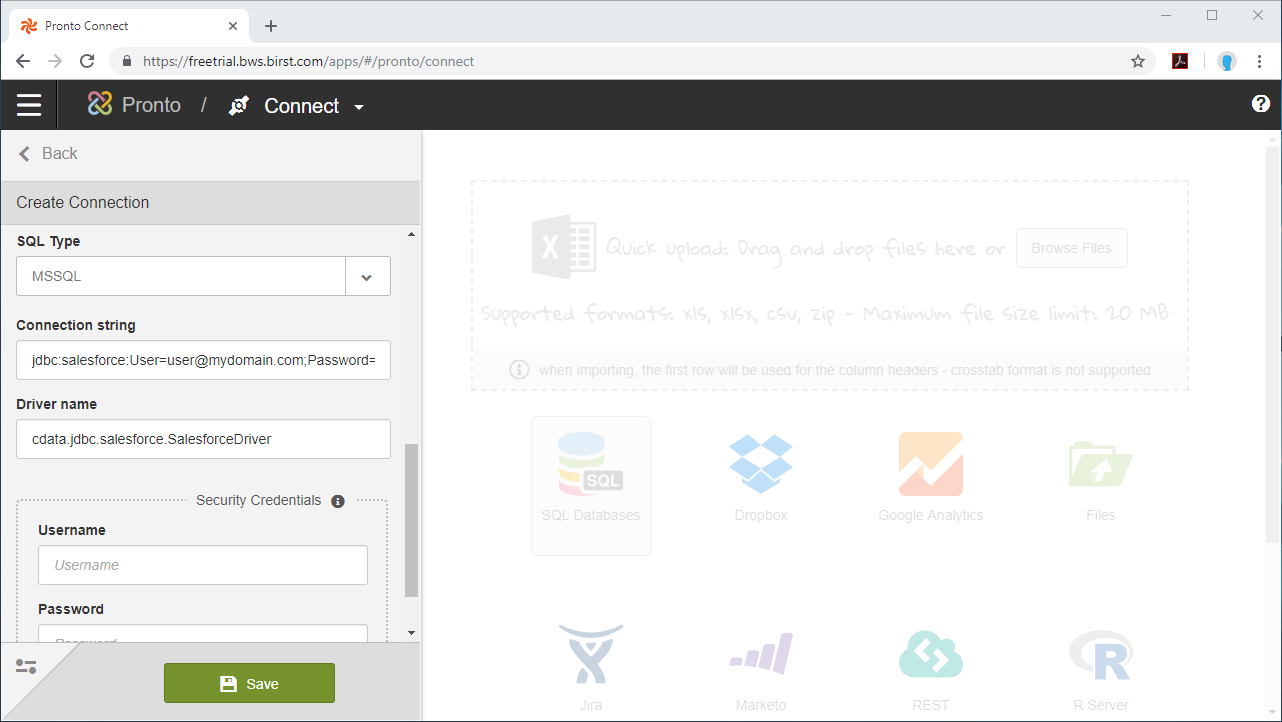
NOTE: Since authentication to SQL Server is managed from the connection string, you can leave Security Credentials blank.
Configure SQL Server Data Objects
Now that the connection is configured, we are ready to configure the schema for the dataset, choosing the tables, views, and columns we wish to visualize.
- Select the Schema (e.g. SQL).
- Click on Tables and/or Views to connect to those entities and click Apply.
- Select the Tables and Columns you want to access and click Done.
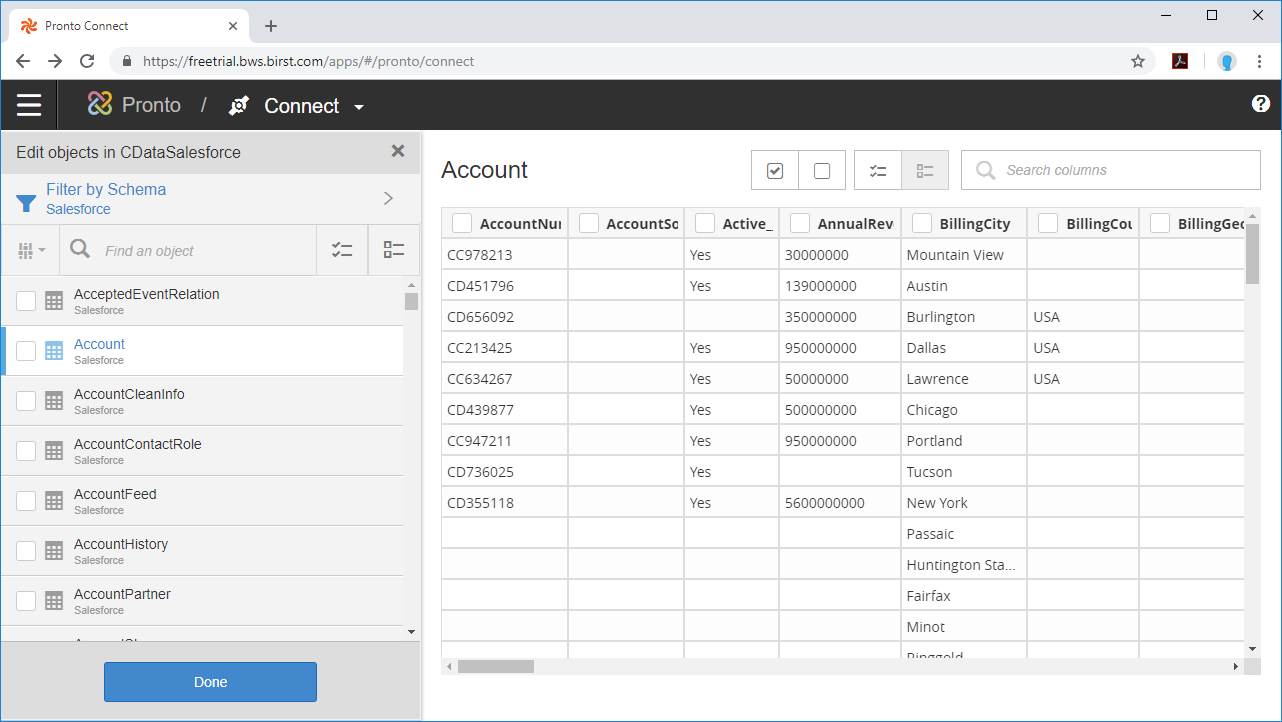
With the objects configured, you can perform any data preparation and discover any relationships in your data using the Pronto Prepare and Relate tools.
