Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →Use the CData ODBC Driver for Microsoft Teams in SAS for Real-Time Reporting and Analytics
Connect to real-time Microsoft Teams data in SAS for reporting, analytics, and visualizations using the CData ODBC Driver for Microsoft Teams.
SAS is a software suite developed for advanced analytics, multivariate analysis, business intelligence, data management, and predictive analytics. When you pair SAS with the CData ODBC Driver for Microsoft Teams, you gain database-like access to live Microsoft Teams data from SAS, expanding your reporting and analytics capabilities. This articles walks through creating a library for Microsoft Teams in SAS and creating a simple report based on real-time Microsoft Teams data.
The CData ODBC Driver offers unmatched performance for interacting with live Microsoft Teams data in SAS due to optimized data processing built into the driver. When you issue complex SQL queries from SAS to Microsoft Teams, the driver pushes supported SQL operations, like filters and aggregations, directly to Microsoft Teams and utilizes the embedded SQL engine to process unsupported operations (often SQL functions and JOIN operations) client-side. With built-in dynamic metadata querying, you can easily visualize and analyze Microsoft Teams data in SAS.
Connect to Microsoft Teams as an ODBC Data Source
Information for connecting to Microsoft Teams follows, along with different instructions for configuring a DSN in Windows and Linux environments (the ODBC Driver for Microsoft Teams must be installed on the machine hosting the SAS System).
You can connect to MS Teams using the embedded OAuth connectivity. When you connect, the MS Teams OAuth endpoint opens in your browser. Log in and grant permissions to complete the OAuth process. See the OAuth section in the online Help documentation for more information on other OAuth authentication flows.
When you configure the DSN, you may also want to set the Max Rows connection property. This will limit the number of rows returned, which is especially helpful for improving performance when designing reports and visualizations.
Windows
If you have not already, first specify connection properties in an ODBC DSN (data source name). This is the last step of the driver installation. You can use the Microsoft ODBC Data Source Administrator to create and configure ODBC DSNs.
Linux
If you are installing the CData ODBC Driver for Microsoft Teams in a Linux environment, the driver installation predefines a system DSN. You can modify the DSN by editing the system data sources file (/etc/odbc.ini) and defining the required connection properties.
/etc/odbc.ini
[CData MSTeams Sys]
Driver = CData ODBC Driver for Microsoft Teams
Description = My Description
OAuthClientId = MyApplicationId
OAuthClientSecret = MySecretKey
CallbackURL = http://localhost:33333
For specific information on using these configuration files, please refer to the help documentation (installed and found online).
Create a Microsoft Teams Library in SAS
Connect to Microsoft Teams in SAS by adding a library based on the CData ODBC Driver for Microsoft Teams.
- Open SAS and expand Libraries in the Explorer pane.
- In the Active Libraries window, right-click and select New.
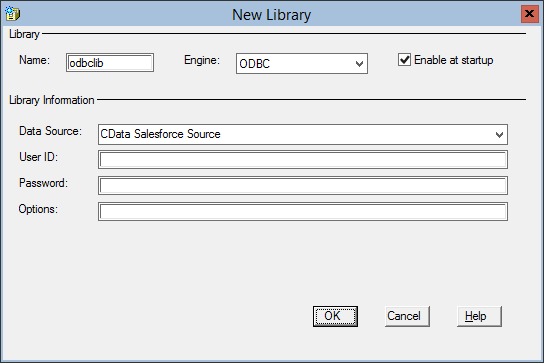
- Name your library (odbclib), select ODBC as the Engine, and click to Enable at startup (if you want the library to persist between sessions).
- Set Data Source to the DSN you previously configured and click OK.
![Creating a library for Microsoft Teams in SAS.]()
Create a View from a Microsoft Teams Query
SAS natively supports querying data either using a low-code, point-and-click Query tool or programmatically with PROC SQL and a custom SQL query. When you create a View in SAS, the defining query is executed each time the view is queried. This means that you always query live Microsoft Teams data for reports, charts, and analytics.
