Discover how a bimodal integration strategy can address the major data management challenges facing your organization today.
Get the Report →DataBind Charts to JSON Services
Use the standard ADO.NET procedures for databinding to provide bidirectional access to JSON services from controls in the Visual Studio toolbox. This article demonstrates a graphical approach using wizards in Visual Studio, as well as how to databind with only a few lines of code.
DataBinding facilitates two-way interaction with data through UI controls. Using the CData ADO.NET Provider for JSON streamlines the process of binding JSON services to Windows Forms and Web controls within Visual Studio. In this article, we will demonstrate using wizards to establish a binding between JSON services and a chart that dynamically updates. Additionally, the code walk-through section will guide you through the creation of a chart using just 10 lines of code.
Binding Data to a Chart
DataBinding to a Chart consists of three steps: Instantiate the control, configure the data source, and databind.
Configure the Connection and Select Database Objects
To create a chart control and establish a connection to JSON, follow the steps outlined below using the Data Source Configuration Wizard. Within the wizard, you'll have the option to choose the specific JSON entities you wish to bind to.
- In a Windows Forms project, drag and drop a Chart control from the toolbox to the form. In the Data section of the Chart properties, select DataSource and then select Add Project Data Source from the menu.
![Add a data source to be bound to the chart.]()
- In the Data Source Configuration Wizard that appears, select Database -> Dataset.
- In the Choose Your Data Connection step, click New Connection.
In the Add Connection dialog, click Change to select the CData JSON Data Source.
Below is a typical connection string:
URI=C:/people.json;DataModel=Relational;See the Getting Started chapter in the data provider documentation to authenticate to your data source: The data provider models JSON APIs as bidirectional database tables and JSON files as read-only views (local files, files stored on popular cloud services, and FTP servers). The major authentication schemes are supported, including HTTP Basic, Digest, NTLM, OAuth, and FTP. See the Getting Started chapter in the data provider documentation for authentication guides.
After setting the URI and providing any authentication values, set DataModel to more closely match the data representation to the structure of your data.
The DataModel property is the controlling property over how your data is represented into tables and toggles the following basic configurations.
- Document (default): Model a top-level, document view of your JSON data. The data provider returns nested elements as aggregates of data.
- FlattenedDocuments: Implicitly join nested documents and their parents into a single table.
- Relational: Return individual, related tables from hierarchical data. The tables contain a primary key and a foreign key that links to the parent document.
See the Modeling JSON Data chapter for more information on configuring the relational representation. You will also find the sample data used in the following examples. The data includes entries for people, the cars they own, and various maintenance services performed on those cars.
When you configure the connection, you may also want to set the Max Rows connection property. This will limit the number of rows returned, which is especially helpful for improving performance when designing reports and visualizations.
![Connection properties for the selected data source in the Add Connection dialog. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
- Choose the database objects you want to work with. This example uses the people table.
![Select database objects. (Salesforce is shown.)]()
DataBind
After adding the data source and selecting database objects, you can bind the objects to the chart. This example assigns the x-axis to [ personal.name.first ] and the y-axis to [ personal.name.last ].
- In the Chart properties, click the button in the Series property to open the Series Collection Editor.
- In the Series properties, select the columns you want for the x- and y-axes: Select columns from the menu in the XValueMember and YValueMember properties.
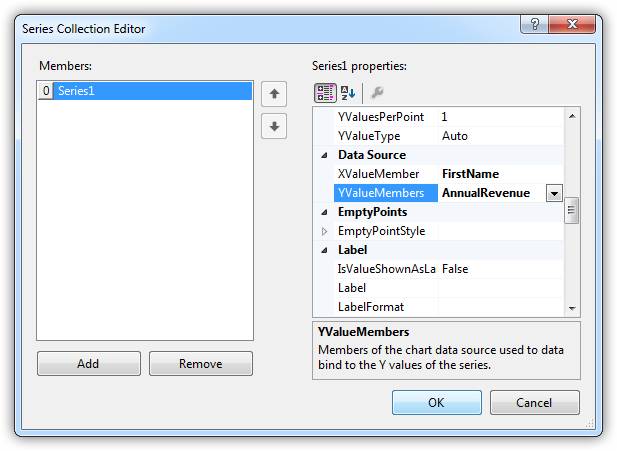
The chart is now databound to the JSON services. Run the chart to display the current data.

Code Walk-through
DataBinding to JSON services requires only a few lines of code and can be completed in three easy steps.
- Connect to JSON.
- Create the JSONDataAdapter to execute the query and create a DataSet to be filled with its results.
- DataBind the result set to the chart.
Below is the complete code:
JSONConnection conn = new JSONConnection("URI=C:/people.json;DataModel=Relational;");
JSONCommand comm = new JSONCommand("SELECT [people].[personal.age] AS age, [people].[personal.gender] AS gender, [people].[personal.name.first] AS first_name, [people].[personal.name.last] AS last_name, [vehicles].[model], FROM [people] JOIN [vehicles] ON [people].[_id] = [vehicles].[people_id]", conn);
JSONDataAdapter da = new JSONDataAdapter(comm);
DataSet dataset = new DataSet();
da.Fill(dataset);
chart1.DataSource = dataset;
chart1.Series[0].XValueMember = "[ personal.name.first ]";
chart1.Series[0].YValueMembers = "[ personal.name.last ]";
// Insert code for additional chart formatting here.
chart1.DataBind();