Build a Visualization
After you prepare your data and define relationships between the connected objects, you are ready to build your visualization.
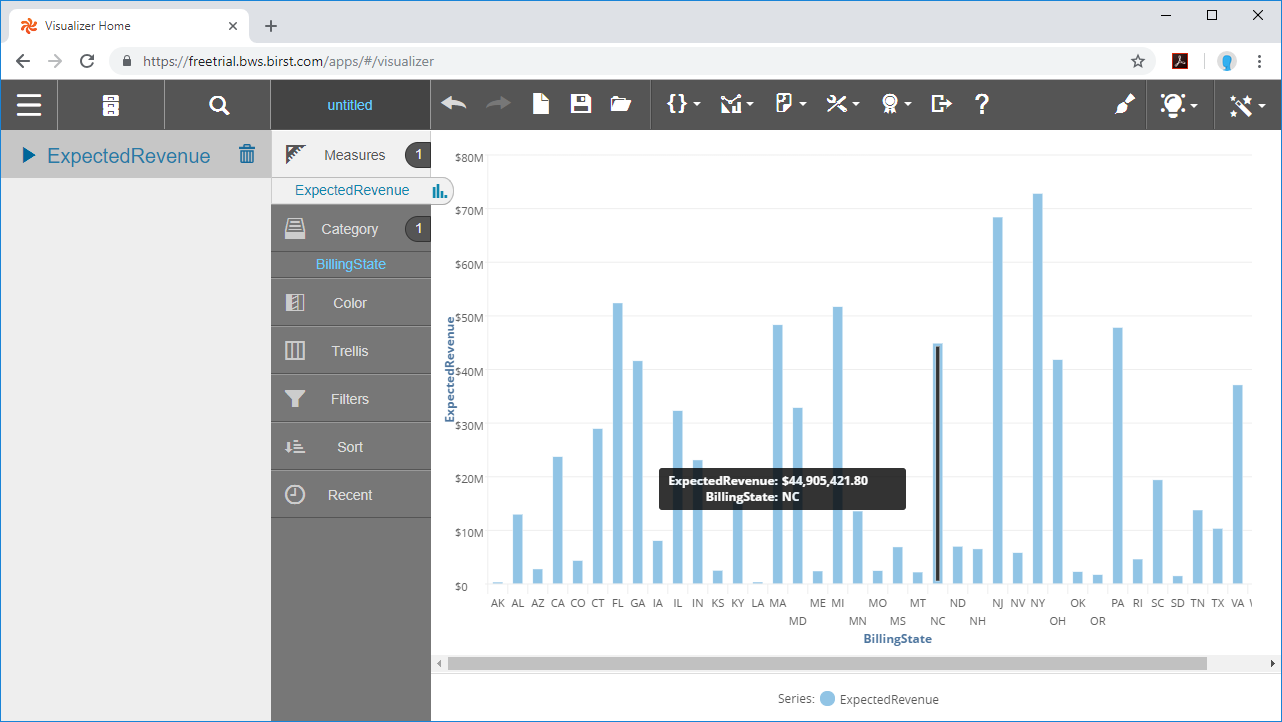
- Select the Visualizer tool from the menu.
- Select Measures & Categories from your objects
- Select and configure the appropriate visualization for the Measure(s) you selected.
Using the CData JDBC Driver for SQL Server with the Cloud Agent and Birst, you can easily create robust visualizations and reports on SQL Server data. Download a free, 30-day trial and start building Birst visualizations today.