Using the Query Tool
- In SAS, click Tools -> Query
- Select the table sources and the table(s) you wish to pull data from. Then, click OK.
![Selecting table(s) to visualize.]()
- Select columns and right-click to add filtering, ordering, grouping, etc.
![Selecting columns(s) to visualize and configuring the query.]()
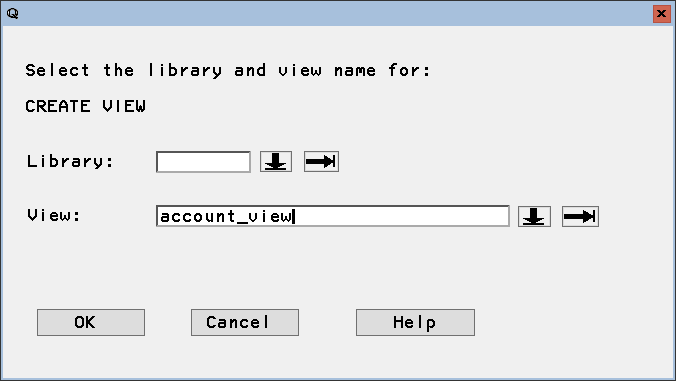
- Create a local view to contain the query results by right-clicking the SQL Query Tool window, selecting Show Query, and clicking Create View. Name the View and click OK.
![Create a local view to work with Microsoft Teams data.]()
Using PROC SQL
- In SAS, navigate to the Editor window.
- Use PROC SQL to query the data and create a local view.
NOTE: This procedure creates a view in the Work library. You can optionally specify a library in the create view statement.proc sql; create view teams_view as select subject, location_displayname from odbclib.teams where Id = 'Jq74mCczmFXk1tC10GB'; quit; - Click Run -> Submit to execute the query and create a local view.
Report On or Visualize Microsoft Teams Data in SAS
With a local view created, you can report, visualize, or otherwise analyze Microsoft Teams data using the powerful SAS features. Print a simple report using PROC PRINT and create a basic graph based on the data using PROC GCHART.
Print an HTML Report
- In SAS, navigate to the Editor window.
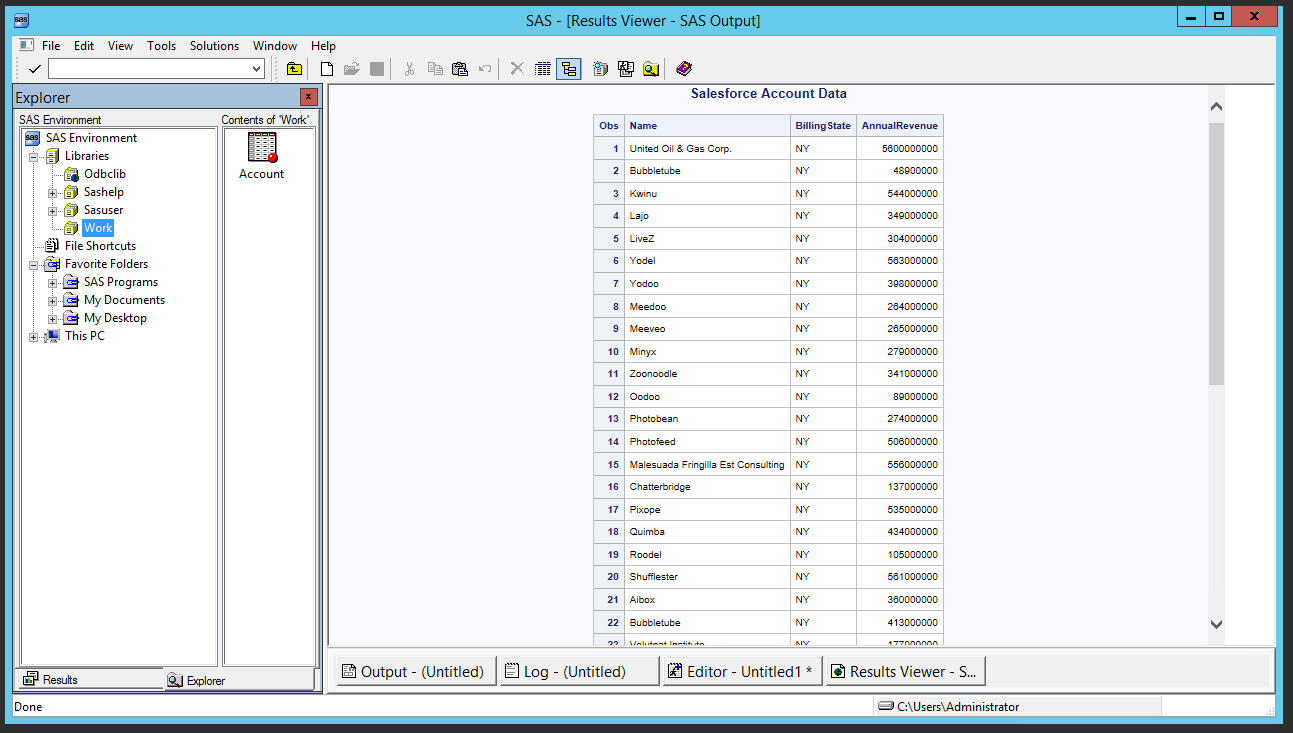
- Use PROC PRINT to print an HTML report for the Microsoft Teams Teams data.
proc print data=teams; title "Microsoft Teams Teams Data"; run;
![A simple Microsoft Teams data report.]()
Print a Chart
- In SAS, navigate to the Editor window.
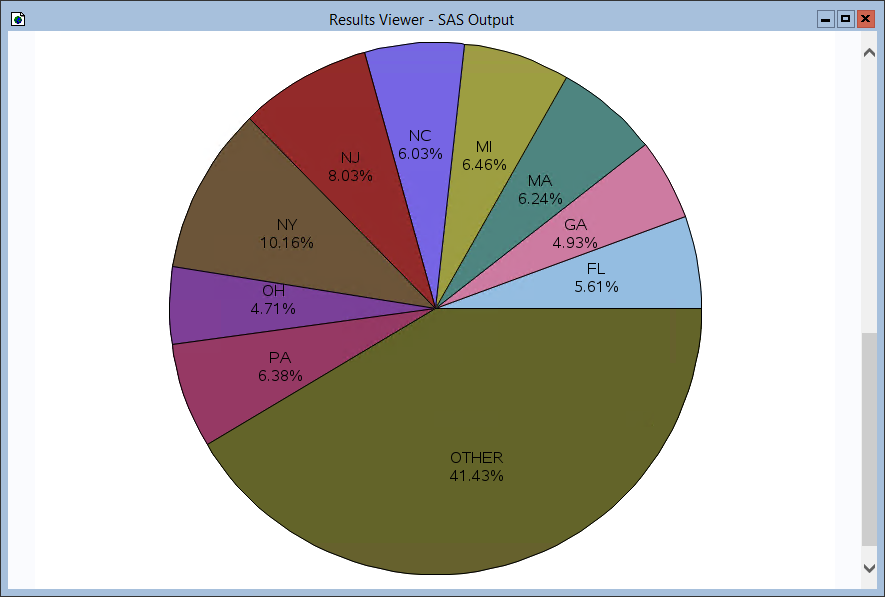
- Use PROC GCHART to create a chart for the Teams data.
proc gchart data=teams; pie subject / sumvar=location_displayname value=arrow percent=arrow noheading percent=inside plabel=(height=12pt) slice=inside value=none name='TeamsChart'; run;![A simple Microsoft Teams data chart.]()